
SOC 2 compliance isn’t just about ticking boxes—it’s about demonstrating that your organization can securely manage data and protect client privacy.
Achieving SOC 2 compliance requires a deep understanding of the Trust Service Criteria (TSCs) and the specific controls necessary to meet them. The SOC 2 framework, defined by the AICPA, offers flexibility, allowing you to choose the criteria that align with your organization’s and your customers’ needs.
This article will break down the mandatory and optional requirements for SOC 2 across the five TSCs, helping you implement the necessary controls and strengthen your security posture.
| TL;DR SOC 2 requirements aren’t absolute. They are, at best, a broad set of guidelines that can accommodate the framework’s security practice for various businesses. While Security is a mandatory SOC 2 requirement, Availability, Confidentiality, Privacy, and Processing Integrity aren’t. Organizations can select other criteria based on their business needs. There are two types of SOC 2 Reports: Type 1 and Type 2. SOC 2 Type 1 reports evaluate the design of an organization’s security controls at a specific time. In contrast, the latter evaluates both the design and operating effectiveness of those controls over a specified period. |
What Requirements of SOC 2 Compliance does AICPA focus on?
The AICPA “Points of Focus” aren’t mandatory requirements; they serve as supportive measures to help organizations implement controls effectively. Described as ”important characteristics of the criteria’, these points offer guidance on physical access controls, configuration management, and vendor management. While not mandatory, they provide valuable insights into what more can be done to meet SOC 2 compliance requirements, enhancing the overall security stance of the organization.
Continuous compliance is the next big thing! Get there first with Sprinto
SOC 2 Requirements List
There are five Trust Services Criteria that businesses are evaluated on during a SOC 2 audit. They are Security, Availability, Confidentiality, Processing Integrity, and Privacy. Each TSC defines relevant compliance requirements your organization must meet using internal controls. They are therefore, best seen as focus areas of your information security program.
“If you are handling sensitive customer data or looking at Enterprise-Scale customers, especially in the US, SOC 2 becomes a table-stakes requirement for a sales engagement.”
Devika Anil: Lead Auditor at Sprinto
Great advice adds up. Get more from the brightest minds in GRC — Subscribe to our newsletter
Security is an essential SOC 2 requirement and has been discussed extensively in the following section along with the other TSCs.
1. Security
The security principle is the only criterion that is a compulsory requirement in the SOC 2 audit.
The security criteria are also referred to as Common Criteria (CC) as many of the controls used to evaluate a system are common to the remaining four TSC.
For instance, the risk management criteria for security apply to the remaining four TSCs – privacy, availability, confidentiality, and processing integrity. The common criteria, therefore, establishes the overlap amongst all the TSCs and summarizes it as a comprehensive set of criteria for the security TSC.
The security TSC lays down broad guidelines to ensure the security of customers’ information across its entire life cycle – from creation, use, processing, transmission, and storage. Organizations can achieve the same through deploying access control, firewalls, and other operational and governance controls.
These controls discourage unauthorized access or removal of data, unapproved alteration, destruction or misuse of software (such as code repos), and unsanctioned disclosure of confidential information, to name a few.
Security has 9 Common Criteria (CC), of which five are essential requirements for SOC 2 compliance and based on the COSO framework.
There are four more Common Criteria series.
- Controls over Logical and Physical Access in SOC 2
- Systems and Operational Controls for SOC 2
- Controls for SOC 2 Change Management
- SOC 2 Risk Mitigation Controls
Automate controls with the help of Sprinto. Talk to our experts now
2. Availability
Availability refers to the accessibility of information used by your organization and of the products or services provided to your customers. While the criteria don’t set a minimum acceptable performance level, they address controls to support accessibility for operation, monitoring, and maintenance.
This principle focuses on business continuity, disaster recovery plan & test, backups & replication, and infrastructure & capacity monitoring. The availability criteria ensure your systems adhere to operational uptime and performance standards.
It is easy for cloud-hosted businesses such as yours to meet the criteria because of the cloud’s natural characteristics.
It consists of three criteria:

SOC 2 requirements for availability include:
- Securely backup systems and have disaster recovery and business continuity plans to minimize downtime.
- Establish capacity management baselines and take steps to avoid availability issues from exceeding system limits.
- Identify potential environmental threats like natural disasters that could disrupt service and take precautions against them.
3. Confidentiality
The confidentiality criteria help safeguard confidential information throughout its lifecycle by restricting access and disclosure of private information such that only an authorized set of people or organizations can access it. Confidential information includes IP, financial data, and other business-sensitive details.
Typically, such confidential information would be specific to your contractual commitments with your customers. Establishing access control and proper privileges is oft-used control here.
It consists of two criteria:

SOC 2 requirements for confidentiality include:
- Have procedures to identify confidential information when it is created or received. Establish policies determining retention periods for that data.
- Ensure secure destruction of confidential data after retention periods expire. Have processes in place to permanently delete sensitive information.
4. Processing Integrity
The processing integrity principle evaluates your cloud environment to determine whether your data processing is timely, accurate, valid, and authorized. You can use quality assurance procedures and SOC tools to monitor data processing.
It comprises five criteria, which are:

SOC 2 requirements for processing integrity include:
- Maintain detailed records of all system inputs and outputs, confirming proper distribution of outputs.
- Have procedures in place to swiftly identify and fix any errors in the system.
- Clearly define all data processing activities to ensure products and services conform to specifications.
5. Privacy
The privacy principle lists guidelines to protect Personally Identifiable Information (PII) from breaches and unauthorized access. It can be implemented by deploying access controls, two-factor authentication, and encryption, to name a few.
An interesting aside here – privacy is different from confidentiality in that it applies to only personal information whereas confidentiality applies to different types of sensitive information.
The Privacy criteria details the following categories in its SOC requirements:
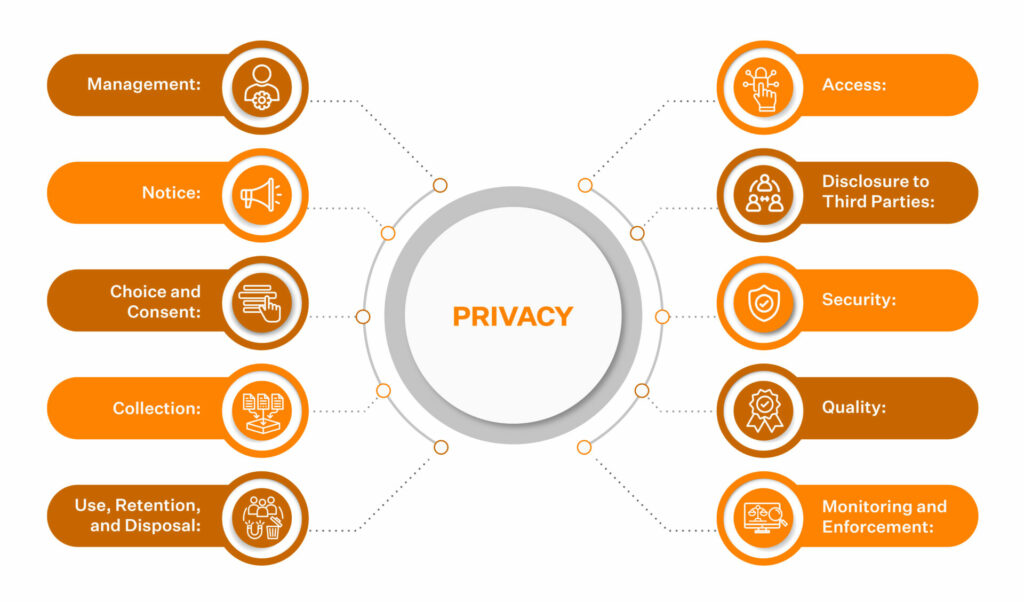
SOC 2 requirements for privacy include:
- Obtain consent from individuals before collecting sensitive personal information. Clear communication of data practices and policies is essential.
- Write privacy policies and other explanations of data practices in plain, easy-to-understand language, avoiding jargon.
- Only collect data through legal means and from reliable sources. Processes should be in place to verify data accuracy and lawfulness of collection methods.
Also, check out the difference between SOC 2 automation and manual work
Download Your SOC 2 Self Assessment Template
Unlock SOC 2 certification requirements with Sprinto
Streamlining SOC 2 compliance becomes a swift and efficient process with Sprinto’s compliance automation. Instead of the usual six-month journey, Sprinto expedites SOC 2 certification by automating 90% of compliance tasks, enabling businesses to focus on core objectives.
With support for 200+ integrations, it swiftly sets up controls for diverse cloud applications. Sprinto’s intuitive dashboard provides real-time insights into control statuses, while prompt notifications ensure rapid action on security gaps. Its continuous 24/7 monitoring also conducts over a million monthly checks, ensuring ongoing control assessment for cloud services.
“Our audit was a cakewalk. There was no instance of non-compliance across Type 1 and Type 2 reviews!” says Bhargava, MNN, Engineering Lead at Zipy.
Check out: How Zipy used Sprinto to get compliant and ace SOC2 Type 1 and Type 2 audits.
SOC 2 Report Types
A SOC 2 report comes in two types – SOC 2 Type 1 and SOC 2 Type 2.
A SOC 2 Type 1 report attests that your internal controls have been effectively designed to meet SOC 2 compliance requirements at a particular point in time; it’s like a snapshot. The SOC 2 Type 1 audit reviews the design of an organization’s internal controls at a point in time.
SOC 2 Type 2 report, on the contrary, confirms that the controls in place are working effectively too over a period of time. During a Type 2 audit, your audit will test both the design and operating effectiveness of your internal controls over a period (typically three to six months).
A SOC 2 type 1 and SOC 2 type two report has a specific use case. An example of this would be when a customer requests a vendor for a SOC 2 attestation as a part of their contract. The vendor in question will go through a process of aligning their internal controls, running the necessary checks, training their staff, and applying for a SOC 2 type 1 attestation, which audits the company’s controls and evidence against the requirements of SOC 2 at that point in time. Once the attestation process is complete, the company presents it to the customer. The company then conducts a SOC 2 Type 2 audit and attestation after six months (the observation/assessment period). The company is also required to conduct a SOC 2 Type 2 attestation annually to stay compliant.

The scope of the audit is determined by the TSCs you have chosen for your SOC 2.
Check out the difference between SOC 1, SOC 2 and SOC 3.
Are SOC 2 Type 1 and Type 2 Requirements Same?
As we discussed earlier, SOC 2 Type 1 and Type 2 are report types, requiring an audit. When companies need to demonstrate SOC 2 quickly to close some deals, then they get the audit done with the current data security systems and controls in place.
However, the SOC 2 requirements for Type 1 and Type 2 are similar. The only major difference is that the Type 1 audit doesn’t require a continuous monitoring period. Whereas, before you apply for the Type 2 audit, you will have to meet these SOC 2 Type 2 requirements for the observation period of 3 to 6 months.
Get SOC 2, the Sprinto Way
SOC 2 can be unwieldy and cumbersome if you don’t plan ahead. But with Sprinto, your compliance journey is a well-thought-out and planned process. Sprinto replaces all the manual, error-prone, repetitive busy work with automation. What’s more, Sprinto’s team of compliance experts guide you throughout the process.
Get SOC 2 the easy way with Sprinto. Our automated platform replaces manual work with smart workflows to collect evidence, document controls, identify compliance gaps, and enable you to adhere to relevant security standards. Lean on our compliance experts so you can focus on your core business. Sprinto maps controls to criteria, schedules audits, tracks progress, and partners with your security processes end-to-end. Ready to see how it’s done? Speak to our experts today.
FAQs
1. Does obtaining a SOC 2 report guarantee compliance?
No, SOC 2 does not guarantee total compliance. It provides independent validation that a service organization has controls and security measures in place to meet Trust Services Categories. However, auditors only evaluate a sample of controls over a period of time. Organizations still need to maintain compliance between audits and stay up-to-date with evolving regulations.
2. What does it take to become SOC 2 compliant?
To become SOC 2 compliant, organizations must identify controls mapping to criteria, provide evidence of control effectiveness over time, undergo SOC 2 audit by CPA firm, remediate gaps, obtain SOC 2 Type 1 and/or Type 2 report, and renew annually.
3. What types of organizations would benefit from SOC 2 certification?
SOC 2 applies to any service organization that stores, processes or transmits customer data. It is especially relevant for technology companies providing SaaS, cloud services, data hosting, infrastructure, blockchain, digital assets, and other technology solutions. SOC 2 also applies to organizations in healthcare, finance, insurance, retail, and other sectors handling sensitive customer information.
4. What is the difference between SOC 1 and SOC 2 report?
SOC 1 primarily concerns control environments that affect financial reporting, which is especially important for service organizations impacting clients’ financial statements.
Meanwhile, SOC 2 assesses security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy controls, showing how well controls operate in systems beyond financial reporting areas.
5. What are SOC 2 compliance requirements?
SOC 2 requirements are not explicitly laid down by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) in the form of a checklist or document. Instead, the AICPA provides Points of Focus and establishes Trust Service Criteria (TSC), serving as essential characteristics that guide organizations in implementing security controls.
An organization achieves SOC 2 compliance after undergoing an audit by a third-party auditor who assesses the effectiveness of internal controls against five trust categories. These are Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy.
Gowsika
Gowsika is an avid reader and storyteller who untangles the knotty world of compliance and cybersecurity with a dash of charming wit! While she’s not decoding cryptic compliance jargon, she’s oceanside, melody in ears, pondering life’s big (and small) questions. Your guide through cyber jungles, with a serene soul and a sharp pen!
Explore more SOC 2 articles
SOC 2 Compliance Overview
SOC 2 Preparation and Documentation
SOC 2 Audit and
Reporting
SOC 2 Differences and Similarities
SOC 2 Updates & Management
SOC 2 Industry-Specific Applications
research & insights curated to help you earn a seat at the table.








