General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) Compliance
Pritesh Vora
Oct 01, 2023

Key Points
- GDPR is a legal framework that provides guidelines for the collection and processing of the personal data of EU citizens and the transfer of personal data outside the European Union.
- Cloud-computing companies must be GDPR-compliant if they have an EU customer base, even if they are not located within the European Union.
- Non-compliance with GDPR leads to harsh fines of up to 4% of annual global turnover (~ €20 million), damaged company reputation, and liability to bear compensation claims. Even the top cloud services companies cannot escape the strict rules of the GDPR.
Introduction
The widespread adoption of cloud services has also brought challenges in the form of cybersecurity threats and multiple privacy regulations across different jurisdictions.
Pew Research Center found that 79% of respondents were concerned about how their personal data was gathered and processed by companies and the government.
Customers that rely on multiple cloud-hosted companies have little control over the flow of their data across different data centers. It’s no surprise that customers are concerned about data protection and security in the cloud.
The GDPR requires all companies that process the personal data of EU citizens to follow specific guidelines on how to collect, store, and use the information. B2B and cloud-hosted companies are among the ones most impacted by this regulation.
Austria’s ban on the use of Google Analytics on European websites demonstrates just how powerful the GDPR is. Google Analytics cannot provide sufficient protection as per Article 44 because it is required to provide data access to US authorities.
In this guide, we will explain everything you need to know about the GDPR in simple, easy-to-understand language.
What is General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a digital privacy legislation that regulates how companies collect, process and protects the personal information of European Union (EU) residents. The law also governs personal data transfer outside the EU.
GDPR compliance strengthens privacy rights by giving users (called data subjects) control over how their personal data is gathered, shared, and used. They are entitled to (a) have their personal data protected, (b) used in a lawful and fair manner, (c) corrected if they ask for information to be altered, and (d) made available if they ask for a copy.
The regulation came into effect on May 25, 2018, and replaced the Data Protection Directive 95/46/ec.

GDPR guidelines were drafted with an eye on three main goals:
- Establish a baseline set of standards for cloud-hosted companies that handle EU citizens’ data
- Replace the 28 separate EU member state privacy laws and the 1995 Data Protection Directive with a unified privacy law
- Update privacy laws to align with technological advancements in personal data processing and movement
The official GDPR regulation comprises 88 pages of rules, scenarios, compliance requirements, and enforcement techniques. It has 99 Articles and 173 Recitals of the Regulation.
Check out this video on GDPR principles:
Why is GDPR Important?
GDPR has a significant impact on cloud-hosted companies with respect to security control mechanisms and implementation of operations.
Some of the key GDPR importance are:
- Getting the consent of users for data processing
- Anonymizing gathered data to protect privacy
- Providing notifications for data breaches within 72 hours
- Safely carrying out the transfer of data across borders
- Requiring specific companies to appoint a data protection officer to oversee GDPR compliance
Any cloud-hosted company that markets its services or products to EU citizens is subject to GDPR compliance requirements, even if it is located outside the European Union.
Non-compliance to GDPR guidelines will require cloud-hosted companies to pay stiff fines apart from suffering a tarnished reputation. Penalties may be up to 2% or 4% of total global annual turnover or €10 million – €20 million.
Get GDPR compliant to avoid penalties
What Is Classified as Personal Data Under GDPR?
Under GDPR, personal data refers to information that can identify you or relate to you, either on its own or in combination with other available information.
- Business information like company names and email addresses operated by multiple people is not considered personal data. E.g. support@company.com
- Business email addresses and phone numbers owned and operated by a single person are considered personal data. E.g. juliawallace@company.com
Personal data may include the following:
- Name
- Residential address
- Contact information
- Race
- Identification numbers (bank account, passport)
- Access cards
- IP address, cookie data, RFID tags
- Location data/geotagging
- Audio-visual/audio recordings
- Health records
- Social media posts
- Religious and political opinions
Pseudonymous data is also considered personal data if it is relatively easy to identify the person using it.
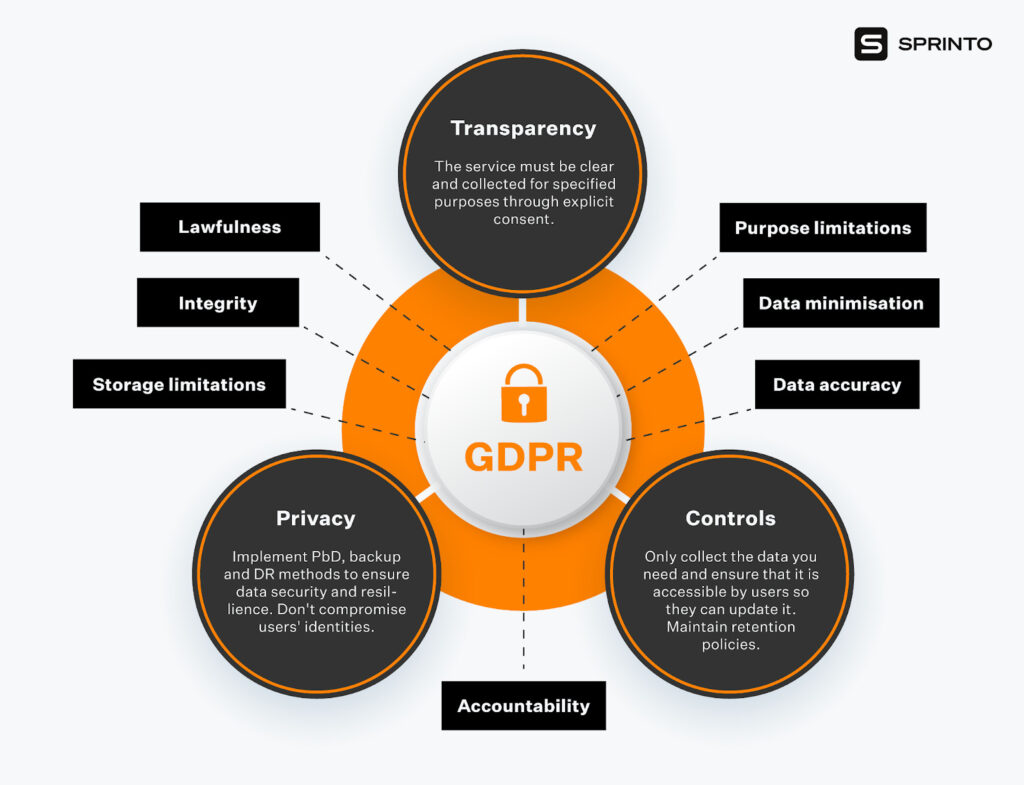
Some useful concepts to help navigate GDPR are:
- If a cloud-hosted company is collecting or using your personal data, you are a data subject. The company holding the data is the data controller.
- The data controller can give permission to another person or company to process your personal data on its behalf. This person or company is called a data processor.
- Handling your personal data, including storing it is known as processing.
Also, some of the relevant articles of GDPR for cloud-hosted companies are:
- Article 5 – Principles around handling and processing of personal data
- Article 6 – Lays the foundation for personal data processing
- Articles 12-22 – Talks about the rights of data subjects
- Articles 25 and 32 – Guidelines on how to implement measures to protect personal data
Under GDPR, companies need to establish one of these six lawful bases to be allowed to process data: consent, legal obligation, contract, public task, vital interests, and legitimate interest.
Cloud-hosted and B2B companies typically rely on consent and legitimate interest.
- They can gain verifiable consent through, say, a sign-up form. Users can withdraw consent at any time and companies must stop processing when consent is withdrawn.
- If they’re relying on legitimate interest for B2B marketing, they must stop processing when a user objects.
What Is a “Breach” Under GDPR?
Under GDPR, a personal data breach is defined as a breach of security that results in its accidental or illegal destruction, modification, or loss. It may also cause unauthorized disclosure of or access to personal data. The breach is likely to pose a risk to a person’s rights and freedoms.
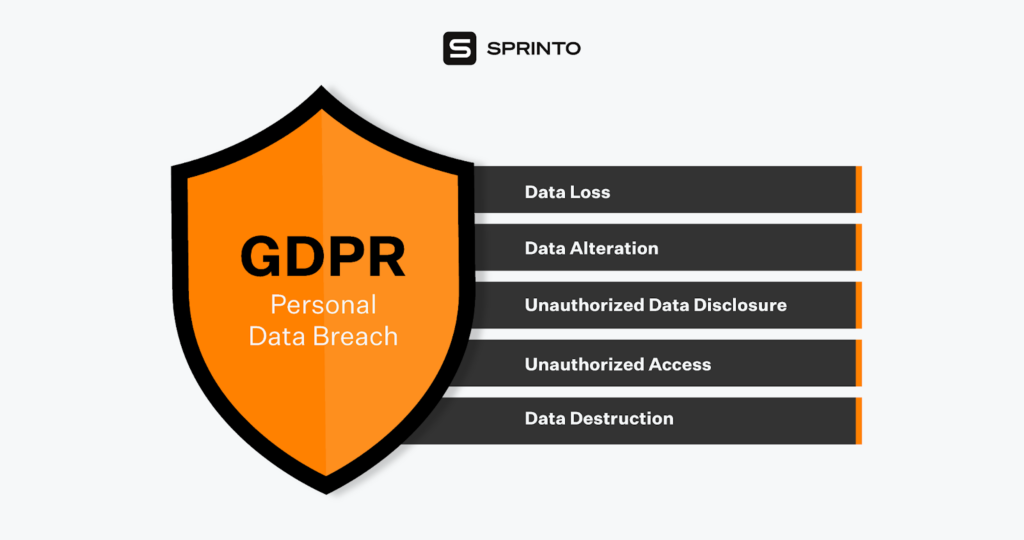
Some of the biggest data breaches that led to the drafting of the GDPR :
- Equifax
In 2017, Equifax, a credit reporting service, suffered a major data breach that affected 143 million US customers and 694,000 UK customers. The customers’ names, passwords, birth dates, social security numbers, and partial credit card details were compromised.
The UK Information Commissioner’s Office fined the company the maximum possible amount under the pre-GDPR Data Protection Act, which is £500,000.
- Facebook/Cambridge Analytica
A British data science firm, Cambridge Analytica, scraped the Facebook profiles of more than 50 million users without their consent. The data was used to inform Trump’s 2016 presidential campaign.
Data was acquired through a personality quiz app called “this is my digital life”, which requested access to the Facebook profiles of the people taking the quiz.
Facebook was also fined £500,000 for the breach.
These real-world data breach examples reveal how a breach can have far-reaching consequences. The GDPR and similar data protection legislation aim to protect people from such violations of privacy.
Check out the list of GDPR software that can help you avoid data breaches.
Which Companies Are Affected by the GDPR?
Any company or business that stores or processes personal data of EU citizens must be in compliance with GDPR.
92% of US companies consider GDPR a top priority for data protection regulation.
Ask yourself these questions to know if the GDPR applies to your company:
- Does the company market to customers in the European Union?
- Does the company have employees that work in the European Union?
- Or does the company have a current customer base in the European Union?
Companies that accept payments in Euros also fall under GDPR.
Specific criteria for companies required to be GDPR-compliant are:
- A presence in an EU country
- Processing or storing the personal data of EU citizens, even if it isn’t located in the European Union
- More than 250 employees
- Less than 250 employees but performing data processing that affects the rights and freedoms of data subjects or involves certain types of sensitive personal data
EU-based companies in cloud services, telecommunications, insurance, and e-gaming automatically fall under the GDPR.
Some of the ways in which B2B and cloud-hosted companies can comply with the GDPR:
- Keep valid, up-to-date records of all data processing activities, including internal records.
- Update the content and language of your privacy policy to be relevant, easy to access, and easy to read and understand.
- Review or identify the legal basis for processing personal data.
- Review systems to ensure that GDPR user rights are covered.
- Maintain valid records of consent and handle consent in a GDPR-compliant way.
- Use the principle of data minimization: the more types of data are processed, the greater the risk.
Who Will Be in Charge of Compliance In Your Company?
The GDPR compliance establishes the need for several positions to oversee compliance in cloud-hosted companies: data controller, data processor, and data protection officer (DPO).
- The data controller is the entity responsible for determining the purpose and lawful basis for the processing of personal data. The controller also ensures that outside contractors are GDPR-compliant.
- The data processor is the individual responsible for processing personal data on behalf of the data controller. Data processor collaborates with the data controller.
- The data protection officer is appointed by the data controller and data processor as per GDPR guidelines to oversee data protection and monitor GDPR compliance. This includes training staff and raising awareness. Cloud-computing companies should provide initial and refresher training about GDPR guidelines. They should also have a mechanism in place to record these training sessions.
The GDPR requires a company to appoint a DPO if:
- It is a public authority or entity
- Its core activities need large-scale, systematic, and regular monitoring of data subjects e.g. tracking of online behavior
- Its core activities consist of large-scale processing of special categories of personal data or data related to criminal convictions and offenses.
Articles 37, 38, and 39 of the GDPR talk about the designation, position, and tasks of the data protection officer respectively.
What Happens if Your Company Fails to Comply With the GDPR?
The ramifications are severe if you fail to comply with GDPR guidelines:
- Financial penalties
Companies that violate the rules of the GDPR and suffer data breaches are levied harsh fines. The maximum amount is 4% of a company’s annual global turnover or €20 million.
Under the Data Protection Act, the maximum fine for failing to stop a data breach was far less: £500,000.
The Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) considers the following points when deciding whether to levy a fine:
- Severity and length of the data breach
- The type of personal data compromised in the breach
- Whether the data breach was negligent or intentional
- Whether the company has suffered a previous data breach
- Or whether the data breach impacted the rights and freedoms of the affected individuals
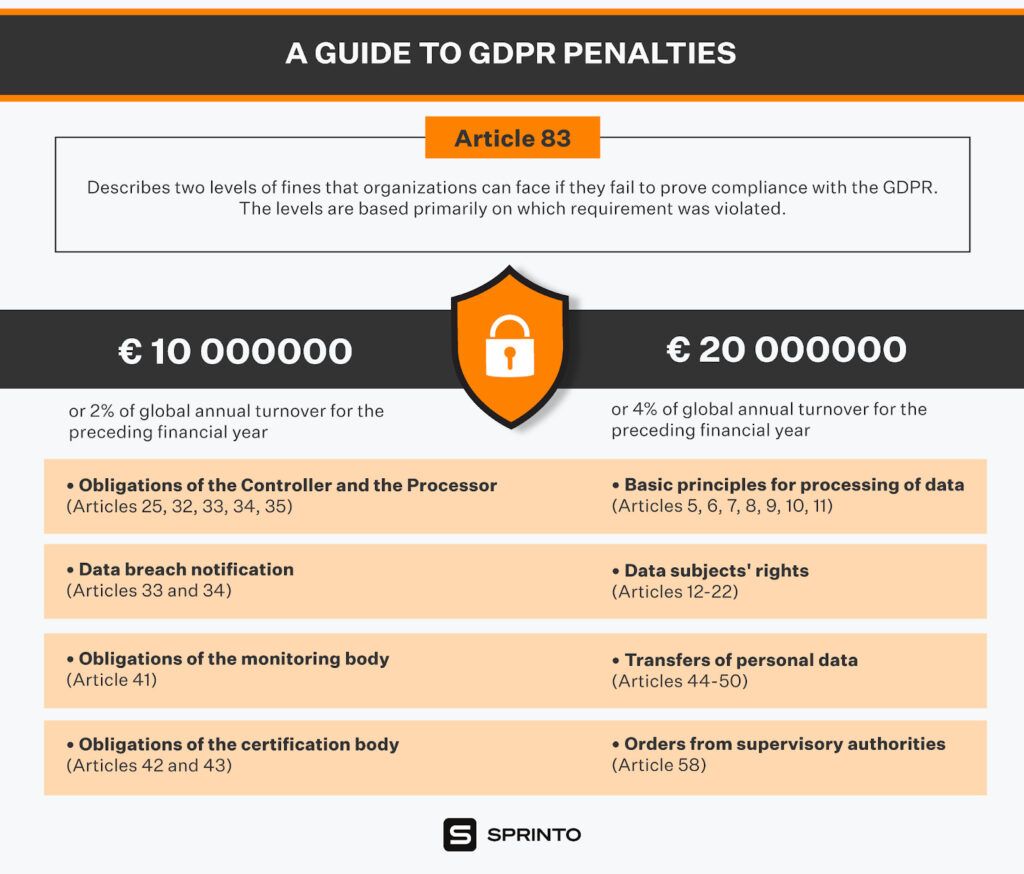
Some examples of data breaches that have attracted huge fines are:
- British Airways was handed a fine of €20 million for “unacceptable” failure to protect its customers. It is the largest fine levied by the ICO so far. The major 2018 breach led to the theft of booking information of more than 400,000 people.
- Marriott Hotels was fined £18.4 million for a data breach that affected over 339 million guests. The first part of the breach occurred in 2014 and affected the Starwood Hotels group, which was acquired by Marriott two years later. However, until 2018, the hacker had access to all affected systems that included names, email addresses, phone numbers, passport numbers, VIP status data, arrival and departure information, and loyalty program numbers.
- Google was fined $57 million by France’s data protection authority, CNIL, for not complying with GDPR guidelines in the way it handled ad personalization. It didn’t take specific or unambiguous user consent to process data for ad personalization. Users did not understand the “plurality of services” in which their personal data is used and processed.
GDPR regulations apply to even the top Internet companies of the world. Smaller businesses may not attract the same magnitude of fines but they are held to the same high standards.
- Tarnished reputation
You may be able to pay fines, but can you repair the damage to the company’s reputation just as easily? Companies should raise awareness and conduct regular training to educate their staff about GDPR compliance.
- Compensation for damages
Under GDPR, individuals have the right to claim compensation for material or non-material damages due to violation of the guidelines. Major breaches could result in a large volume of compensation claims.
Conclusion
You must have gained a thorough understanding of the core principles of GDPR by now. It is clear why GDPR compliance is vital for your cloud-hosted company.
Avoid heavy financial penalties and damage to company’s reputation by becoming GDPR compliant.
Get your GDPR compliance today with Sprinto by automating and streamlining the audit process.
FAQ: GDPR Compliance
1. What does GDPR compliant mean?
Being GDPR compliant requires that you integrate data protection into your processing activities and business practices from the design stage to the entire data processing lifecycle. This is called “data protection by design and by default.”
It protects the personal data and privacy of EU members for transactions that occur inside the EU member states. It also regulates the commercial movement of personal data outside the European Union.
2. What is GDPR compliance?
The GDPR is a legal framework that establishes guidelines for the gathering and processing of personal data from EU citizens. The Regulation applies regardless of where the company is located as long as it markets its services and goods to EU customers.
GDPR compliance requires that companies that collect data from people in the EU countries follow the strict rules laid out by it.
3. How to be GDPR compliant?
The GDPR establishes seven key principles that should be used to create an actionable plan for ensuring compliance:
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency – Data processing should be done lawfully. It should not be unexpected and the owner of the data should be informed about the processing activity.
- Purpose limitation – Restrict data processing to certain identified purposes. Record and specify these purposes in a privacy notice to owners of the personal data.
- Data minimization – Process personal data only to the level to which it is necessary.
- Accuracy – Ensure the accuracy and recency of personal data. Delete or correct inaccurate data.
- Storage limitation – Store personal data only if you require it.
- Integrity and confidentiality (security) – Put in place security measures to safeguard personal data from unauthorized or illegal processing and accidental loss, destruction, or damage.
- Accountability – Be responsible for handling personal data, keep records of processing activities, and have mechanisms in place to prove compliance with data processing principles.
Pritesh Vora
Pritesh is a founding team member and VP Growth & Marketing at Sprinto. He comes with over a decade of experience and is a data-driven dynamo in growth strategy, sales, and marketing! His strategies have crafted the success of not one, but two early-stage SaaS startups to 7-digit revenues within a year – he’s your go to guy for all things growth.
Grow fearless, evolve into a top 1% CISO
Strategy, tools, and tactics to help you become a better security leader
Found this interesting?
Share it with your friends
Get a wingman for
your next audit.
Schedule a personalized demo and scale business

Sprinto: Your growth superpower
Use Sprinto to centralize security compliance management – so nothing
gets in the way of your moving up and winning big.


