
To be or not to be. In this context, understanding whether or not to be GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) compliant for your organization is the biggest challenge. As a business owner who spends a lot of time on product development and business expansion, the challenge is the compliance process know-how.
GDPR for Dummies, aims to explain the data protection regulation – GDPR compliance law and all its essentials to the Founders (CXOs) and technologists (CTOs, VP-Engineering) out there who are looking for a guide to this complex procedure.
Understanding GDPR for Dummies
Before GDPR, data privacy was a joke; nobody knew where user information got transferred across the internet and who had access to it. The European Union (EU) in May 2018 released the first version of GDPR, which aimed at protecting the privacy and integrity of personal data of the citizens of Europe.
Businesses under the purview of this law were given two years to make the necessary changes required to become compliant.
It was a big deal!
GDPR focused on laying a rule guide for businesses that deal with user data to define how user data should be processed.
This empowered the user (individual) to control their rights over their data and gave them the power to decide what happens with it and when.
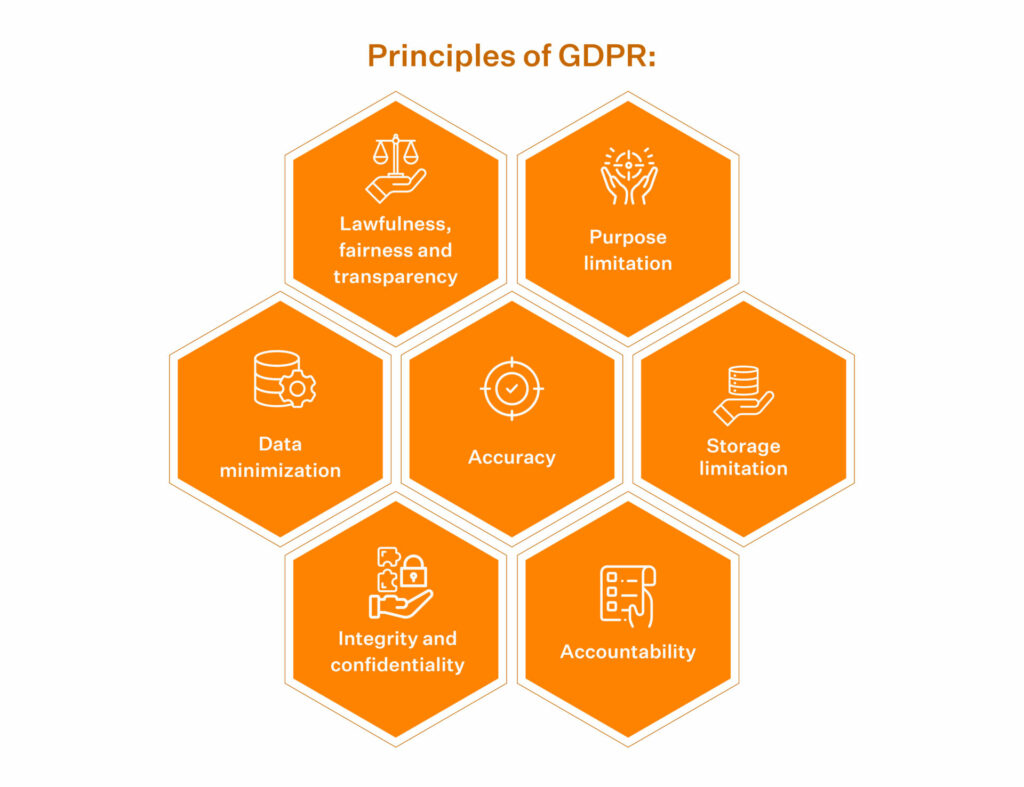
The rule guide is famously known as the principles of GDPR.
Why do we need GDPR?
The need for GDPR was to protect the individual’s interests from the business’s interests. Sounds harsh.
Let us explain in this dummies guide to GDPR. Personal data is a $3 trillion industry. In comparison, the annual global drug revenue is estimated to be around $400 billion.
Businesses such as Facebook and Google make a lot of money selling personal data to advertisers.
But, would you trust the advertisers who acquired this user data after paying a hefty sum to have your best interests at heart? Probably not.
Thus arises the need for a regulation that ensures that the privacy and integrity of the user data are not compromised.
As business owners trying to become GDPR compliant, you should know why you would need to show the world a clean bill of compliance. To begin with, it instils trust. The second part is the most crucial; it shows the world that your business has what it takes to deal with personal data in a way that is globally accepted, and this also covers the critical angle of having security measures in place to protect your data from malicious attacks.
The third one is the hefty administrative fines that come knocking in the event of non-compliance.
Must Read:What Includes in GDPR Training Courses – Scope of Compliance Training
What is Personal Data GDPR Summary for Dummies?
Personal data is any information that can identify a specific individual from different attributes.

Just one attribute of personal data is insufficient to reverse engineer the process to pinpoint the source/trace the individual. Personal data is like a jigsaw puzzle; the big picture starts showing itself when enough pieces are aligned together.
You cannot store personal data in your repositories indefinitely as a business processing personal data. You will have to inform the data subject (individual) of the reason for collecting personal data, what you intend to do with it, how long their data will be used for processing and what you would do after that task is finished (disposing of their data).
Good read: Understanding GDPR Fines and How to Avoid Them
Who is Covered by GDPR
These three different bodies are covered under GDPR differently, we will present them below in our GDPR for dummies guide.
Data Controllers:
Data Controllers (public or private) are the organizations that start the data collection process from individuals. Data controllers are responsible for the data they collect and must abide by a set of rules and regulations for processing user data and ensuring that data privacy and integrity are not compromised.
Data Processors:
Data Controllers usually contract Data Processors for processing activities. Data processors are generally within the EU and sometimes outside the EU region. GDPR requires Data Processors to be compliant with the law when processing data. If Data Processors are outsourcing their processing activities to other organizations, it is the processor’s responsibility to ensure that the other organizations are GDPR compliant.
Data Subjects:
Data Subjects are individuals whose data is collected and processed by Controllers and Processors. GDPR has granted data subjects rights to decide how organizations process their data.
Dummies Guide to GDPR Data Processing?
Data Processing under GDPR is when any user data is dealt with in the following ways.
- Stored
- Handled
- Used
- Destroyed
You are processing data if your business deals with one or more of the above-mentioned methods. Hence, you are responsible for ensuring the privacy and integrity of the data in context.
As a Data Processor, it is essential to know that data subjects can revoke their data from being processed in a few instances. In such cases, you will have 30 days to acknowledge the requests and make necessary changes within your business environment to ensure that the request is acted upon. After that, you could be slapped with heavy administrative fines by the regulatory authorities.
Here are three situations where a data subject can revoke their data from processing activities:
- Processing of data for scientific/historical research
- Processing of data for direct marketing
- Processing that is based on profiling
Are There any Exceptions to GDPR?
Of course, there are exceptions to GDPR. For example, not every business operating within the European Union’s geographical boundaries needs to comply with the GDPR law. Article 85 and Article 91 discuss these exceptions and how businesses can apply for these exceptions.
That said, other conditions mentioned in the GDPR law warrant an exception. One such exception is when an individual threatens the rights and freedom of others; they are no longer under the purview of GDPR.
Other instances where GDPR is not applicable are:
- Defense concerns
- Crime prevention
- Financial security
- Prosecution of a crime
- Suspected tax evasion
- Public health concerns
- Freedom of information
Where Does GDPR Apply?
In this GDPR for dummies guide you will find as a business, as long as you process data of the residents of the European Union, the GDPR law applies to you.
For example, if you are a business based out of the Philippines and are processing user data from the residents of the EU, you are required to be compliant.
One could argue that they comply with the privacy laws laid out by their local governing bodies, but, somehow, the world now prefers being GDPR compliant as a standard norm for showcasing your proficiency in protecting the privacy and integrity of user data.
GDPR for Beginners, What is a Data Breach? Why is it Dangerous?
A data breach is a scenario where malicious attackers/hackers access your database. A data breach is a worst-case scenario in which a business spends thousands of dollars and hundreds of human hours building security measures and implementing best practices.
Even the largest and most funded companies worldwide become victims of data breaches. One of the instances is when Facebook was attacked, and bad actors got access to 500 million users’ data.
A data breach is risky, for access to sensitive data becomes available to unauthorized users and the implications of how they use said personal data are terrifying.
As a business aiming to become GDPR compliant and taking the time to consume the GDPR quick guide, you must ensure that you store the least amount of user data in your business environments as possible. But, of course, the less you hold, the less you lose.
Also, your organization must follow a ‘privacy by default model’ to ensure that all your systems are built as securely as possible.
In the event of a breach, as a Processor, you are required to report the incident to supervisory authorities of GDPR within 72 hours and explain to them why the breach occurred, the impact, and the steps you’ve taken to overcome it.
Also check: GDPR Data Mapping: Essential Practices and Compliance Strategies
GDPR Compliance and the United States
In 2016, the European Union and the United States of America agreed to define how they would protect personal data.
It’s important to note that any organization in the United States of America will have to be GDPR certified by the US Department of Commerce or the EU Supervisory Authority. This is because the EU has claimed the US privacy laws to be inadequate; hence, to be certified by these bodies, organizations must include additional measures to ensure ‘adequate’ levels of data protections measures are included.
If you are a business based in the US, the Data-Privacy shield certification alone will not help you become GDPR compliant, but it’s a great start in the right direction.
You can get help from specialized compliance experts like Sprinto to help you get started in your compliance journey.
Steps to Become Compliant a Dummies Guide

Becoming GDPR compliant is not that easy. But, that said, it is not an impossible task as well, hence the GDPR for dummies guide.
Many US-based news sites are blocking users from the EU region as they still have not figured out how to become GDPR compliant. You don’t need to be one of them.
Here are the main things you need to focus on in the first leg of your journey in complying with GDPR.
But, keep it in mind that this is not the in-depth GDPR compliance manual. This is only to get you started.
1.Website
Does your business collect any personal information from EU residents (name, email ID, cookie consent, and more)?
If yes, you are required to become compliant.
2.Deploy Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA)
If your business processes personal data and any data you process is deemed high risk, you must deploy necessary measures (usually more than regular instances) to secure said high-risk data.
Impact Assessments allow you to understand the nature of risk your business is exposed to processing high-risk data.
Here are a few examples of high-risk data:
- Using new technology
- Marketing or advertising to children (under 16 years of age)
- Location tracking
- Processing genetic data (DNA/RNA)
3. Deploy Data Breach Notification Measures:
You are required to inform the authorities of the breach and its specifics within 72 hours from the incident’s occurrence.
Have a dedicated resource within your business who is tasked with this activity. Ensure that necessary training is imparted to help identify a breach and proceed with the required next steps.
4. Spend time drafting your privacy policies:
As a business owner, seek legal counsel and spend time drafting a custom-built privacy policy for your business.
A good privacy policy should include:
- Include contact details of the company and its representatives
- Describe why the company is collecting the data
- Say how long the information will be kept on file
- Explain the rights users have
- Be written in simple language
- Name the recipients of the personal data (if the company shares data with another organization)
- Include contact details for an EU representative and the DPO (if necessary)
5. Consent form
Include a cookie consent form when collecting user data and include segments that will allow them to choose what data processing activities they are consenting to. In other words, keep your methods of obtaining consent as transparent as possible.
How does Sprinto help?
The GDPR compliance journey is long, exhaustive, and costs many dollars if you take it on yourself or include any generic specialist. With the GDPR for beginners, we’ve tried to simplify that to a certain extent. That said, we understand that a single article cannot prepare you with the knowledge and know-how of this law. So, we’re here to help, should you need it.
Sprinto has helped hundreds of businesses become compliant. We use a perfect mix of automation and human involvement to ensure that your GDPR compliance journey is seamless. With us, you will clearly understand what lies in your journey, the tasks that can be automated and the tasks that would need human involvement.
This helps you keep the costs down and prioritize your activities without affecting your business development.
Vimal Mohan
Vimal is a Content Lead at Sprinto who masterfully simplifies the world of compliance for every day folks. When not decoding complex framework requirements and compliance speak, you can find him at the local MMA dojo, exploring trails on his cycle, or hiking. He blends regulatory wisdom with an adventurous spirit, navigating both worlds with effortless expertise
Explore more
research & insights curated to help you earn a seat at the table.





















