Sensitive Personal Data – Special Category under the GDPR Article 9
Vimal Mohan
Aug 17, 2022

The European Union commissioned the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) compliance to ensure that Data Subjects (users) are provided with laws and rights to ensure the Privacy and Integrity of their personal data.
As an organization processing personal data, it is imperative to understand that not every data type is the same and that some data sets require additional security measures and processing rules. Generally known as Special Categories of data, these need you to adhere to specific laws and regulations during processing. This article aims to help you understand the nuances of what constitutes Sensitive Personal Data and the conditions to process them.
Article 9 of the GDPR focuses on processing of Special Categories of data.
Let’s take a closer look at ‘Special Category Data.
Why do the personal data processing principles matter?
The GDPR law talks about the six data processing principles in Article 2, Article 5, Article 29 and so on. While the absolute way to process Personal Data is not defined, almost every other article within the law connects with the six principles. They are:
- Lawfulness, fairness and transparency.
- Purpose limitation.
- Data minimization.
- Accuracy.
- Storage limitation.
- Integrity and confidentiality.
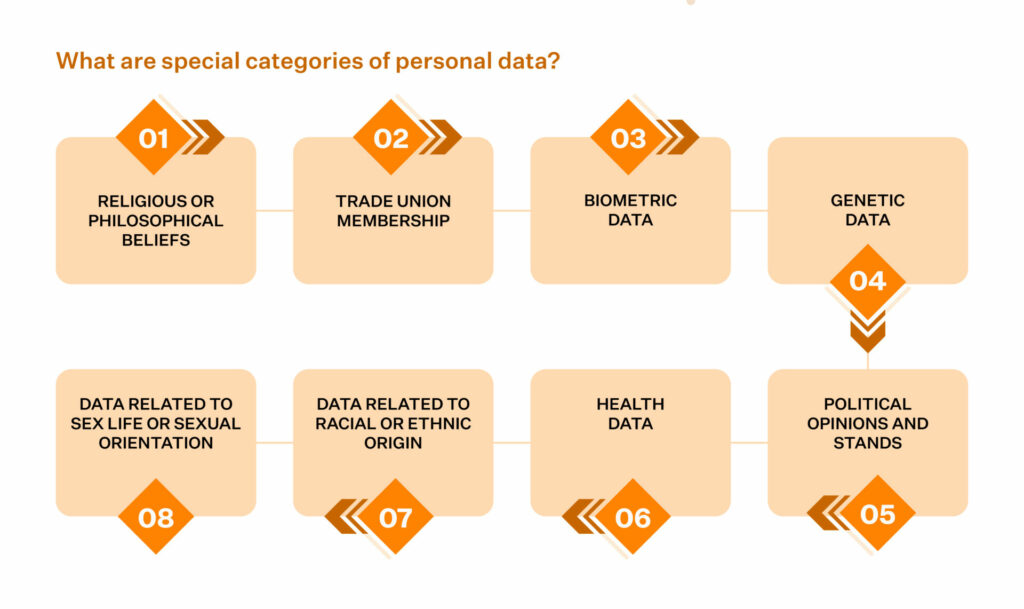
What are the special categories of Personal Data in Article 9 of the GDPR?
The types, as mentioned earlier, of data, are termed special categories. Any data that can invariably lead to a person’s specific identity depending on the nature and degree of inference or reference is included in this type of data.
Here are a few examples of Special Categories of Personal Data are:
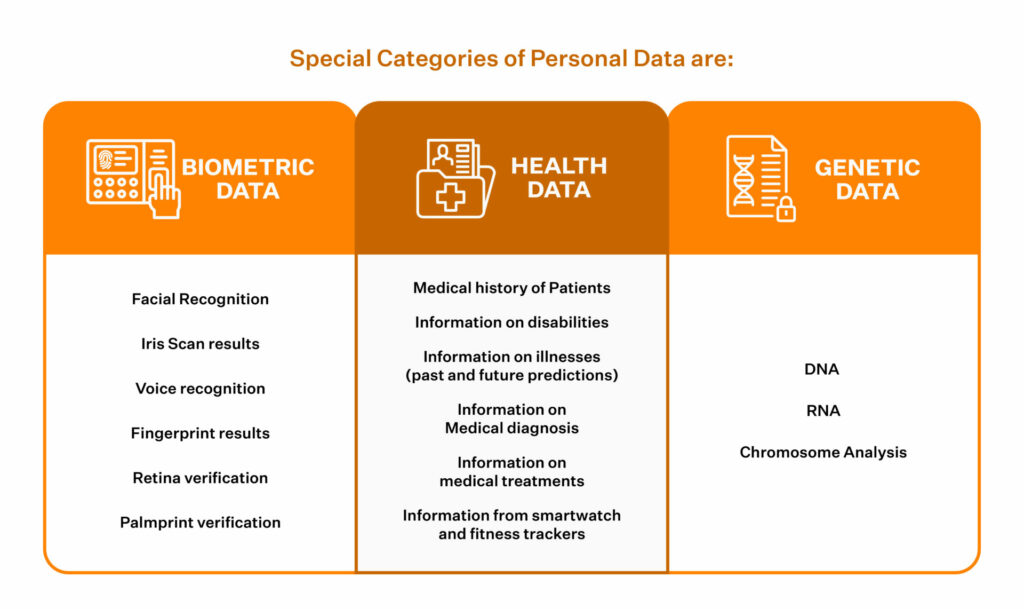
Organizations is prohibited from processing such data under a few exceptions.
What are the rules under Article 9 of GDPR?
If you are processing data that is classified under Article 9 GDPR Special Categories, it is essential to understand the risks associated with the activity. Your organization should have the security measures and policies in place to ensure that you comply with data minimization, the need for processing, transparency, and the rights of the Data Subject.
You must have a Data Processing Impact Assessment (DPIA) done for processing special category data and look into the measures and policies needed to ensure data integrity.
You must be compliant with Article 6 and Article 9 of GDPR. That is, you must be able to provide evidence for the purpose and basis of processing these data types.
What are the conditions for processing GDPR Special Category Data?
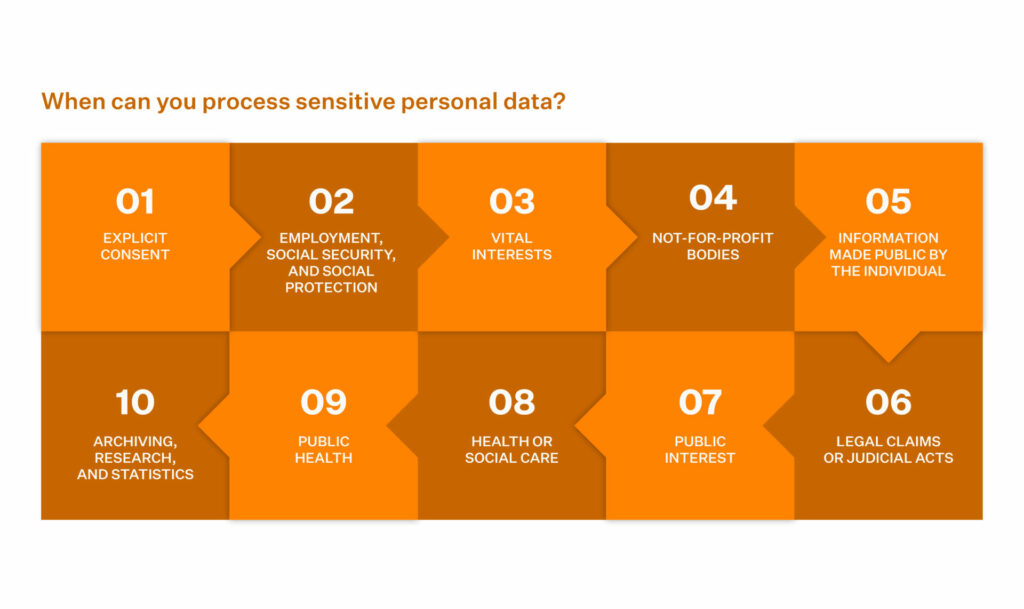
Article 9 GDPR – Special Category Data states that when one or more of these below-mentioned conditions are implied, an organization can process ‘Special Category Data.
- Explicit consent
- Employment, social security and social protection (if authorized by law)
- Vital interests
- Not-for-profit bodies
- Made public by the Data Subject
- Legal claims or judicial acts
- Reasons of substantial public interest (with a basis in law)
- Data concerning health or social care (with a basis in law)
- Public health (with a basis in law)
- Archiving, research purposes, and statistics (with a basis in law)
Exemptions to the prohibition of processing Sensitive Personal Data in Article 9 GDPR
According to Recital 52, the prohibitions on processing special categories of Personal Data are lifted if a member state requests the data processing of the Union or the Union itself.
It is also applicable if the processing is done in public interest in the following fields:
- Employment law
- Social Protection law (pensions are in the scope of this)
- Health security reasons (context: communicable diseases)
- Healthcare management
- Archiving
- Public Interest
What is the difference between Personal Data and Sensitive Personal Data?
The primary difference between Personal Data and Sensitive Data is the nature of the information. Processing Sensitive Data as a Controller or a Processor requires you to adhere to a specific set of rules as processing Special Category Data can subject the user to high risk.
In processing, member states can also include conditions prohibiting Controllers and Processors from processing Genetic, Health, or Biometric Data.
When can you process Sensitive Data GDPR?
- Explicit Consent: Organizations (Controllers) can process Sensitive data when Data Subjects (Users) give explicit consent to said processing. A user can revoke this consent at any time.
- Employment, Social Security, and Social Protection: Suppose the Controller processing Special Category Data is authorized by law. Or in cases where the controller is fulfilling their obligations concerning Employment, Social Security, and Social Protection law. That said, the Controller must ensure that the Data Subject’s rights are not compromised.
- Vital Interest: Sensitive data can be processed if it is essential to safeguard a user’s or another individual’s interests. This is also when the user is no longer capable of giving their consent (physically and legally).
- Not-for-profit: When a not-for-profit body is allowed to process Special Category Data, they have the required safeguards to ensure data integrity and security. This processing is limited to their members, ex-members, or individuals who constantly communicate with the non-profit body. No information obtained from processing Special Category Data should be made public unless the non-profit has explicit consent from the Data Subject.
- If the Data Subject has already made their Special Category Data public, an organization can process their data.
- Special data can be processed when it is necessary to defend legal claims. If the law sanctions it, special data can be processed if there is a risk to the public interest. Even under such conditions, the controller should ensure that the rights and interests of the Data Subjects are not violated.
- Processing of Special Category Data in healthcare is talked about in Recital 53. Processing can be done if the purpose of processing falls in ‘preventive’ or ‘occupational medicine’ when assessing:
- The working capacity of the employee,
- Medical diagnosis
- The provision of health and social care
- Provision of health treatment
- Management of health
- Management of social care systems and services
- Public Health: Processing of Special Category Data is allowed when the state anticipates a cross-border threat to its healthcare, and this processing could prevent or help control the effect of a contagious disease. The processing should be in line with the laws of the state authorizing the activity, and the controller should ensure that the rights and freedom of the Data Subjects are not compromised.
- For Archiving, Historical Research, and Statistics
Identify and Process Data Types Smartly with Sprinto
We’ve helped 100+ cloud-hosted organizations become compliant. More often than not, organizations become non-compliant due to their inability to identify and differentiate the data types they process.
By automating the compliance process, Sprinto gives you the edge by giving you a holistic view of your organization’s processing activities and the policies and measures you need to incorporate to achieve and maintain a continuous compliance posture. Contact us today to get started on your GDPR compliance journey.
FAQ
What are the exemptions to processing sensitive data under Article 9 of GDPR?
The exemptions are:
- Employment law
- Social Protection law (pensions are in the scope of this)
- Health security reasons (context: communicable diseases)
- Healthcare management
- Archiving
- Public Interest
When can you process special category data?
According to Article 9 of GDPR, special category data can be processed when one or more of these conditions are met. The conditions are:
- Explicit consent
- Employment, social security and social protection (if authorized by law)
- Vital interests
- Not-for-profit bodies
- Made public by the Data Subject
- Legal claims or judicial acts
- Reasons of substantial public interest (with a basis in law)
- Data concerning health or social care (with a basis in law)
- Public health (with a basis in law)
- Archiving, research purposes, and statistics (with a basis in law)
Vimal Mohan
Vimal is a Content Lead at Sprinto who masterfully simplifies the world of compliance for every day folks. When not decoding complex framework requirements and compliance speak, you can find him at the local MMA dojo, exploring trails on his cycle, or hiking. He blends regulatory wisdom with an adventurous spirit, navigating both worlds with effortless expertise
Grow fearless, evolve into a top 1% CISO
Strategy, tools, and tactics to help you become a better security leader
Found this interesting?
Share it with your friends
Get a wingman for
your next audit.
Schedule a personalized demo and scale business

Sprinto: Your growth superpower
Use Sprinto to centralize security compliance management – so nothing
gets in the way of your moving up and winning big.


