A survey of small and medium-sized businesses indicates that 94% reported experiencing a cyberattack in 2024, making structured security frameworks like ISO 27001 highly relevant, even outside the enterprise segment.
Having a certification is rapidly shifting from “nice-to-have” to table stakes. Whether driven by customer and regulator demands or simply the reality of today’s threat landscape, ISO 27001 has become basic hygiene for any organization serious about protecting its data and earning trust.
Let’s understand how the ISO 27001 standard works, its requirements, core clauses, controls, implementation workflow, challenges, timelines, cost, and everything else.
- The ISO 27001 standard is broken down into Clauses 4–10 and Annex A, which comprises 93 controls on context-setting, leadership, planning, operations, evaluation, and continuous improvement.
- Implementation typically follows a seven-step workflow, from defining scope and assessing risks to documentation, control implementation, and certification audits.
- Maintaining compliance requires ongoing monitoring, annual audits, risk reviews, and continuous control validation, and not a one-time certification push.
What is ISO 27001 compliance?
ISO 27001 compliance is a result of an organization implementing a systematic, risk-based Information Security Management System (ISMS) that meets the requirements of the international standard ISO/IEC 27001. It involves identifying information risks, selecting and applying appropriate security controls from Annex A, and continually managing and improving security processes to ensure ongoing effectiveness.
The official ISO 27001 certification (achieved through an audit by an accredited body) proves to customers, partners, and regulators that the organization has independently verified protections in place for confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.
The scope of ISO 27001
The scope of ISO 27001 defines exactly what parts of the organization (business units, locations, services, processes, and information assets) are covered by the ISMS and will be audited for certification.
Correct scoping prevents certification surprises and keeps the project manageable and valuable. Scoping “the entire organization” often turns ISO 27001 into an endless, budget-draining nightmare that delays value and risks failure.
Meanwhile, scoping too narrowly (across a single server or department) creates a fragile certificate that customers and auditors won’t trust and leaves most real risks unprotected. We’ll learn more about this in the coming sections.
ISO 27001 vs SOC 2 vs NIST
ISO 27001, SOC 2, and NIST are three widely recognized security frameworks, but they serve different purposes and apply to different types of organizations.
Here’s a comparison between each framework:
| Framework | What is it? | Focus area | Who is it for? | Certification / Attestation |
| ISO 27001 | A global standard for building an Information Security Management System (ISMS) | Risk-based security management and controls | Organizations of any size in any industry, worldwide | Formal certification by an accredited body |
| SOC 2 | A U.S.-based attestation standard under AICPA | Trust Service Criteria (security, availability, integrity, confidentiality, privacy) | Mostly SaaS and service providers handling customer data | Auditor-issued attestation report (Type I or Type II) |
| NIST CSF / NIST 800-53 | A U.S. government-backed security and risk management framework | Detailed controls for cybersecurity and federal data protection | Government agencies and organizations working with them; also adopted widely by enterprises | No formal certification; self-assessment or third-party assessment |
Clause-by-clause requirements of ISO 27001
ISO 27001’s core Clauses 4 to 10 guide organizations in defining context, ensuring leadership commitment, planning and supporting security efforts, operating controls effectively, and continually evaluating and improving their ISMS.
They form the core requirements that ensure information security becomes a systematic and sustainable part of organizational practice.
Clause 4: Context of the organization
Clause 4 requires an organization to step back and understand its environment before building an ISMS. This includes identifying internal and external factors, stakeholder expectations, and the scope of information security.
Essentially, it ensures the ISMS is designed around real business needs rather than assumptions or templates.
Clause 5: Leadership
ISO 27001 emphasizes that leadership cannot be hands-off. Top management is expected to demonstrate commitment, set the direction for information security, and make sure roles and responsibilities are clearly defined.
Without this kind of support, an ISMS usually struggles to gain traction across the organization.
Clause 6: Planning
For Clause 6, organizations prepare for risks and opportunities related to information security. This clause covers ISO 27001 risk assessment, risk treatment, and setting measurable objectives. The idea is to plan security activities thoughtfully, instead of reacting to issues as they arise.
Clause 7: Support
Clause 7 focuses on building the foundation that an ISMS needs to operate properly. This includes providing resources, ensuring personnel are competent, raising awareness, and maintaining accurate documentation. Think of it as the operational toolkit behind the ISMS.
Clause 8: Operation
Clause 8 moves into actual execution. Organizations must implement risk treatment plans, operate security processes, and manage any outsourced functions. It’s where security measures are consistently implemented and adhered to according to established controls.
Clause 9: Performance evaluation
Organizations need to measure whether the ISMS is working. Clause 9 requires monitoring, internal audits, and management reviews. These activities help identify gaps, confirm effectiveness, and ensure decisions are based on evidence.
Clause 10: Improvement
Finally, ISO 27001 expects organizations to maintain and improve their ISMS over time. Organizations should correct issues, address non-conformities, and look for ways to enhance their ISMS based on added organizational context. The overall goal is to maintain the system’s resilience against evolving risks.
What are ISO 27001:2022 Annex A controls?
Annex A of ISO 27001 lists 93 practical security controls (updated in the 2022 version) grouped into four themes: Organizational (37), People (8), Physical (14), and Technological (34). These are essentially a globally accepted “best-practice checklist” to protect confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.
- Organizational (37 controls): Organizational controls define the governance layer of security, including policies, assigned roles, third-party management, and the utilization of threat intelligence.
- People (8 controls): People-focused controls center on secure hiring practices, due diligence, ongoing training, and security awareness programs.
- Physical (14 controls): Physical controls safeguard the organization’s facilities and equipment through measures such as entry restrictions, device security, and clear desk rules.
- Technological (34 controls): Technology controls manage how systems are accessed, secured, and maintained. For example, through authentication, encryption, and secure development practices.
Are all 93 controls applicable to your business?
No, not all 93 controls are mandatory for every organization. You only need to implement the controls that are relevant to your risks after your risk assessment (Clause 6).
Through the Statement of Applicability (SoA), you justify which controls you apply and why others are not applicable, making the standard flexible for a tiny startup or a global bank alike.
How do these controls translate in reality? Examples
Controls act as modular building blocks, providing structure and flexibility to scale security, meet buyer requirements, and mitigate risk exposure. Each control has attributes (e.g., cybersecurity, data protection) that help you filter and prioritize implementation according to business needs.
For example:
- A.5.23 – Information security for cloud services ensures your SaaS usage isn’t a blind spot
- A.8.10 – Information deletion enforces clean records for sensitive data
Together, these controls turn abstract security goals into concrete, repeatable actions that strengthen your operational resilience.
What does being ISO 27001 compliant actually mean?
Being ISO 27001 compliant can mean a lot of things for a business, and the value it brings can differ from one organization to another. At its core, it reflects the organization’s understanding of its internal dynamics, external obligations, and broader business goals.
Here’s what it can mean for:
1. Internal context
Internally, ISO 27001 compliance means your ISMS reflects your real-world context, security culture, processes, team structure, tech stack, and constraints, not a generic template out of touch with reality.
For instance, in a SaaS environment, it relates to how product teams ship code, how customer data flows through environments, how decisions are made, and which internal systems or skills gaps could compromise or undermine security controls.
2. External context
Externally, ISO 27001 compliance means your security program is aligned with the world you operate in. For example, regulations (GDPR, HIPAA), customer and investor expectations, market pressures, or even cloud provider dependencies.
For customers, it signals that you manage their data with predictable, independently validated discipline. For external evaluators, like auditors, prospects, and partners, it provides a trusted, standardized benchmark to assess your security maturity without relying on assumptions.
3. Business context
In the business context, being ISO 27001 compliant means information security is explicitly tied to revenue, growth, and strategy rather than sitting as a cost center in IT.
For startups and SaaS leaders, this manifests as security objectives that support initiatives such as entering new geographies, closing larger enterprise deals, reducing downtime, or enabling faster but safer releases, all driven by a risk-based approach.
What did Anaconda, a unified AI platform, achieve from ISO 27001?
Anaconda needed a consistent way to implement and validate controls across teams, replacing spotty, manual processes that created gaps. As David Mason shared, “We didn’t have the maturity in our procedures to validate controls.”
Furthermore, their rapidly growing customer base of 95% of the Fortune 500, required clear, verifiable proof of security without long explanations or bespoke questionnaires.
From a more business perspective, ISO 27001 helped Anaconda cut engineering busywork, accelerate sales cycles, and reduce security questionnaires by more than half. This enables the team to focus on strategic security improvements rather than tactical compliance tasks. Read the full case study.
How to get ISO 27001 compliant
Although every company’s ISO 27001 compliance journey can look slightly different, some core steps are generally followed.
From defining the scope of your ISMS to completing the formal certification audit, the process can be broken down into a precise sequence of actions that helps organizations build structure, reduce risk, and demonstrate security maturity in a systematic manner.
Here are the seven steps to get ISO 27001 compliant:
Step 1: Define ISMS scope
The first step involves identifying which parts of the business, such as departments, locations, processes, and systems, will be included in the ISMS. Organizations typically define boundaries based on where sensitive information is stored, processed, or transmitted.
In a real scenario, you usually select systems, assets, and business units from built-in inventories. If you’re using a compliance automation platform, it maps them, links relevant Annex A controls, and maintains a dynamic scope document that updates as your environment changes.
Step 2: Build a risk assessment methodology
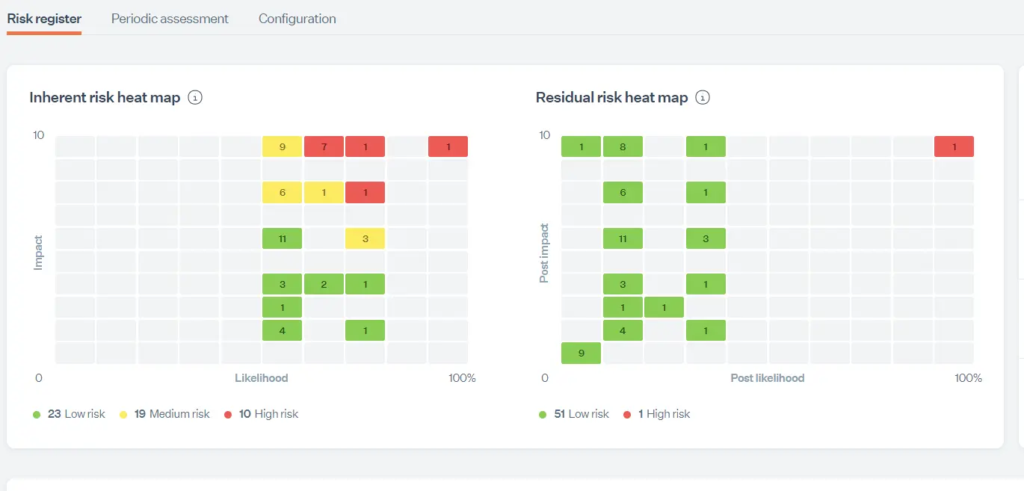
The foundation for risk management starts with establishing a repeatable method for identifying risks, analyzing their impact and likelihood, and selecting appropriate treatments. This consistency ensures that decisions aren’t subjective or ad-hoc, but grounded in a defensible, auditable process.
Use predefined risk frameworks and automated scoring models in your platform. You can then log risks directly, link them to assets, assign treatment plans, and let the system calculate residual risk and automatically generate compliant risk registers.
Step 3: Create mandatory documentation
ISO 27001 requires several essential documents, including the Information Security Policy, Risk Assessment Report, Statement of Applicability (SoA), and procedures for incident management, access control, and disaster recovery, among others.
You’ll find templates for these in your compliance tool. Use it to auto-populate sections where possible, version-control documents, track approvals, and maintain audit-ready records.
Step 4: Implement controls
Once you’ve identified the applicable Annex A controls, you will action them in this step. Control implementation encompasses all technical, organizational, physical, and personnel-related safeguards, including tasks such as enforcing access controls, establishing backup procedures, and training employees.
Controls are mapped to evidence requirements. Use the tool to automatically assign tasks, integrate with systems (such as AWS, Google Workspace, or HR platforms) to fetch evidence, and monitor control status. Rely on automated tests, screenshots, and logs to reduce manual effort.
Step 5: Conduct an internal audit
Before certification, an internal audit evaluates whether the ISMS meets ISO 27001 requirements and is functioning effectively. If appointed, the internal auditor checks documentation, processes, and control performance.
Run internal audits using built-in checklists or automated workflows. Track findings, assign corrective actions, store artifacts, and generate audit reports automatically to demonstrate compliance readiness.
Step 6: Conduct management review
In this step, leadership reviews ISMS performance, risk posture, audit results, and improvement opportunities. Ensure that top management stays aligned with security objectives and provides the necessary resources.
In Sprinto, you can use dashboards that provide real-time metrics like risk levels, control health, audit findings, and incident trends. Furthermore, you can generate management review reports and keep a record of decisions, attendance, and approvals required for ISO 27001 evidence.
Step 7: Undergo certification audit (stage 1 + stage 2)
Prepare all necessary documentation, evidence, and system access for both stages of the ISO 27001 certification audit, which is conducted by an accredited external auditor.
Stage 1: Documentation review: The auditor examines your ISMS documentation, such as the defined scope, risk assessment methodology, risk register, and mandatory policies, to confirm that the foundational requirements of ISO 27001 are properly established.
Stage 2: Implementation review: In this phase, the auditor verifies that your controls are not only documented but also effectively implemented. Through evidence review, staff interviews, and control walkthroughs, they assess whether the ISMS functions as described and meets the standard’s operational expectations.
During each of the audit stages, auditors may identify non-conformities or areas where your ISMS does not meet ISO 27001 requirements. Failing an ISO 27001 audit is not uncommon, especially on the first attempt.
What happens next depends on the severity of the findings:
- Major NCs: Significant failures that affect the reliability or completeness of the ISMS. Certification cannot proceed until the issues are resolved. You may need a follow-up audit to re-evaluate those areas.
- Minor NCs: Smaller gaps that don’t undermine the ISMS but still need correction. You can still pass conditionally, provided you submit a corrective action plan and resolve the issues within the required timeframe.
- Observations: Not NCs, but potential risks or weaknesses to be aware of. If there are many unresolved findings, the auditor may delay certification until you demonstrate compliance.
Download an easy ISO 27001 checklist
ISO 27001 mandatory documents and records
Here are the mandatory documentations you cannot miss while complying with ISO 27001:
- Scope of the ISMS: This sets out exactly which systems, teams, and locations fall under your ISMS.
- Information Security Policy: It outlines the organization’s guiding principles and direction for information security.
- Risk Assessment and Risk Treatment Process: This documents the methods used to identify, evaluate, and address risks.
- Statement of Applicability (SoA): The SOA provides a formal list of chosen controls and why each one is included or excluded.
- Risk Treatment Plan: This document outlines the specific actions planned to reduce or manage identified risks.
- Information security objectives: These are the measurable security goals that support your organization’s overall strategy.
- Risk Assessment and Treatment Report: It captures the outcomes of the risk assessment exercise and how each risk is being handled.
- Inventory of assets: This is a centralized record of information assets that need protection.
- Acceptable Use of Assets Policy: This policy defines the behavioral expectations for how employees should use company resources.
- Incident Response Procedure: This procedure outlines how the organization detects, reports, and manages security incidents.
- Register of statutory, regulatory, and contractual requirements: This document tracks all external obligations that impact information security.
- Security operating procedures for IT management: These procedures describe the day-to-day IT routines necessary to maintain secure operations.
- Definition of security roles and responsibilities: Security roles and responsibilities define who is accountable for specified security-related duties.
- Definition of security configurations: This document sets the baseline configurations that systems and devices must adhere to.
- Secure system engineering principles: These principles guide the design and construction of security systems.
Here are all the mandatory records you need to provide during audits:
- Training and competence records: These demonstrate that all personnel possess the skills and awareness needed for their roles.
- Monitoring and measurement results: These results provide evidence showcasing how the ISMS performs over time.
- Internal audit program: This is a documented plan outlining when and how internal audits will be conducted.
- Internal audit results: These records document the findings of the audit and help identify compliance gaps.
- Management review results: These are official documentations of leadership discussions, decisions, and follow-up actions.
- Corrective action results: These records demonstrate how non-conformities were identified, addressed, and resolved.
- User activity, exception, and security event logs: These logs help trace actions and events that may affect security.
ISO 27001 costs, timelines, and team requirements
ISO 27001 can be cumbersome if done in an unstructured manner. For most businesses, expect a few months of focused work, a cross‑functional core team, and a mix of internal time, tools, and external audit fees.
Cost
The traditional ISO 27001 certification cost (Stage 1 + Stage 2) typically costs between $30,000 and $60,000, depending on size, scope, and auditor.
Note that the total certification cost (including internal work, tools, and support) can range from $50,000 to $200,000, with early-stage startups sometimes incurring costs closer to $10,000 to $50,000 when they keep the scope small and utilize automation.
Timelines
If you’re taking the DIY route, ISO 27001 implementation typically takes 6–9 months, but with a consultant, it can be reduced to roughly 3–6 months.
With a GRC platform like Sprinto, the timeline for ISO 27001 is typically at 6 to 8 weeks for audit‑readiness. With the platform’s new AI features and some groundwork, this can be further reduced.
Team and roles
You do not need a big dedicated security department, but you do need a small core team with clear ownership.
This can typically include an internal lead (often a founder, COO, or security/compliance owner), a technical owner from engineering or DevOps, and support from HR and legal/ops for people and vendor controls, with control owners mapped across these functions.
If you’re looking for a completely hands-off compliance process for ISO 27001, explore Sprinto AI.
Managing ISO 27001 risks, challenges, and pitfalls
Even with a solid plan, organizations often run into common challenges while working toward ISO 27001 compliance. These issues can slow progress, increase costs, or create unnecessary complexity if they’re not managed early. Here are some of the most frequent pitfalls teams encounter:
1. Incorrect ISMS scoping
Businesses often either ‘boil the ocean’ by scoping everything and becoming overwhelmed or scope too narrowly, leaving critical assets or processes out, which leads to gaps and audit findings.
The corrective action here is to revisit Clause 4.3 properly: map information assets, processes, locations, and stakeholders, align scope with business objectives and risk appetite, and document a clear, justified scope statement that actually reflects how the organization works.
2. Putting too many controls in place
Many teams assume ISO 27001 means “implement all Annex A controls at full strength,” which leads to over‑engineering, burnout, and controls that exist on paper but never work well in practice.
If you encounter this issue, revisit the risk assessment exercise, update the risk treatment plan, and refine the Statement of Applicability to commit only to controls that are necessary and realistically sustainable.
3. Using too many disconnected tools
Organizations frequently spread controls and evidence across ticketing tools, spreadsheets, shared drives, and point security products, which is the new normal.
The solution here is to adopt a GRC tool that can integrate with almost any tool and pull evidence against your Annex A controls.
Sprinto has 300+ standard integrations along with an open API, so you don’t have to worry about what tools you’re using and how much you need to protect.
4. Treating the ISMS as a one-time effort
Many businesses surge to certification, then let internal audits, risk reviews, and management reviews slide until just before surveillance or recertification audits.
Instead, organizations need to conduct periodical cycles of risk assessment, internal audits, management reviews, and control monitoring, with clear KPIs and owners. This will enable evidence to accumulate continuously, and the ISMS genuinely improves rather than being reactivated every three years.
Post certification: Maintaining ISO 27001 compliance
Maintaining ISO 27001 compliance after certification is about proving your ISMS works every day, not just every three years.
Once certified, your organization enters a three‑year cycle where accredited bodies conduct annual surveillance audits over the course of two years, followed by a full recertification audit in the following year. These surveillance audits typically sample 30–40% of controls each year, acting as health checks on your ISMS and surfacing whether your risk treatment, operations, and documentation are being maintained in practice.
To stay ready, many organizations now adopt Continuous Control Monitoring (CCM) tools that automatically test key controls, flag failures in near real-time, and reduce the cost and errors associated with purely manual evidence collection.
Staying compliant also means keeping policies, risks, and decisions fresh rather than static. Good practice is to run at least annual internal audits and risk assessments, with scheduled policy and risk review cycles that align with the surveillance audit calendar.
ISO 27001 in 2026: Has anything changed?
The current version remains ISO/IEC 27001:2022, with its sole amendment (Amd 1:2024) adding climate action changes by requiring organizations to assess if climate change is a relevant issue in their ISMS context (Clause 4.1).
Although ISO 27001 has not undergone any revisions since 2022, the way businesses approach it has evolved.
The standard supports AI-assisted ISMS implementation via tools for baseline drafting, risk assessment, and monitoring. Sprinto AI enhances this further by automating evidence collection, mapping controls to real-time system data, and guiding teams through compliance tasks with AI-driven recommendations.
Expedite ISO 27001 compliance with Sprinto
Sprinto goes beyond checklists and templates. Sprinto’s AI-first platform guides your setup, refines your controls, ensures strict documentation, mitigates risk, and automatically gathers certification-grade evidence.
Here’s why global teams are choosing Sprinto for ISO 27001 compliance:
- Engineering-light, no-code implementation: Get compliant without heavy engineering involvement thanks to Sprinto’s intuitive, no-code workflow.
- Transparent, predictable pricing: No hidden advisory fees, surprise renewals, or paywalled support—your total cost of ownership stays low.
- Expert-led audit readiness: Sprinto prepares your evidence, organizes documentation, and streamlines auditor access for smooth ISO 27001 audits.
- AI-native GRC capabilities: Build custom GRC agents, map any custom framework instantly, and gain real-time risk intelligence across your stack.
- Designed for scaling teams: Sprinto adapts to complex environments, multi-framework roadmaps, and advanced compliance needs.
Frequently asked questions
1. Which industries benefit the most from ISO 27001?
Industries that deal with sensitive or regulated data benefit the most from ISO 27001, as it helps prove security maturity, reduce risk, and build trust with customers.
Startups and SaaS companies gain an edge since ISO 27001 certification often becomes a ticket when selling to enterprise customers who demand proof of strong security controls.
2. What are the main principles of ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 is built on the principles of Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA). These three elements form the foundation of an effective ISMS.
3. What is the purpose of ISO 27001?
The purpose of ISO 27001 is to systematically identify risks to information assets and apply appropriate security controls. It ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data while aligning with business and regulatory requirements.
4. How does ISO 27001 help build customer trust and close deals?
ISO 27001 helps build customer trust by proving that your organization follows a structured, independently audited security framework. Enterprise buyers increasingly demand demonstrable security baselines before signing contracts.
5. Who in an organization is responsible for ISO 27001 compliance?
The responsibility for ISO 27001 compliance is shared across the organization, but led from the top. Senior management is ultimately accountable, providing direction and resources for the ISMS. A CISO, Information Security Officer, or ISMS Manager typically oversees the day-to-day implementation, managing risk assessments, controls, and audits.
Pansy
Pansy is an ISC2 Certified in Cybersecurity content marketer with a background in Computer Science engineering. Lately, she has been exploring the world of marketing through the lens of GRC (Governance, risk & compliance) with Sprinto. When she’s not working, she’s either deeply engrossed in political fiction or honing her culinary skills. You may also find her sunbathing on a beach or hiking through a dense forest.
Explore more ISO 27001 articles
ISO 27001 Overview & Requirements
ISO 27001 vs Other Frameworks
ISO 27001 Audit & Certification Process
ISO 27001 Management & Assessment
ISO 27001 Implementation & Automation
ISO 27001 Industry-Specific Applications
research & insights curated to help you earn a seat at the table.













