ISO 27001, the gold information security standard, is quite comprehensive and structured in its approach. Most companies either feel overwhelmed about where to start or try to over-engineer things. Our ISO 27001 checklist solves for just that.
It saves you time by minimizing the guesswork and provides the roadmap you need to accelerate the certification process. Read on for a step-by-step guide.
- An ISO 27001 checklist breaks the standard into actionable steps for ISMS implementation and audit readiness.
- It covers scope definition, risk assessment, controls, documentation, training, and audits.
- Checklists improve accountability and reduce missed requirements.
- Sprinto supports checklist-driven implementation with automated evidence collection.
Why ISO 27001 checklist is crucial for any organization?
An ISO 27001 checklist is crucial to simplifying framework implementation. It breaks down key points on ISMS scoping, conducting risk assessments, the essentials of SOA (statement of applicability), selecting key controls, and conducting internal audits.
Here’s why you need that ISO 27001 checklist:
Simplifies Compliance
An ISO 27001 checklist helps break down complex requirements into simple, actionable tasks. It acts as a step-by-step guide to establishing, implementing, and maintaining an ISMS, helping organizations stay on track.
Enhances accountability
The checklist helps assign tasks and responsibilities for various aspects of ISMS to relevant stakeholders. Tracking progress becomes easier with the checklist, and reporting channels are clearly defined, promoting accountability and ownership.
Facilitates audits
The checklist facilitates internal audits by providing a list of items that need to be reviewed and verified. It also helps organizations prepare for external audits by ensuring the completeness of requirements such as policies, procedures, risk assessments, and records.
ISO 27001 Checklist (An Implementation roadmap)
An ISO 27001 checklist assesses an organization’s compliance with the ISO 27001 standard and outlines requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS).

Here are 13 key items of the ISO 27001 audit checklist to get certified:
1. Form an ISO 27001 Internal Team
Treat this team as your task force for ISO Compliance Checklist. They will own and lead the compliance initiative, as well as work and coordinate with all the other stakeholders to take the process to its completion. The team can comprise an Infosec Officer (you can internally nominate one if needed) and key members from your IT team.
- Define roles and responsibilities: Ensure the roles and responsibilities are etched out for PeopleOps, the Engineering team, the IT departments, and other teams involved in the process
- Equip them with the right level of awareness: Check if each team member understands the security expectations.
2. Build your ISMS
Before you can build an ISMS, you must scope and design it. The ISMS scope defines which information and information assets you intend to protect and is based on your:
- Organization Structure
- Business Needs & Locations
- Business Critical Processes & Products
Here are some good practices to build your scope:
- Define the scope clearly: The scope must include your organization’s systems, processes, physical locations, services, and products, to name a few that must be protected.
- Understand your data: Since each business is unique and handles different types of data, you’ll need to determine what kind of data you have to protect before you build an ISMS.
- Determine scope boundaries: Not everything can be in scope, so it’s important to narrow it down to systems, services, products, and platforms that are critical touchpoints for handling sensitive data.
Remember, any organizational assets outside the scope would be treated as those external to your company. The scope must be defined as a separate document or as part of your overall information security compliance policy. And don’t forget to get management approval for the scope.
3. Create and Publish ISMS Policies, Procedures & Documentation
The ISO 27001 implementation checklist is heavy on documentation and requires the organization to set up policies and procedures to control and mitigate security risks to its ISMS.
Policies you need to have in place:
- Information Security Policy
- Mobile Device Policy
- Remote Access / Teleworking Policy
- Access Control Policy
- Clear Desk and Screen Policy
- Acceptable Use of Information Assets Policy
- Communications (Information Transfer) Policy
- Secure Development Policy or Plan
- Supplier Management Security Policy)
Mandatory documents for the management of the ISMS:
- Scope of ISMS
- Statement of Applicability (covered in detail later)
- Inventory of Assets
- Risk Assessment and Treatment Plan (covered in detail later)
- Security Roles & Responsibilities
Mandatory procedures required:
- Information Classification and Management
- Asset Management
- Vulnerability Management
- Management of (Removable) Media and Storage Devices
- User Access Management
- Working in secure areas
- Change Management
- Capacity Management
- Anti-Malware
- Backup and Recovery
- Information Security Incident Management
- Business Continuity Plan
Additional documents needed:
- Job Descriptions of employees dealing with Information Security
- Training of Staff
- Audit Plans
- Internal and External Audits and the results
- Maintenance Plans and Performed Maintenance Work
- Logs, KPIs, Key Figures, Configuration Files, and Network Plans
- Minutes of the Meetings (capturing discussion of risks and overall security topics)
Automate the evidence-collection process with the help of Sprinto
4. Conduct Risk Assessment & Treatment
Risk assessment is an important activity to meet your ISO 27001 requirements. Here’s how you can meet it:
- Assess risks across assets and systems: Conduct an internal risk assessment to understand how assets and systems may be exposed to threats
- Prioritize security risks: Identify the risks that could impact data confidentiality, integrity, and availability for these, assign a probability of their occurrence, and peg the impact levels (high to low).
- Begin with Risk treatment: Based on risks identified and prioritized, select controls for mitigation. For example, you can select role-based access controls and MFA for unauthorized access. Annex A (2022 version) specifies 93 controls across four categories covering policies, access controls, and supplier relationships.
Therefore, risk treatment (remediation) involves procedures/measures to be taken to decrease the identified risks to an acceptable level. The risk assessment methodology and measurement must be agreed upon in advance and applied consistently.
Sprinto integrates with your cloud environment to identify misconfigurations and vulnerabilities – with precision and accuracy. It offers a 360-degree view of risks to help IT teams manage risks proactively from a single console.
Don’t just identify risks at a surface level. Sprinto helps you build true risk resilience by analyzing the impact of each risk using industry level benchmarks. Create your own risk register by adding custom risks and assigning impact scores.
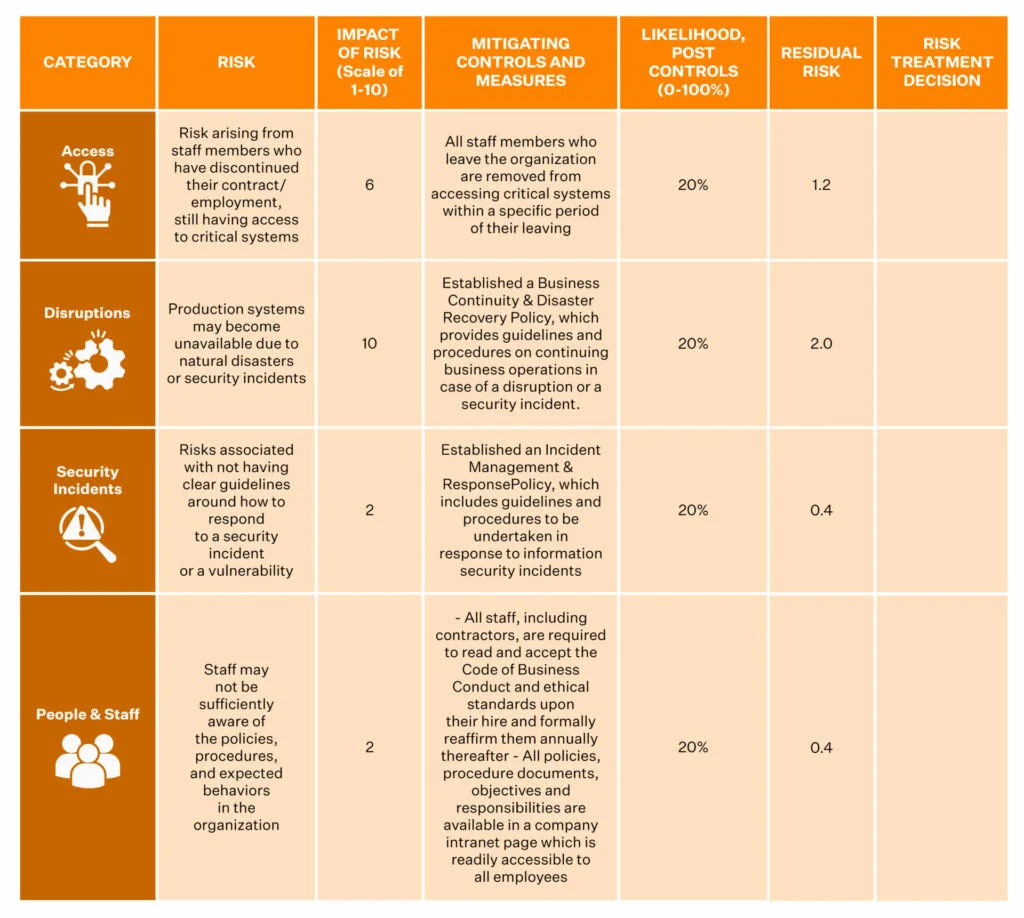
Again, have clear documentation of it all as part of your ISO 27001 Compliance Checklist.
5. Ready the Statement of Applicability (SOA)
The SOA for ISO 27001 is a list of all of the controls from Annex A that apply to your organization.
- The SOA should reveal which controls the organization has chosen to mitigate the identified risks.
- It should also include justifications for the inclusion and exclusion of controls. It should point to the relevant documentation on the implementation of each control.
There are 11 ISO 27001 requirements (mandatory), with 114 security controls grouped into 14 sections (Annex A). To know more about the controls listed in Annex A, you can refer to the ISO 27002 standard that details the controls.
Case Study
Sprinto gave Intellect the confidence to achieve its ISO goals. Here’s how!
6. Implement ISMS Policies and Controls
Implementing the ISMS policies and controls is the most critical step in your ISO 27001 checklist. You can consider the oft-used Plan Do Check Act (PCDA) cycle for implementation. Its elements include:
- Plan – Identify the challenges & threats, and note the requirements & control objectives
- Do – Implement and test solutions, processes and technologies to lower risk and operational failure
- Check – Monitor and review the performance of the ISMS
- Act – Update and improve your ISMS based on the results of any outputs or failures
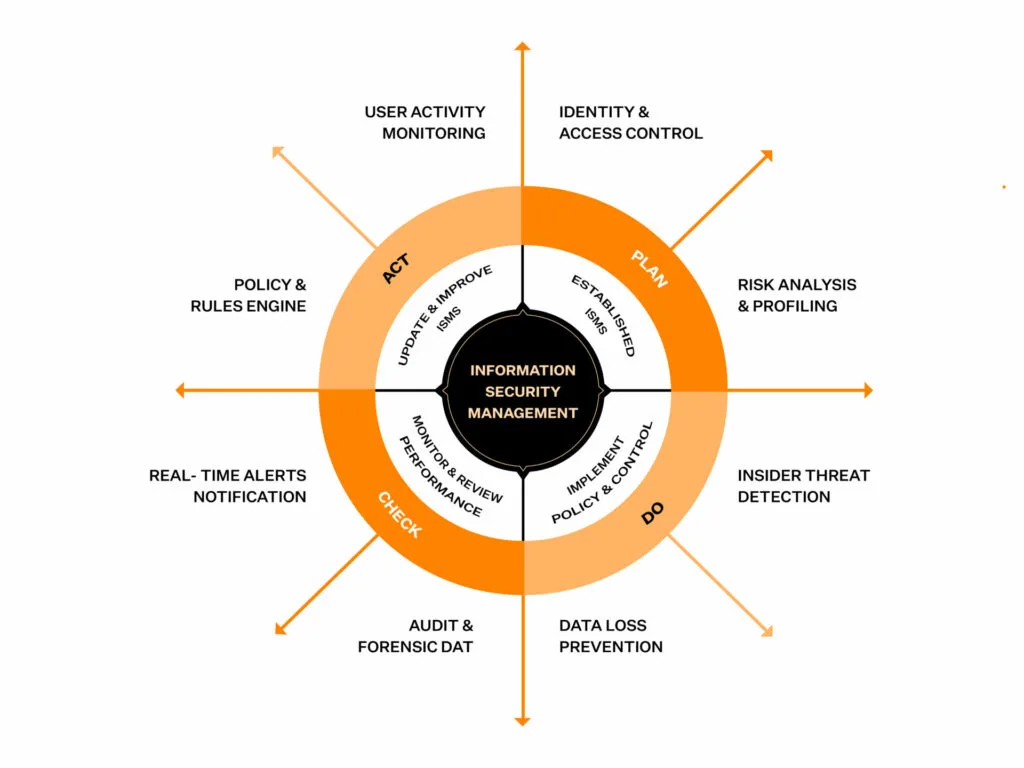
Additionally, remember to
- Ensure your ISMS meets the mandatory requirements of clauses 4-10 of ISO 27001 audit checklist and the select controls from Annex A.
- At this point, you must also create a communication plan to inform your employees about the policies and procedures and set a plan rolling to track their feedback and reviews.
Implement the right controls with the help of Sprinto.
7. Conduct Employee Awareness & Training Programmes
Employees are the first line of defence in the event of cyber attacks, breaches and hacks. Therefore, employee awareness and certification training play a significant role in the ISO 27001 standards.
- Provide ongoing security training: You must ensure your employees receive relevant and regular infosec education and training and periodic updates on organizational policies and procedures.
- Prepare them for real-world risks: You must also train your employees on how to respond to some of the common risks your organization faces as per the ISO 27001 checklist.
Sprinto helps you train your employees, conduct tests after completing a module and documents them in a repository to help you provide evidence.
8. Monitor ISMS, conduct Gap Analysis, and Remediate
The best way to evaluate your ISMS is to monitor and review it.
- Ensure ongoing improvement: Monitor the ISMS, do a gap analysis, remediate, test more and monitor – this endless cycle can help you strengthen your ISMS. Remember, continual improvement is the name of the game.
- Close the loop with evidence: Post remediation, gather evidence to demonstrate how the ISMS meets the standard’s requirements as per your ISO 27001 checklist. This can include MFA screenshots, access logs, training records, policy documents and internal audit reports.
We have a free resource for you to check your gap analysis stage.
Download ISO 27001 gap analysis template
Case Study
Check out how Sprinto helped Equalture get ISO 27001 compliant and increase sales velocity
9. Undergo Internal Audit
Internal audits are executed internally to evaluate whether their ISMS meets the standard’s requirements. These audits can be conducted by an internal team (aka ISO 27001 internal auditor) as designated by the senior management or contracted out to external auditors.
The internal audit is much like the reconnaissance of ISO 27001 audit checklist before the external audit. It looks for gaps, non-conformities, and vulnerabilities in the ISMS. The internal audit will assess ISMS performance and review your documentation before producing an internal audit report.
Here’s a look at what the internal audit will be like:
Documentation Review
- The internal auditor will review all the documentation, ensure the audit scope covers ISMS adequately and evaluate the controls to the ISO Standard for compliance.
Field Review
- The internal auditor will review the ISMS, conduct penetration tests, and collect evidence to demonstrate what’s working and isn’t.
- They will also talk to different teams and understand how they comply with the ISMS.
Internal Audit Report
Based on their findings and analyses, the auditor will present an internal audit report to the management as per the ISO 27001 checklist.
- The report will contain the scope, objective and extent of the audit.
- It will also detail which policies, procedures and controls are working and which aren’t with evidence.
- The report also details correction actions and recommendations, limitations, and other observations.
- It includes remediation suggestions and course corrections before your organization can present itself for an external audit. The report is presented to the management.
Management Review
The management goes through the internal audit report. The auditor and the management can discuss the list of major and minor non-conformities and action plans and review whether the organization is ready for the external audit and ISO certification as per the ISO 27001 compliance checklist.
10. Internal Audit – Stage 1
Organizations are ready to undergo an external audit once the internal audit gives a clean chit. The process of the external audit is the same as that of an internal audit, the difference being that it leads to certification (or recertification, as the case may be).
The accredited ISO 27001 External Auditor reviews the documentation you created for ISO 27001, compares it to the ISO standard and checks for compliance.
- The auditor will ask to see all the documents created for the ISMS and will review them to ensure you have all the mandatory documents in place.
- While organizations can define the scope of their ISMS, smaller organizations should keep the entire organization in scope.
- The Stage 1 ISO 27001 audit will end with an Audit Report, which will include an assessment of your ISMS, scope and certification, improvement areas and audit readiness, among other things.
- You should perform Stage 1 and Stage 2 ISO 27001 audits within six months. Stage 1 Audit may otherwise need to be repeated.
Curious about ISO 27001 Compliance Costs?
11. External Audit – Stage 2
The main audit entails an evidential audit (on a sample basis) to ascertain if your organization is operating the ISMS per the ISO standards.
The external auditor will check if your organization’s documents, policies, procedures and controls are implemented and operating effectively as per the standard and whether it helps meet your organizational objectives.
The auditor will also evaluate the effectiveness of the preventive and corrective actions and review the actions from the Stage 1 ISO 27001 audit to ensure the improvement requests have been incorporated.
At the end of the Stage 2 ISO 27001 audit, the auditor will submit a report including observations and a summary of the findings. It will detail minor nonconformities, major nonconformities and opportunities for improvement (OFI). Note that in case of major nonconformities, certification doesn’t require you to go through the entire process all over again.
- You must rectify the major nonconformities and share evidence of correction action with the auditor.
- Minor nonconformities, typically, do not affect the recommendation for certification. But several minor non-conformities can add up to your disadvantage.
Use Sprinto’s partner auditor program to get certified. Collect evidence with high accuracy to demonstrate good security practices and pass audits with ease.
12. Post Certification, undergo Periodic Surveillance Audits
The ISO 27001 certification holds a validity of three years; it, however, requires the organization to undergo Periodic Surveillance Audits every year.
The Periodic Surveillance Audits are mandatory to maintain your ISO 27001 certification and aren’t as comprehensive as the Stage 2 ISO 27001 audit.
The audit is mostly done at the end of the first year and the second year after certification. The auditor goes through a similar process as was followed in Stage 2 ISO 27001 audit and reviews nonconformities and corrective actions, document updations, maintenance and performance of the ISMS, among other things.
As per the ISO 27001 checklist, the second surveillance audit would probably go over different aspects of your ISMS.
- Review audit findings with management: A report detailing the findings and nonconformities is submitted to the management at the end of the audit.
- Work on non-conformities: In case of major nonconformities, you must take corrective action and share evidence within three months.
Failure to do this could risk your certification. Minor nonconformities, if any, also need to be corrected and their evidence shared with the auditor. These, however, don’t have a bearing on your certification status.
Ace your surveillance audits using the Sprinto dashboard that helps you improve the control measures like policies and processes while tracking them automatically and continuously.
13. Perform Continual Improvement
Just like your organization, the ISMS needs to grow and evolve too. For instance, the addition of vendors and software, identification of new threats, and changes/updates in policies and procedures have a bearing on the ISMS, and must, therefore, be assessed for their risk and treated with a relevant control/measure to mitigate it.
- Document annual risk assessments: Perform annual risk assessments, and document all the changes in risk assessments and their treatment plans.
- Reevaluate ISMS scope: The scope of the ISMS too can change. So, ensure the ISMS and its objectives continue to remain appropriate and effective.
- Align with management: Ensure you have the management buy-in for the changes/updates.
Doing this helps to ace your recertification audits at the end of the third year. And much like your Stage 2 ISO 27001 audit, the recertification audit examines nonconformities from earlier audits and OFIs. It reviews the overall effectiveness of your ISMS, the scope of your certification, and its appropriateness (if it’s appropriate three years later too).
The audit also includes a review of policies, procedures, and controls and their operational effectiveness, corrective and preventive actions, evaluation of internal audits, and management reviews, to name a few.
Automate >80% of your ISO 27001 tasks with Sprinto
What are the mandatory documents required for ISO 27001?
For ISO 27001 certification, organizations must maintain a set of mandatory documents to demonstrate compliance with the standard’s requirements for an Information Security Management System (ISMS). These include:
- Scope of the ISMS: Defines the boundaries and applicability of the Information Security Management System within the organization.
- Information security policy and objectives: Outlines the organization’s commitment to information security and specific, measurable security goals.
- Risk assessment and risk treatment methodology: Describes the process for identifying, analyzing, and addressing information security risks.
- Statement of Applicability (SoA): Lists all Annex A controls, indicating which are applicable and how they are implemented or justified.
- Risk treatment plan: Details actions to mitigate identified risks, including timelines and responsibilities.
- Risk assessment report: Summarizes the findings of the risk assessment process, including identified risks and their evaluation.
- Definition of security roles and responsibilities: Specifies the roles and duties of individuals responsible for information security tasks.
- Inventory of assets: Lists all information assets, including their ownership and classification.
- Acceptable use of assets: Defines rules for the appropriate use of organizational assets to ensure security.
- Access control policy: Establishes rules for granting, managing, and revoking access to information and systems.
- Operating procedures for IT management: Documents processes for secure operation and maintenance of IT systems.
- Secure system engineering principles: Outlines guidelines for designing and developing systems with security in mind.
- Incident management procedure: Describes the process for identifying, responding to, and recovering from security incidents.
- Business continuity procedures: Details plans to maintain critical operations during and after disruptions.
- Statutory, regulatory, and contractual requirements: Identifies legal, regulatory, and contractual obligations related to information security.
- Records of training, skills, experience, and qualifications: Documents evidence of personnel competence in information security roles.
- Monitoring and measurement results: Records data from evaluating the performance and effectiveness of the ISMS.
- Internal audit program: Outlines the schedule and methodology for conducting internal ISMS audits.
- Results of internal audits: Documents findings and recommendations from internal audits of the ISMS.
- Results of the management review: Records outcomes of management’s periodic review of the ISMS performance and effectiveness.
- Results of corrective actions: Documents actions taken to address nonconformities and improve the ISMS.
- Logs of user activities, exceptions, and security events: Maintains records of system activities, anomalies, and security incidents for monitoring and analysis.
ISO 27001 checklist implementation tips
The ISO 27001 checklist is crucial since it points information security teams to useful data on what they’ll need to do to step-by-step prepare for compliance.
An ISO 27001 checklist speeds up the certification process and guarantees that teams won’t miss anything throughout the course of compliance.
Here are some tips before you make your ISO 27001 checklist:
1. Get more knowledge on the framework:
It is pretty much obvious that having a clear understanding of ISO 27001 will help you create your checklist with much better accuracy.
2. Pinpoint the scope:
It is essential to understand the scope of implementation. You should know which processes, assets, and other tasks that should be covered in the project.
3. Gather insights about your organization:
Try to understand the unique aspects of your organization, such as its business objectives, team sizes, and their complexity, etc. This will help you create a thorough checklist.
4. Test the checklist and review procedures and policies:
You should test the ISO 27001 checklist and see if there are gaps in the policies and procedures. If found, try to mitigate them.
These are some of the prerequisites that you should follow before making your ISO 27001 checklist. But what if you don’t need to worry about any of these? This is where Sprinto comes in.
Sprinto is a compliance automation solution that automates your ISO 27001 compliance journey from the start till the day of the audit. Not just that, Sprinto takes your organization’s needs into perspective and provides you with the most personalized experience.
How to become ISO 27001 certified the Sprinto Way
It’s a big checklist, we understand. And, yes, there is quite a lot to accomplish before you get audit-ready.
Sprinto offers a tech-enabled solution that saves you the effort and does the work without human intervention 10x faster. In just 3 simple steps, using a pipeline of automated workflows, we help you get certified.
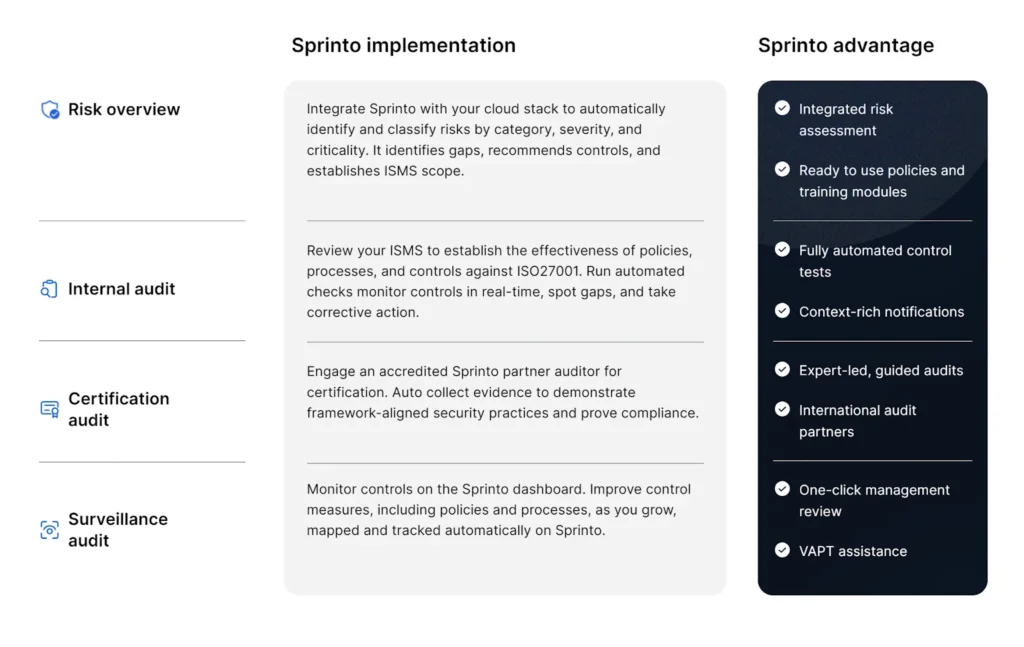
Book a demo with us and see how Sprinto can help you go through an uncomplicated, resource-light ISO 27001 audit and certification. (also check out the detailed Sprinto review to know more)
Frequently asked questions
What are the five audit checklists of ISO 27001?
The five steps to conduct internal audits for ISO 27001 are:
- Set up an internal team
- Ensure ISMS scope and plan are in sync
- Review documentation
- Collect evidence
- Incorporate internal audit findings
What is the frequency of ISO surveillance audits?
ISO surveillance audits are conducted in the first two consecutive years after the initial certification. After that, it will be conducted in the first two years after the recertification audit.
For how long is an ISO certification valid?
ISO certifications are valid for three years from the date of its issue. After that, you have to undergo surveillance audits.
Does ISO 27001 have to be implemented throughout the entire organization?
Yes. You have to implement ISO 27001 throughout the organization where information systems are being used.
Anwita
Anwita is a cybersecurity enthusiast and veteran blogger all rolled into one. Her love for everything cybersecurity started her journey into the world compliance. With multiple certifications on cybersecurity under her belt, she aims to simplify complex security related topics for all audiences. She loves to read nonfiction, listen to progressive rock, and watches sitcoms on the weekends.
Explore more ISO 27001 articles
ISO 27001 Overview & Requirements
ISO 27001 vs Other Frameworks
ISO 27001 Audit & Certification Process
ISO 27001 Management & Assessment
ISO 27001 Implementation & Automation
ISO 27001 Industry-Specific Applications
research & insights curated to help you earn a seat at the table.










