The GRC in cybersecurity gives organizations a unified framework to manage governance, risk, and compliance as one coordinated system.
As digitization accelerates, the attack surface has grown as fast, from phishing and ransomware to supply chain exploits. According to the Global Cybersecurity Outlook survey, 72% of cyber leaders say security risks are increasing year over year.In this environment, GRC is the foundation of cybersecurity governance, linking business strategy with real-time risk management in cybersecurity and ongoing regulatory compliance.
TL;DR
| In the context of cybersecurity, GRC is a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating cyber risks, while ensuring compliance with relevant regulatory standards, and industry best practices. It provides a framework for aligning security practices with business objectives. |
| GRC in cybersecurity enhances operational efficiency by eliminating data silos and integrating cybersecurity practices into broader operations. |
| The future of GRC in cybersecurity includes predictive A.I., blockchains for immutable audit trails, and quantum-resisting security. |
What is GRC in cybersecurity?
GRC in cybersecurity is a structured framework that combines governance, risk management, and compliance into a single, coordinated model for managing digital risk. A mature GRC framework for cybersecurity connects leadership accountability with technical execution. It bridges the gap between IT operations and business oversight by helping organizations:
- Govern cybersecurity through defined policies, roles, and accountability structures.
- Manage risks systematically by identifying, assessing, and mitigating threats to information assets.
- Maintain compliance with SOC 2, ISO/IEC 27001:2022 standards, NIST CSF, HIPAA, and GDPR.
This framework ensures that every control and cybersecurity policy directly supports the organization’s strategic and regulatory objectives.
The three components of GRC
Together, these GRC components form the backbone of cybersecurity governance—ensuring that every action taken to secure data or systems aligns with business objectives and regulatory requirements.
1. Governance
- Defines roles, responsibilities, and decision authority across teams
- Establishes control policies and oversight structures that guide how cybersecurity objectives are achieved
- Ensures leadership accountability through measurable goals, reporting mechanisms, and escalation paths
- Aligns risk and security priorities with overall business strategy
In action: Governance makes cybersecurity measurable and reportable—connecting executive oversight with operational outcomes.
2. Risk Management
- Identifies and prioritizes threats, vulnerabilities, and business impacts across assets and vendors
- Uses structured models (like NIST CSF and ISO/IEC 27005) to assess likelihood and potential damage
- Enables continuous risk monitoring to catch drift and evolving threats early
- Develops treatment plans that define how risks will be mitigated, transferred, accepted, or monitored
In action: Risk management in cybersecurity ensures decisions are based on measurable exposure, not assumptions.
3. Compliance
- Maps internal controls to relevant frameworks such as SOC 2, ISO/IEC 27001:2022, GDPR, and HIPAA
- Validates that controls are implemented, tested, and evidenced continuously
- Automates documentation, reducing manual work and audit fatigue
- Demonstrates accountability to auditors, customers, and regulators through ongoing visibility
In action: Compliance becomes an ongoing validation process, strengthening credibility while keeping teams ready for any audit.
Why is there a need for organizations to have GRC in cyber security?
GRC in cybersecurity helps organizations turn fragmented security efforts into a coordinated, measurable governance and risk control system. It creates a foundation where every security action has ownership, evidence, and accountability, transforming cybersecurity from reactive protection to proactive assurance.
Most mid-market companies face the same challenge: security work happens in silos. IT tracks incidents, compliance chases evidence, and leadership reviews outdated reports. A GRC framework connects these moving parts so risk visibility, control ownership, and compliance status live in one place.
Practically, GRC in cybersecurity helps organizations:
- Clarify accountability: Through defined roles and decision pathways, the GRC framework aligns leadership, IT, and compliance teams under one structure—eliminating confusion about who owns specific risks and controls.
- Enhance visibility: By linking risks, controls, and incidents in a single system, GRC provides real-time oversight and enables early detection of control drift or emerging threats.
- Align security with business goals: With GRC guiding priorities, cybersecurity initiatives are tied to measurable risk appetite and strategic objectives—turning security into a growth driverdriver of growth rather than just a compliance function.
- Simplify regulatory compliance: The GRC process streamlines how policies and controls map to frameworks like SOC 2, ISO/IEC 27001:2022, and GDPR, keeping audits predictable and documentation consistent.
- Improve decision-making: Centralized reporting through GRC converts technical risk data into business insights that leadership can act on—supporting better resource allocation and strategic planning.
When GRC is automated, it stops being paperwork, and it becomes the operational backbone of secure growth. According to OCEG’s GRC Capability Model, organizations with integrated GRC functions are three times more confident in evaluating performance and risk controls than those with siloed programs. That confidence translates directly into faster decision-making and fewer compliance failures.
How to Implement GRC in Cybersecurity (Step-by-Step)
GRC enables cybersecurity by swiftly identifying any security gaps, streamlining the compliance process, and providing clear metrics to measure the success of the security performance.
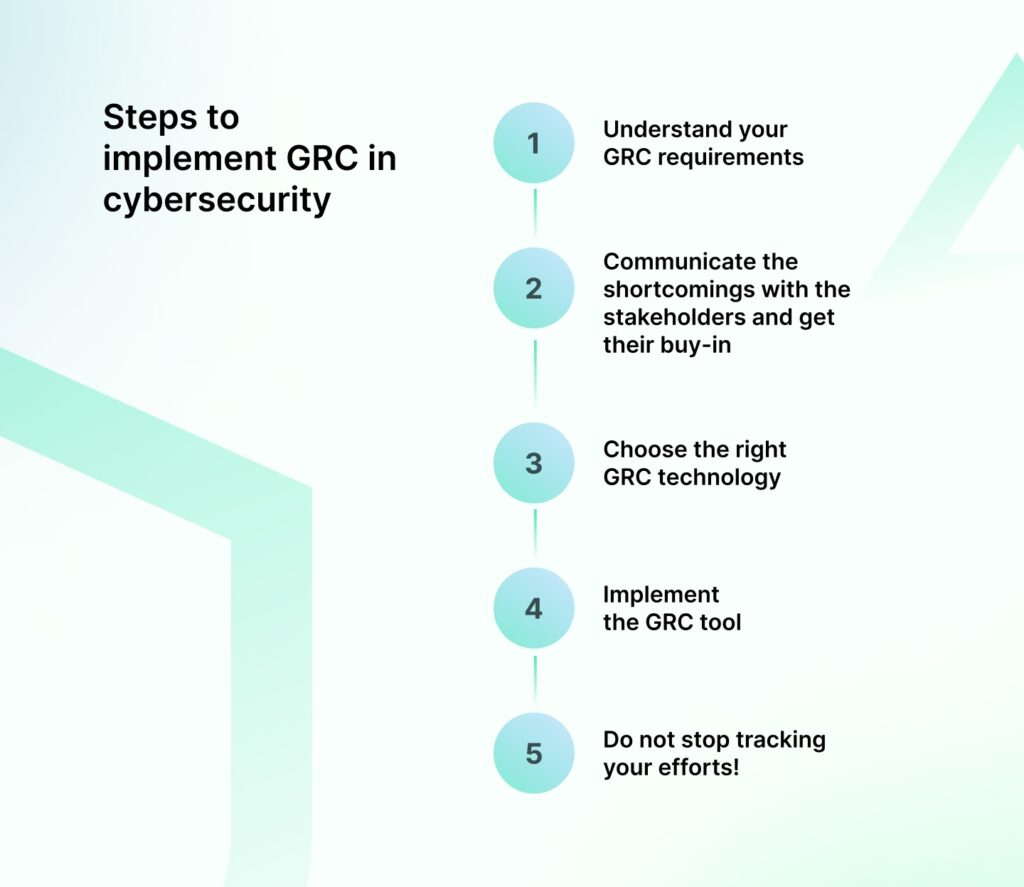
Here’s how you can implement GRC in cybersecurity:
Step 1: Understand your GRC requirements
Understand your current cybersecurity and GRC mechanisms. By asking yourself a set of questions, you can understand where you stand:
- What is our current GRC structure?
- How does the existing GRC structure support or hinder the security and compliance efforts undertaken by the company?
- What internal policies and procedures are currently in place?
- How well do we understand our current cybersecurity posture?
- How many resources can we allocate to GRC functions?
- How well do our business priorities align with our risk management system?
- What is the scope of our risk tolerance?
- What are the biggest annoyances and challenges we face regarding compliance?
- How are we tracking our current changes in cybersecurity?
- What are the current compliance standards that we are adhering to? Are they relevant to the industry we’re in?
- And How well do these standards align with our business objectives and the requirements of our customers?
These can be tailored to your organization, but they provide a basic framework for you to get started.
Step 2: Communicate the shortcomings with the stakeholders and get their buy-in
You need to build consensus and support among the stakeholders. Present your findings from step 1 and communicate ahead of time what the roadmap needs to be. To resonate with them;
Here’s a tip: Translate these risks into business terms. Talk about potential financial loss, highlight operational disruptions, and focus on the loss of market share.
Here are a few things you can include in your presentation:
- An estimated cost of implementing a GRC tool.
- The timeline
- What could be the tangible benefits of implementing a GRC tool?
- Business areas that might be affected by the tool.
Emphasize that this is not just another I.T. venture but an investment in the future of the business. Convincing the board to write a check is always going to be difficult. Remember to have grit, precision, reason, and patience.
You are going to need inputs from stakeholders every step of the way, so establish a clear line of communication to ensure transparency,
Step 3: Choose the right GRC technology
Identify specific areas that need improvement, such as risk management, compliance management, risk identification, policy reporting, etc. Your requirements should be based on the shortcomings of your current cybersecurity posture and processes. Considering your findings from step 1, you should have a clear idea of where your focus should be.
When you are thinking about getting a tool, consider the following:
- Integrations: The tool should integrate with your existing ERP, SIEM, or identity management systems to maintain data consistency.
- U.I.: To avoid user adoption, choose an intuitive tool with a good interface.
- Scalability: A GRC tool should grow with you. It should be able to handle increasing volumes of data and the complexity that comes with it.
- Customization: Check for customization options. Instead of working around the GRC platform, it should be adaptive to your customs and processes.
- Reports: These reports are important as software’s reporting capabilities determine how smooth the conversation between stakeholders and I.T. professionals will be. The tool should be able to generate visual reports for better understanding.
- Customer reviews: Check the positive and negative reviews of the product on product sites like G2 and Capterra.
Sprinto addresses all the considerations above. Sprinto is a cloud-based GRC platform with great automation capabilities.
Sprinto strengthens your GRC posture by addressing these concerns. As a cloud based platform, it offers scalability to handle growing data. You can layer multiple frameworks on top of each other without needing an additional lift. It has features like common control cross-mapping, reusability, and risk modules that come in handy.
Sprinto also integrates with over 200 cloud apps and services and connects with your existing tech stack. It ensures that your GRC efforts are centralized without disrupting your workflow or changing your infrastructure.
Sprinto understands that not everyone is an IT expert, which is why the platform is user-friendly, intuitive, and accessible. Our platform doesn’t just achieve compliance; it maintains it, too, with minimal efforts. Sprinto constantly monitors your systems and alerts you ahead of any potential threats.
And our customers love us!
Step 4: Implement the GRC tool
Now that you have finalized the tool, brace it for impact. Create a cross-functional security team to oversee the implementation process and assign clear roles and responsibilities.
Remove redundant or outdated data systems and ensure you are migrating clean data.
To ensure that the new GRC works seamlessly, here are a few things to do:
- Determine which of your existing systems, such as H.R. or I.T. asset management tools need to be integrated with the GRC tool.
- Check the Application Programming Interface, or API, and the connector availability. Having prebuilt APIs significantly reduces time and effort. It also ensures that data flows consistently and accurately between systems.
- Set up user authentication and ensure that access controls are accurately placed.
- Set up test environments to ensure data flows smoothly and accurately between departments.
- Plan for contingencies. It’s better to have it and not need it than to need it and not have it.
- Continuously monitor controls with the help of security monitoring tools and instantly remediate any anomalies as and when they arise.
These things will ensure that your Governance, Risk, and Compliance efforts are carried out smoothly.
Step 5: Do not stop tracking your efforts!
Review and monitor your efforts regularly. This involves understanding the key performance indicators and ensuring they are met. Also, breach detection mechanisms should be implemented to identify and contain threats early before escalation.
Conducting thorough checks periodically to ensure you cover all your bases is always advisable.
GRC’s integration with cyber security. What is it, and why should you do it?
Integrating GRC in cybersecurity means having a unified approach for governance, risk management, compliance, and cybersecurity. It all gets tied together to create unified efforts toward your organization’s security.
GRC’s integration with cybersecurity looks like this:
- GRC enforces cybersecurity policies like data protection, incident response, access controls, etc.
- It ensures that everyone, including senior management and employees, is aligned with the organization’s cybersecurity priorities.
- Through risk identification and prioritization, GRC focuses on cybersecurity risks. This allows the organization to focus on threats critical to their data systems and I.T. infrastructure.
- GRC facilitates compliance with laws, regulations, and other frameworks, ensuring that cybersecurity practices meet legal and industry-specific requirements.
- The compliance aspect of GRC helps organizations respond and recover from cybersecurity incidents by mitigating risks.
Why GRC in cybersecurity matters (and its key benefits)
While most organizations recognize the need for GRC, few realize its full potential. When implemented well, GRC in cybersecurity evolves from a compliance requirement into a performance system that drives predictability, maturity, and measurable business value.
The strategic impact of GRC:
- Ensures comprehensive risk coverage: A mature GRC framework helps identify, assess, and mitigate risks across every business layer, from data handling to vendor management, ensuring no threat vector is overlooked.
- Aligns cybersecurity with business goals: GRC ensures security initiatives and compliance programs work closely with business priorities, balancing protection with growth and efficiency.
- Elevates risk visibility: Mature GRC programs go beyond detection to prediction, using data from controls, audits, and incidents to anticipate risks before they surface.
- Drives operational maturity: By unifying governance, risk, and compliance workflows, GRC replaces reactive firefighting with continuous improvement, reducing control failures and audit rework.
- Accelerates multi-framework compliance: A single mapped control set supports multiple frameworks such as SOC 2, ISO/IEC 27001:2022, and GDPR, cutting audit prep time and compliance costs as standards expand.
- Reinforces governance culture: GRC operationalizes accountability, embedding policy adherence and role ownership into daily workflows rather than relying on periodic audits.
- Delivers measurable ROI: Automation, evidence reuse, and centralized risk insights reduce redundant work, shorten audit cycles, and deliver tangible savings across compliance operations.
- Builds long-term resilience: With continuous monitoring, transparent reporting, and cross-functional visibility, GRC strengthens organizational trust, turning compliance into a competitive advantage.
- Enhances incident response: Through predefined risk mitigation strategies and continuous monitoring, GRC enables faster detection, quicker response, and reduced impact of security incidents.
Cyber threats are evolving faster than static controls can keep up. GRC enables organizations to adapt dynamically predicting, prioritizing, and preventing risk across the business.
Types of cybersecurity frameworks under GRC in cybersecurity.
While appropriate frameworks may vary, here are some of the most common and widely accepted cybersecurity frameworks in 2024
ISO
International Standard for Organization or ISO frameworks are a benchmark on cybersecurity standards. These standards demonstrate an organization’s commitment to security and quality of data. These are some of their key standards:
- ISO/IEC 27001: This is the cornerstone of the ISO standards. It is a standard that establishes, manages, implements, and improves an Information Security Management System.
- ISO/IEC 27002: It complements ISO 27001 by outlining the best practices and recommendations for information security controls.
- ISO/IEC 27005: This standard focuses on cybersecurity risk management and provides guidelines for risk identification, assessment, treatment, and more.
- ISO/IEC 27017: An extension of ISO 27001, ISO/IEC 27017 focuses on ISMS for cloud computing, which basically involves managing the risks associated with cloud services.
- ISO/IEC 27018: This standard protects personally identifiable information or PII on the cloud.
- ISO/IEC 27032: It provides standards for improving cyber security.
ISO certifications are time-consuming, but ensure a good cybersecurity posture. This gives you a competitive edge and allows you to venture into enterprise-level deals.
NIST
The NIST cybersecurity framework, or CSF, is a voluntary framework that helps organizations better understand, manage, and mitigate cybersecurity risks. The 2nd version of CSF was unveiled in 2023 and was introduced with many upgrades, the key being introducing the GOVERN function. The function includes the following:
- Organizational Context: This aspect focuses on understanding the broader organizational context, such as the mission, objectives, and environment. It lays the foundation for aligning cybersecurity efforts with the business’s overall goals.
- Roles, responsibilities, and authorities: This outlines who’s responsible for different aspects of cybersecurity and ensures accountability.
- Policy: This aspect establishes the tone of security culture by establishing the organization’s cybersecurity principles. It ensures that they align with the expectations set by senior management.
- Risk management: It involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating cybersecurity risks to ensure that efforts are focused on critical areas.
- Oversight: Involves monitoring and reviewing the controls and following up to measure the effectiveness of the cybersecurity program.
- Cybersecurity supply chain risk management: It addresses the risks associated with third-party vendors and partners.
The NIST framework provides a common language to manage cybersecurity, making cross-functional communication and communication easier.
CIS controls
The Center for Internet Security is an effective framework for organizations looking to improve their cybersecurity. The CIS benchmarks consist of 18-level controls, each safeguarding a specific aspect.
These controls are divided into 153 safeguards and categorized into three groups:
- Basic
- Foundational
- Organizational
These are implemented based on the maturity of the organization.
CIS controls focus on a risk-based incremental approach to cybersecurity. You are encouraged to start at the most critical level and gradually strengthen your cybersecurity posture.
CIS controls are also mapped to other regulatory compliances, such as HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS, to aid compliance efforts. Moreover, CIS controls are periodically updated to reflect emerging cybersecurity trends and ensure that threat mitigation strategies remain current and effective.
GRC in Cybersecurity vs. Information Security Management: What’s the Difference?
While GRC in cybersecurity and Information Security Management (ISM) both aim to protect organizational assets, they operate at different strategic and scope levels.
Think of GRC as the governance and decision-making framework that defines why and how security aligns with business objectives. At the same time, ISM focuses on the execution layer, the GRC compliance tools, policies, and processes that enforce those decisions.
Here’s a quick breakdown of how they differ:
| Aspect | GRC in Cybersecurity | Information Security Management (ISM) |
| Purpose | Aligns governance, risk, and compliance efforts to achieve business objectives securely. | Protects information assets through defined policies, controls, and incident response mechanisms. |
| Scope | Enterprise-wide — covers governance structures, risk frameworks, and regulatory compliance. | Operational — focuses on confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. |
| Focus Area | Decision-making, accountability, compliance readiness, and risk visibility. | Day-to-day security operations, control implementation, and monitoring. |
| Key Activities | Risk assessment, control alignment, audit management, policy governance. | Security policy enforcement, vulnerability management, access control, and incident handling. |
| Output | Strategic assurance business decisions made with confidence in risk posture. | Technical assurance — systems, networks, and data remain protected and compliant. |
| Ownership | Shared across leadership (CISO, Compliance, Risk, Legal). | Primarily, the IT and Security Operations teams. |
| Framework Examples | SOC 2, ISO 27001, NIST CSF, GDPR, HIPAA. | ISO 27002, NIST SP 800-53, CIS Controls. |
| Goal | Drive continuous compliance and risk-informed business performance. | Maintain secure systems and protect information assets. |
In short, GRC defines the “why” and “what” of cybersecurity, while Information Security Management delivers the “how.” Together, they create a closed loop—GRC guides strategy, and ISM operationalizes it.
What will the future look like for GRC in cybersecurity?
The coalition of GRC and cybersecurity can be morphed into a “Digital security ecosystem,” which goes beyond the traditional approach. It focuses on building stakeholder confidence, maintaining compliance, and predicting and mitigating cyber risks.
Here’s what we think the future could look like:
- Predictive GRC: We might not be far away from a technology that incorporates AI and runs on it—an AI-driven platform that monitors and predicts risks before they materialize. The question is, do we trust AI to protect us against AI?
- Blockchain for GRC: Immutable audit trails as blockchains create a permanent record for transactions. Data stored on blockchains is encrypted and stored on a distributed network, which makes it resistant to tampering and attacks.
- Quant compliance: GRC frameworks would need to adapt to quantum-resistant cryptography, as quantum computing is advancing at a staggering rate. This would mean new paradigms for data storage and protection.
We believe that the future of GRC is not just integrations but rather a complex ecosystem that would be impenetrable.
FAQs
What is GRC in cybersecurity?
GRC in cybersecurity stands for Governance, Risk, and Compliance. it helps to manage cybersecurity by incorporating the GRC process, which involves creating policies, procedures, managing risks, and adhering to regulatory compliances.
What is the role of GRC in security?
The role of GRC in cybersecurity is as follows:
- Align security practices with the overall goals of the organization.
- Identify, assess, and mitigate security risks.
- Ensure regulatory compliance.
- Provide a better understanding of the cybersecurity and the maturity of the organization.
- Enhance the security posture and improve decision-making.
What is a GRC used for?
GRC helps organizations manage their security posture holistically, balancing risk, regulatory and compliance requirements, and business objectives.
What KPIs and KRIs should a GRC program track?
A mature GRC program tracks KPIs to measure performance and KRIs to monitor risk trends.
Key KPIs:
- Control effectiveness rate
- Audit closure time
- Evidence automation rate
- Policy compliance rate
Key KRIs:
- Number and severity of open risks
- Control failure rate
- Vendor risk exposure
- Incident recurrence
Together, these metrics show how well controls perform, where risks are growing, and how effectively compliance supports business goals.
What’s the ROI of GRC in cybersecurity?
GRC delivers ROI by reducing manual effort, audit costs, and risk exposure. Automated control monitoring and evidence collection can cut audit prep time and prevent compliance gaps that lead to fines or downtime. The result: lower costs, faster audits, and stronger trust with customers and regulators.
Heer Chheda
Heer is a content marketer at Sprinto. With a degree in Media, she has a knack for crafting words that drive results. When she’s not breaking down complex cyber topics, you can find her swimming or relaxing by cooking a meal. A fan of geopolitics, she’s always ready for a debate.
Explore more
research & insights curated to help you earn a seat at the table.