The Ultimate PCI DSS Compliance Checklist
Vimal Mohan
Oct 31, 2024
As an organization processing card data via online portals, you should be PCI DSS compliant to avoid penalties and reputational damage. But the process is exhaustive, time-consuming, and expensive.
This article aims to simplify and demystify the PCI compliance framework, help you identify the PCI levels, learn about the 12 PCI DSS requirements checklist, and learn the steps to become PCI DSS compliant.
We’ve also included an exhaustive PCI DSS compliance checklist with 45 checkboxes to help you gain momentum in your compliance journey.
| TL;DR |
| PCI DSS compliance involves implementing key security measures like firewalls, encryption, antivirus software, and strict access controls. |
| There are four levels of PCI DSS compliance—these levels are based on the transaction volumes an organization makes. At an organizational level, compliance can entail extensive audits or the filling out of self-assessment questionnaires. |
| For an organization to get PCI DSS compliant, it must fulfill the 12 requirements, categorized under 6 control objectives. |
Overview of PCI DSS compliance
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) compliance is a set of security standards created by credit card companies to ensure that businesses that process, transmit, or store credit card information do so in a secure manner.
The PCI DSS compliance standards goal is to prevent data breaches and protect sensitive cardholder information.
Global digital card payments grew by an annual rate of 20 percent in 2020 compared to 2019, and this trend is witnessing a non-linear upward growth. In 2020, 900+ million online transactions were processed, which rose to 2.14 billion in 2025.
This upward spike in card transactions also means bad actors and hackers now have a broader pool to target and extract sensitive information maliciously. Sensitive user data had to be protected.
In 2004, the founding members of PCI DSS, i.e. VISA, MasterCard, JCB International, and Discover Financial Services, came together and drafted a regulatory framework to protect user credit card data from fraudulent activities.
Why was PCI DSS implemented?
The PCI DSS compliance framework was implemented to enable organizations processing electronic transactions to implement the processes and policies required to maintain a strong security posture to protect cardholder data.
The latest revision, i.e. PCI DSS version 4, launched in March 2022, introduced reforms to a few existing security rules to make the framework more flexible and easy to use among others, and can be easily implemented with the help of the PCI DSS compliance checklist.

What does a PCI DSS compliance checklist include?
A PCI compliance requirements checklist includes adherence to policies and implementation of controls such as installing a firewall, updating antivirus,, and encrypting data that is transmitted. It requires you to understand the PCI compliance levels in which your business falls and then decide the scope of compliance.
PCI DSS Levels:
There are 4 levels of PCI DSS compliance and depending on the level, the stringency of requirements can vary:
Level 1: Processes over 6 million transactions annually, and any organization that VISA determines as Level 1 should implement Level 1 grade controls.
Level 2: Processes 1 million to 6 million annual transactions. Level 2 grade controls and policy implementation is required.
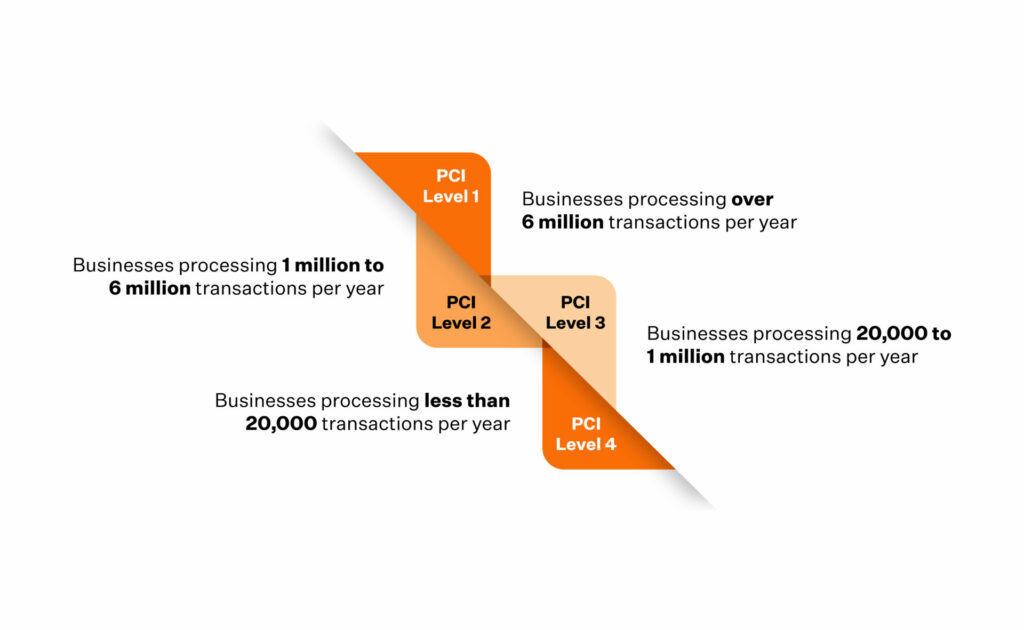
Level 3: Processes 20,000 to 1 million e-commerce transactions in a year. Level 3 grade controls and policy implementation is required.
Level 4: Processes up to 20,000 e-commerce transactions a year and organizations that process up to 1 million total transactions a year. Implementation of Level 4 grade controls and policies is required.
The reporting requirements vary based on levels.
- Level 1 merchants are required to undergo on-site assessment by Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) and submit a Report on Compliance (ROC)
- Level 2, level 3 and level 4 merchants can complete an annual Self- Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ)
All the levels must however conduct quarterly vulnerability scans by Approved Scanning Vendors (ASV) to ensure protection of sensitive information.
The easy path to PCI DSS compliance
PCI DSS compliance checklist
Organizations looking to get PCI DSS compliant must fulfill 12 requirements, categorized under 6 control objectives. These include the control implementation, security policies, and administrative processes designed to protect card data from unauthorized access.

Here’s a detailed 12-step PCI DSS compliance checklist:
1. Install and maintain a firewall
For an organization to remain PCI DSS compliant, all its security systems must be protected from unauthorized traffic from unknown sources. A firewall ensures unregulated inbound or outbound traffic isn’t allowed access to your internal secure systems.
A good firewall configuration must:
- Filter and allow access only to authorized traffic to the business environment
- Automatically decline all unauthorized traffic access
- Protect all your POS devices connected to wireless networks
- Authorize all outbound traffic from your business card storage environments
- Automatically log all the changes implemented, even in instances where changes were implemented by authorized entities in the business environments, with reasons justifying why the said change was necessary.
2. Don’t use default vendor settings and passwords
Do not rely on vendor-generated default usernames and passwords for software, firewalls, routers, POS devices, and more. Also, ensure that the settings have secure configurations instead of leaving them to default.
The second requirement of PCI DSS is to change vendor supplied default settings and use passwords with solid scores.
3. Protect cardholder data
All cardholder information that enters your business environment must be protected. To provide holistic protection, organizations must know how the cardholder data flows through their internal systems – Places it gets stored in, the teams that have access to it, how it leaves your business environment (if applicable), and how to safely dispose of sensitive data.
This requirement also mandates that organizations mask the PAN(Personal Account Number). Masking only makes the last few digits of the card visible.
4. Encrypt transmission
Unlike the earlier requirement, this requirement focuses on protecting the cardholder data environment by deploying encryption methods to protect it from malicious software when transmitted via open, closed, private, and public wireless channels. Often organizations overlook the protection of cardholder data when transmitting them via the internet.
Instances of unauthorized access to sensitive data during transmission have been reported in the past.
5. Use updated antivirus software to protect against malware
Installing basic anti-virus software to prevent malware will not do the job—requirement five details how organizations should constantly update their antivirus software and apply regular patches.
Advanced antivirus solutions must be installed across servers, firewalls, laptops, desktops, and mobile devices with access to business environments. This software should always be active and continuously scan logs.
6. Develop and maintain secure systems and applications
To develop and deploy security systems, knowing which part of your business environment is the least secure is essential. Organizations can reach this conclusion only after conducting an internal risk assessment. A risk assessment gives you complete visibility into your existing security systems and identifies areas that require patching. Deploying new security measures in such areas ensures a strong security posture.
This requirement also recommends organizations to continuously apply patches and remediation measures across their business environments including servers, POS devices, POS operating systems, laptop and desktop operating systems, and firewalls.
Also find out: How to automate PCI DSS compliance process
7. Restrict access to cardholder data
Requirement seven discusses how organizations should control and limit access to sensitive user information. In addition, strong access control measures for employees should be implemented. For example, access may be granted on the basis of seniority, a justified need to access secure data or job-role-based classifications. This requirement also asks organizations to document their access control procedures and regularly review access logs.
8. Assign unique user access IDs
This requirement of PCI DSS enforces organizations to assign unique user IDs to employees. This prevents the occurrence of a security breach and doubles up as an efficient tracking mechanism to isolate and effectively identify the source of an internal breach.
9. Restrict physical access to cardholder data
This requirement focuses on the physical aspects of cardholder data security. Physical assets with access to sensitive data like desktops, paper files, and servers come into the scope of this requirement. Access to physical data should be restricted, and measures to limit unauthorized physical access to such assets should be implemented by using RFIDs(Radio Frequency Identification).
Organizations should also install electronic surveillance systems and store surveillance recordings for a 90-day minimum period.
10. Monitor access to network resources
Bad actors attack physical and wireless networks to gain unauthorized access. Hence, it is crucial to implement security measures for all network resources and constantly log and audit network logs. PCI DSS also requires organizations to send the network activity logs to a centralized server for daily review.
According to this PCI compliance requirement, every organization is required to hold time-synchronized audit trail records of their network activities dating back to one year.
11. Regularly test security systems and processes
Malicious attackers constantly look for vulnerabilities in an organization’s security systems to penetrate their defenses and gain access to sensitive information.
Organizations must conduct periodic tests on their wireless scanners, say every quarter, to identify access points that could be used to gain unauthorized access.
They should also scan their external facing domains and IPs by a PCI DSS-Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV). Every quarter, organizations should conduct vulnerability management scans to test their security systems annually by undergoing penetration tests to determine the weakness in their security net to deploy patches.
12. Create and maintain an information security policy
Organizations should have an internal infosec policy that covers employees, the leadership team, and vendors if any.
The infosec policy should be classified into two sections: internal and third-party. The internal infosec policy should be read and acknowledged by every employee in your organization.
An essential part of the infosec policy is to conduct internal background checks on every employee in your organization. This ensures that the wrong hands don’t gain access to sensitive card data.
Download Your PCI DSS Compliance Checklist
Benefits of implementing PCI checklist
Implementing a PCI DSS checklist is a structured process of understanding security pitfalls and making improvements to fill the gaps. It is a crucial tool to manage security and compliance in the increasing face of security threats.
Here are the benefits of implementing a PCI checklist:
Risk mitigation
The PCI DSS Checklist helps implement controls such as encryption, firewalls, access controls, and more, thereby enhancing overall security posture. It improves incident response procedures by suggesting regular security assessments and helps minimize the risk of data breaches.
Increased customer trust
PCI DSS compliance demonstrates a commitment towards ‘prevention’ rather than just ‘protection’ from incidents. It implies that the organization believes in proactive measures to ensure safe card transactions and enhances customer trust.
Process Optimization
Implementing the checklist not only saves costs of breaches but it brings operational efficiency through adoption of security best practices. Measures such as employee training, better incident response planning, vendor management etc. facilitate process optimization leading to long-term returns for the organization.
Minimizing regulatory consequences
Implementing a PCI DSS checklist helps protect customer data and in turn fulfil legal and regulatory requirements. It saves organizations from fines, penalties, negative publicity and other consequences of non-compliance.
Limitations on card processing
Not implementing the PCI DSS checklist can mean loss of business opportunities. Payment processors or card brands can impose limitations such as restriction on processing payments for specific cards, restriction on processing amount or suspension of processing capabilities.
Investigative audits
An investigative audit may be carried out in case of an incident when you do not follow the PCI compliance checklist. These audits are conducted by the Federal Trade Commission to identify affected systems and understand the root cause.
Legal action
PCI DSS non-compliance can attract lawsuits and legal action from customers. It can cause adverse public perception and can further disrupt operations or an increase in the revenue cycle.
Common mistakes to avoid while implementing the PCI checklist
If you are implementing PCI DSS controls, you should be mindful of some common mistakes management tends to make.
- Filling the wrong SAQ: The Self Assessment Questionnaire, a statement of your compliance with the PCI requirements is specific to the payment type or merchant environment.
There are three categories of forms, and if you don’t select the right one, it could lead to non-compliance. If this leads to a data compromise, you will have 90 days to be compliant.
- Misunderstanding the role of vulnerability scans: Vulnerability scanning is only a compliance requirement that helps you adhere to certain controls. Some VAPT vendors provide a PCI DSS completion badge after these scans, which may lead you to believe you are compliant. However, this is misleading, as this does not equate to compliance.
- Lack of a governance structure: PCI DSS affects many areas within a company, so it’s important to view it as a collective business requirement. It is not just the IT department’s responsibility but a coordinated effort across all departments. You should integrate into overall information security and data protection initiatives.
- Developing policies for the sake of it: Organizations often create policies and documents simply to satisfy the assessor. However, involving key staff in the discussion and analysis process helps align them with their responsibilities. This helps embed compliance into the organization’s culture and not just a checkbox exercise while ensuring accountability and long-term sustainability.
- Insufficient scoping: A PCI DSS audit may not be successful due to insufficient scoping. The scope and complexity of the environment directly influence PCI DSS project timelines and costs, both in terms of effort and money. Although scoping isn’t a formal PCI DSS requirement, it is a highly recommended practice to ensure efficient implementation.
The future of PCI compliance
PCI DSS launched its version 4.0 (V4) in March 2002 by replacing its predecessor version 3.2 to become the most updated PCI DSS compliance framework.
Organizations currently compliant with version 3.2 have till March 2024 to become compliant with Version 4 of PCI DSS.
Objectives of PCI DSS V4:
PCI DSS V4 aims to promote security as a continuous process.
- Every requirement now has assigned roles and responsibilities
- Guidance information will now be available to understand, implement, and maintain security
- The report section is now updated with areas to highlight improvements, offering greater transparency than its predecessor. That’s a win for report viewers.
Security methods to protect user card data must evolve with the changing security landscape. Here are a few new updates that the PCI DSS 4.0 brings:
- The MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) requirement is tighter
- The requirement that details password policy is now updated
- New standards to deal with e-commerce and phishing have been introduced
Increased flexibility allows organizations to reach their security goals in innovative ways.
- Group, shared, and public accounts are now permissioned
- Risk analysis is now targeted. This allows organizations to set their desired frequency for risk analysis
- Customization is now included in deciding how organizations reach their goals for security and compliance.
Better and Improved verification methods will be introduced.
The Sprinto Way of Becoming PCI DSS Compliant
Becoming PCI DSS compliant can be exhaustive and time-consuming. Implementing the hundreds of controls from the PCI DSS checklist, monitoring its many checks and alerts, and keeping a continuous tab on your security posture as you grow can get daunting.
Sprinto automates repeatable tasks and gives you a dashboard overview of your compliance. It also offers a unique continuous monitoring feature that gives your organisation an entity-level compliance health check.
Talk to us to learn how Sprinto is tailored for your compliance needs, no matter your PCI DSS level.
FAQs
How many requirements are in PCI compliance?
PCI compliance, specifically PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) compliance, has 12 main requirements that organizations must follow to secure credit card data. These requirements are organized into six broader categories called control objectives.
How often do PCI compliance requirements need to be reviewed?
PCI compliance requirements need to be reviewed annually, but certain security measures, such as monitoring and testing, should be conducted regularly as part of ongoing security management.
Is PCI Compliance legally required?
PCI Compliance is not a law. However, it is mandated by contractual obligations for payment processors by major credit card companies such as American Express, Visa, Mastercard, Discover and JCB.
What are some common PCI violations?
Some common PCI violations include insecure transmission of data, inadequate network segmentation, weak access controls, default passwords and incomplete security policies among others.
Can I outsource cardholder data processing to a third party?
Yes, as a merchant, you can outsource cardholder data processing to a third party but the ultimate responsibility lies with you. It is crucial to select a PCI DSS-compliant vendor to ensure secure transmission of cardholder data.
How do you comply with PCI DSS?
Complying with PCI requirements can be daunting, especially if you do it for the first time without seeking help. Using the PCI compliance checklist from the article can help you make significant strides in the right direction if you are planning to take the DIY route. Alternatively, you can consult with a compliance expert, and onboard a GRC service provider as well.
Most organizations seek assistance from compliance automation software like Sprinto to smoothen and shorten their compliance journey.
What are the four things PCI DSS covers?
PCI requirements cover these four things:
- To protect cardholder data stored in your business environment.
- To use Antivirus solutions and regularly update them to enable maximum security.
- To ensure that access to cardholder data is regulated by access control systems, i.e. on a need-to-know basis.
- To monitor networks and servers storing cardholder data constantly, saving their logs in a centralized server every 24 hours with time stamps.


Use Sprinto to centralize security compliance management – so nothing
gets in the way of your moving up and winning big.


























