HIPAA Requirements: Ensuring Patient Privacy and Data Security
Meeba Gracy
Sep 26, 2024
HIPAA requirements sets the national standard for the protection of sensitive identifiable health information. As a healthcare service provider, HIPAA compliance is mandatory as it demonstrates that your organization is aligned with the privacy rule, security rule, and other infosec standards.
The penalties for HIPAA non-compliance are severe. When we say severe, it is not just monetary penalties, but also legal consequences. Additionally, your business gets listed on the Office of Civil Rights (OCR) Wall of Shame along with the violation details when non-compliance is detected. You can now imagine what that does to your brand reputation.
In this article, we have elaborated on all the HIPAA requirements, such as the security rule and privacy rule for covered entities, that you should consider.
TL;DR
| HIPAA requirements urge organizations to implement safeguards for protecting PHI and ePHI, limit and control access to health information, and notify individuals and authorities of breaches. |
| The main requirements of HIPAA include the Privacy Rule, the Security Rule, the Breach Notification Rule, and the Omnibus Rule. |
| If you’re in the healthcare field, it’s mandatory to follow HIPAA, a federal law that requires safeguarding PHI. |
What are HIPAA Requirements?
HIPAA requirements are a set of regulations that are basically rules and best practices that healthcare organizations and businesses should follow to protect patients’ sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Types of organizations that should comply with HIPAA:
1. Healthcare Providers
2. Health Insurance Companies
3. Business Associates of covered entities
4. Research Institutions
5. Public Health Authorities
6. Care Facilities
7. Pharmacies
If you have more questions on whether you are a covered entity, we have a simple checklist for you to make the decision:
Download Your Covered Entity Decision Tool
Why Do Organizations Need to Follow HIPAA?
If you are in the healthcare industry, you need to comply with HIPAA because it is a federal law enforcement that mandates the protection of patients’ personal health information. But apart from being a federal standard requirement, there are several ways HIPAA helps.
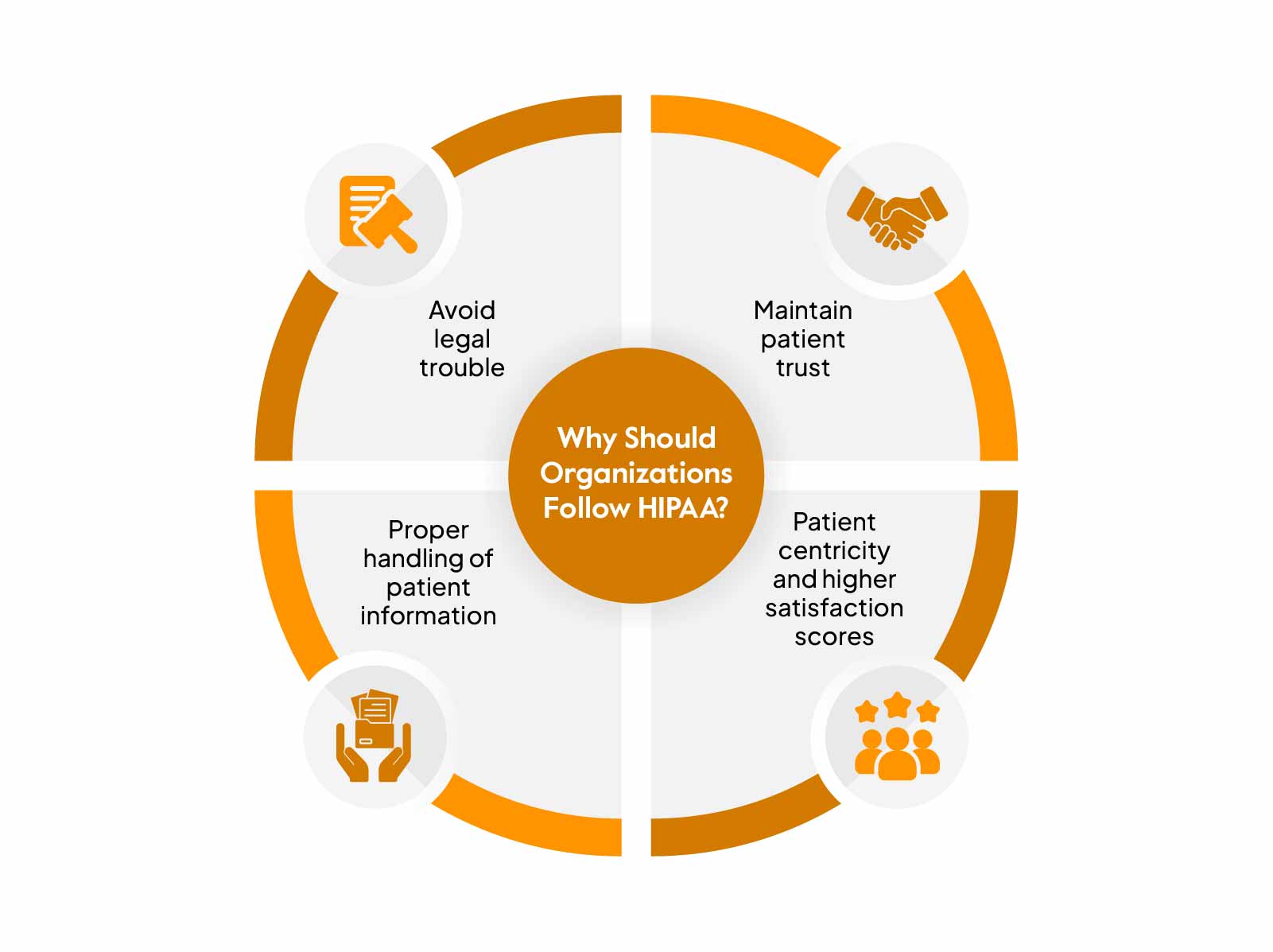
Avoid legal trouble
Failure to comply with HIPAA can result in significant penalties (civil and criminal fines). Also, your business can receive a ban from taking part in federal healthcare programs.
Maintain patient trust
Patients always trust hospitals and health care clearinghouses to keep their personal health information safe. HIPAA serves as a way to demonstrate your business’s compliance efforts to protect patient data.
Proper handling of patient information
HIPAA helps secure patient data by implementing administrative, technical, and physical access requirements. It provides patients with complete control over their medical data. Patients are empowered to request and correct their medical data and are notified when their medical data is disclosed.
Patient centricity and higher satisfaction scores
Patient information is sensitive and it should not land in the wrong hands. HIPAA compliance demonstrates a commitment to patients’ privacy. In the event of a cyberattack, HIPAA-compliant systems can contain data breaches and respond appropriately, thus improving the brands’ perception among its patients and thereby building higher satisfaction.
Well, it is quite clear that following HIPAA guidelines is beneficial for organizations in the healthcare industry. But what are the requirements that you should follow? Let’s check it out!
Also, it’s good to have a fair idea of certification cost as well, here’s a quick guide to HIPAA certification cost
List of HIPAA Requirements
The exact compliance requirements vary as per the organization’s structure and method of operations. However, there are three primary requirements/rules that form the foundation of everything related to HIPAA compliance.
Here are the 4 HIPAA requirements checklist:
1. The HIPAA Privacy Rule
The HIPAA Privacy Rule focuses on patients’ right to privacy. Under this, healthcare providers and related entities must ensure the privacy and security of Protected Health Information (PHI), which includes names, addresses, medical records, financial information, social security numbers, contact information, etc.
PHI can only be used for treatment, research, payment, and legal purposes. Covered entities must get written authorization/consent from patients before using their personal data for any purpose other than the ones mentioned above. Also, PHI handlers should keep the information collected and stored to the bare minimum required to process said information.
Added to that healthcare entities should keep patients informed of their rights and how their PHI is being used. By doing so, patients will have greater control over their sensitive health information.
Implementation of HIPAA Privacy Rule
- Create and implement policies that regulate the use and disclosure of PHI. Ensure employees understand and adhere to these policies.
- Inform patients about their rights and how their information will be used through a Notice of Privacy Practices.
- Limit the disclosure of PHI to the minimum necessary to accomplish the intended purpose.
- Ensure patients can access, request amendments to, and obtain a copy of their health records. They should also be able to request privacy restrictions.
- Implement agreements with vendors and partners who handle PHI to ensure they comply with HIPAA requirements.
2. The HIPAA Security Rule
The HIPAA Security Rule focuses on protecting electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI) from being accessed, tampered with, copied, or destroyed by unauthorized entities. This rule standardizes the measures that ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of ePHI.
To comply with the security rule, covered entities need to maintain three safeguards:
- Administrative: Administrative safeguards are a major part of the HIPAA compliance requirements that establish security measures including risk assessment, implementing security controls, getting equipped to protect ePHI, and staff training.
- Physical: Physical safeguards control access to the physical facilities where ePHI is stored. This includes implementing policies for securing the workstations, servers, routers, and devices through which ePHI can be accessed or transmitted.
- Technical: Technical safeguards address the risks associated with technology. They essentially introduce policies for hardware, software, and technology that control the access to ePHI. Some examples include antivirus software, audit control, data encryption policies, etc.
Implementation of HIPAA Security Rule
- Conduct a risk analysis to identify vulnerabilities in your organization’s handling of PHI.
- Implement security measures to reduce risks and protect PHI from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Develop administrative, technical, and physical safeguards to secure electronic PHI ePHI. This includes measures like data encryption and multi-factor authentication.
- Restrict access to ePHI based on job roles and the minimum necessary standard.
- Implement systems that track and log access and activities involving ePHI.
- Train staff on security protocols and the importance of protecting PHI.
Also check out: List of HIPAA encryption requirements
3. The HIPAA Breach Notification Rule
Nothing is completely secure—irrespective of how secure systems seem, there’s always a chance of a security breach. The breach notification rule addresses what to do when a breach occurs. The organizations must be ready with policies and plans to inform the public and specifically, individuals affected by the breach about what occurred and what to do next.
The HIPAA requirements under this rule include:
- Notifying the affected individuals formally through mail or email about the data breach within 60 days of discovering the breach. (Find out how to send HIPAA complaint Gmail)
- Posting a notice about the breach on the website for 90 days or notifying the public via a news broadcast (if the senstive information of more than 10 affected individuals is not available)
- Providing public notice about the breach through local news outlets (if more than 500 individuals are affected by a HIPAA breach)
- Informing the Secretary of Health within 60 days of the discovery of a breach if more than 500 individuals are affected. If this number is less, then the organization can provide notice by the end of the year.
Implementation of HIPAA Breach Notification Rule
- Create and implement an incident response plan to quickly address security incidents and breaches.
- Establish a process for reporting breaches of PHI to affected individuals, the HHS, and, in certain cases, the media.
Also check out: HIPAA compliance checklist
4. HIPAA Omnibus Rule
The HIPAA Omnibus Rule raises important questions about healthcare professionals’ evolving responsibilities. This rule demands significant changes, starting with the need to revise Business Associate Agreements. But are these agreements enough to ensure compliance?
The rule also requires healthcare providers to verify that their Business Associates adhere to the HIPAA Security Rule, adding another layer of accountability.
With that being said, here are the key provisions of the HIPAA Omnibus Rule:
- Business associates of covered entities are now directly responsible for complying with HIPAA.
- There are stricter limitations on how PHI can be used and disclosed.
- Individuals have more control, with expanded rights to restrict the sharing of their PHI.
- Notices of Privacy Practices must be updated and redistributed to reflect these changes.
- Individuals can also request copies of their PHI more easily.
- Authorization requirements for the privacy of PHI disclosures have been modified.
- The Breach Notification Rule has been finalized, with a revised “harm” threshold.
- A four-tiered financial penalty structure has been introduced for HIPAA violations.
Implementation of HIPAA Omnibus Rule
- Business Associate Compliance: Ensure that all business associates and subcontractors comply with HIPAA rules through updated BAAs.
- Data Protection: Ensure the safeguarding of genetic information and other sensitive patient data as required by the Omnibus Rule.
Cost of HIPAA Compliance
The cost of getting HIPAA compliant can vary depending on a company’s approach, but a mid-range estimate falls between $80,000 and $120,000. This range is influenced by factors such as whether compliance efforts are handled in-house, possibly with the support of compliance software or consultants, or if compliance is fully outsourced to external professionals.
With Sprinto’s cost calculator, estimate the budget you’ll need to set aside to get compliant and start winning more sales deals.
HIPAA Requirements on a Strategic Level

Now that we understand the pillars of HIPAA regulation, let’s sum up the requirements that can help you achieve HIPAA compliance:
- Create and implement policies: The very first step in securing ePHI is to develop and implement efficient cybersecurity policies and standards. Administrative systems and workstations must follow HIPAA requirements while your staff is trained on policies. Policies will also have to be documented and distributed across teams.
- Implement safeguards: To be HIPAA compliant, you need to implement the safeguards discussed above. They ensure the physical and digital safety and access to PHI. Only individuals and systems with authorization should be able to access ePHI.
- Conduct risk assessments and internal audits: HIPAA requirements include conducting an annual risk assessment audit. This covers the administrative, physical, and technical aspects of the organization.Through risk audits, you can identify and patch the gaps in security and avoid criminal penalties associated with non-compliance. (also, check out a detailed article on HIPAA audit)
- Report and investigate violations: Certainly, security breaches are inevitable, and when such violations occur, you need to act on them quickly. Affected individuals will have to be notified and a root cause analysis will have to be conducted to understand why and how the breach occurred. Then, you can work on the remediation and take further actions to resolve the issue and prevent it from happening again.
Training employees
HIPAA training should be comprehensive, but the reality is that it often varies in quality. Training should cover handling electronic patient health information (e-PHI), protecting against security threats, and preventing impermissible uses or disclosures of e-PHI.
Also, employees need to be well-versed in implementing policies and procedures, responding to data breaches, and understanding patients’ rights.
However, many compliance training programs fail to go beyond the basics, leaving employees without the in-depth knowledge required to handle real-world challenges. This lack of thoroughness can lead to gaps in compliance and increase the potential risk of breaches.
Also find out: How to implement HIPAA certification process
How Can Sprinto Help?
On the surface, HIPAA requirements might seem pretty straightforward. But it is anything but straightforward and can quickly become overwhelming. Getting through such a complex set of regulations is no small task.
That’s where Sprinto steps in. We simplify the compliance process by breaking down requirements into clear, actionable steps, allowing you to achieve HIPAA compliance faster and with less stress. Sprinto streamlines control mapping, provides smart notifications, and offers continuous monitoring, ensuring you always stay audit-ready and compliant.
Take Fresha, for example. When they needed to streamline their compliance efforts, they turned to Sprinto. “The moment we saw it, we were extremely impressed—we knew this was exactly the tool Fresha needed to handle compliance,” shared a spokesperson from Fresha. And within 3 months, they were HIPAA compliant.
Ready to jumpstart your HIPAA compliance journey? Our experts are here to help. Get started today! Get started here.
FAQs
1. What are three HIPAA implementation requirements?
The three HIPAA implementation requirements under the HIPAA Security Rule. They are administrative measures that cover procedural security steps, physical measures that limit the access to ePHI, and technical safeguards that address risks associated with the use of technology.
2. What is HIPAA’s minimum necessary requirement?
The minimum necessary standard requires covered entities to implement policies and procedures that limit unnecessary usage and disclosure of protected health information.
3. What’s the official definition of a Covered Entity (CE) under HIPAA?
A Covered Entity is any business entity that falls under the compliance mandate of HIPAA regulations. The covered entities include medical providers (hospitals, private clinics, etc.), insurance providers, and clearinghouses.
4. Is staff/employee training a requirement under HIPAA?
Yes, staff training is a requirement under the HIPAA Privacy Rule. Organizations need to ensure that proper training is provided annually to all employees on HIPAA’s best practices.


Use Sprinto to centralize security compliance management – so nothing
gets in the way of your moving up and winning big.


![HIPAA Certification Cost [Updated 2024 + Free Checklist]](https://sprinto.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/HIPAA-Certification-Cost-Updated-2024-Free-Checklist-1024x675.jpg)
























