As digital landscapes continue to evolve at an accelerated pace, new tools, technologies, and systems are added to them daily. These are necessary tools for businesses to grow, but they also open up doors to new vulnerabilities and threats. This is why cybersecurity has become ubiquitous in our digital world.
Cybersecurity is the process of protecting your network of systems from cyberattacks. These attacks have varied motives, from stealing or altering sensitive information to extorting money.
The impact of these cyberattacks could range from a minor inconvenience, like your laptop shutting down, to a major disruption, potentially leading to significant financial losses.
If you are new to this concept, consider this article your introductory guide. Here, we explore what cybersecurity is, the types of cybersecurity, and how to prevent common security mishaps.
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the practice of safeguarding digital assets, which includes systems, networks, devices, and data, from unauthorized access, malicious attacks, and accidental exposure. It encompasses an approach that ensures the confidentiality, availability, and integrity of information.
This approach aims to safeguard an organization’s infrastructure from data breaches, cyber attacks, natural disasters, and insider risks.
A central goal of cybersecurity is to ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data, wherever it is deployed. Cybersecurity works best when people, processes, and technology combine to prevent, mitigate, and investigate breach attempts.
Why do organizations need to implement cybersecurity?
Organizations should implement cybersecurity to protect their trade secrets, intellectual property, and customer data from unauthorized access. Cybersecurity programs save cost to breaches, demonstrates commitment to good security practices, and in many cases is a mandatory regulatory requirement.
Data is the glue that holds every function and process together – it plays a key role in all decision-making processes in all organizations. Equating it with gold would not be an exaggeration. Tech giants like Facebook and Google would go bankrupt if they stopped collecting data.
Malicious actors know this. Organizations of all sizes are locked in a game of cat and mouse with cyber criminals – as anti-malware technologies become smarter, so do criminals.
Every study or report on cybersecurity trends shows the number of incidents rising across every industry. Don’t believe us? Let the numbers speak for themselves.
A report by IBM found that most organizations have faced more than one data breach. In a bid to compromise for the loss of revenue, 60 percent of organizations increased the price of their products or services. This implies that when you don’t invest in cybersecurity, you pay one way or another. When your competitors have strong security infrastructure, they can charge less by avoiding breaches – which will make your customers switch – a lesson many organizations learned the hard way.
The IBM report also shows the importance of compliance and cybersecurity automation. Organizations with fully deployed security AI and automation spend $3.05 million less in breaches compared to those without these facilities. They also spend less time to contain a breach – 249 versus 323 days.
Breaches don’t just cost money, but set them back significantly in terms of productivity. On average, it takes 277 to contain a data breach. This causes serious workflow disruptions and business downtime, especially for businesses that don’t have a dedicated security team to handle incidents.
Thanks to the pandemic, many businesses have adopted remote work – a huge factor contributing to poor security. With a record number of devices sitting outside the company firewall, the number of incidents won’t fall anytime soon.
While it is possible to recover from financial loss and business downtime, loss of reputation is irreversible damage. Once you make headlines for the wrong reasons, you can bid customer trust goodbye.
Have a look at this video on cybersecurity:
What are the types of cyber security?
Cybersecurity can be roughly classified into five categories. These include:
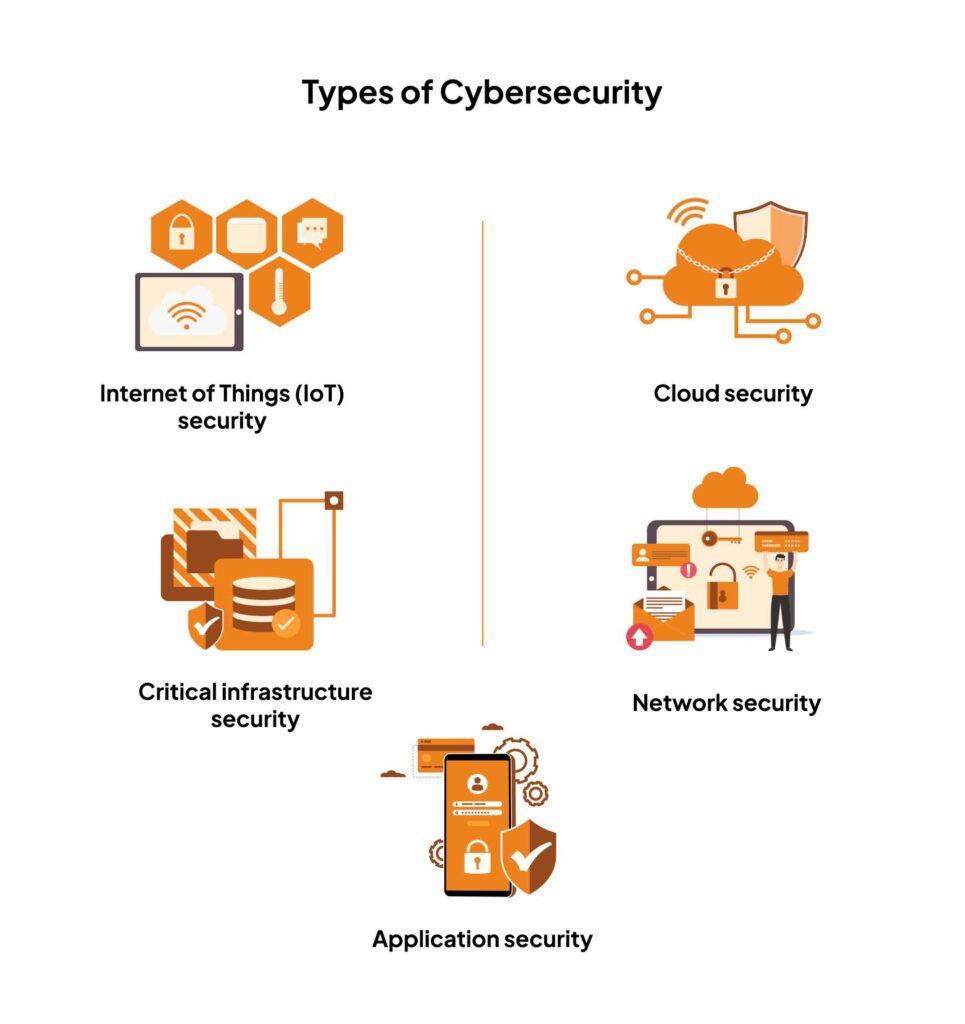
1. Critical infrastructure security
Secures larger, critical infrastructure such as data hosting centers, network communications systems, power supply, and transmission facilities. The idea is to protect these utilities from sabotage or attacks using a contingency and continuity plan.
2. Application security
Protect software application code repositories and other data from unauthorized access and breaches. Regular updates, threat modeling, and validating source code help to secure applications from unwanted risks.
3. Network security
Secures data deployed on computer networks from unauthorized access. It protects hardware and software technologies using a firewall, encryption, two-factor authentication, and antivirus solutions.
4. Cloud security
Secures data deployed on the cloud. This approach combines cyber security tools, system controls, policies, and services to protect your cloud infrastructure.
5. Internet of Things (IoT) security
Smart devices are entering more homes each year, opening another door for cybercriminals. IoT security protects a number of connected devices vulnerable to access by cybercriminals or bots. It works by auto segmentation to monitor activities and using IPS to patch exploits virtually.
Here’s a complete guide to cyber security compliance.
List of 7 Cybersecurity threats
The most common cybersecurity threats include:
1. Phishing
It is a common type of attack used to trick corporate users into disclosing sensitive personal information. Conducted mainly through email, phishing campaigns are designed to make it look like it’s from a legitimate website or a reliable person. These emails generally contain a URL to a scam website which requires them to enter personal information such as credentials, leading to financial loss.
Phishing attacks are getting more advanced, making it harder for end users to detect.
There are three types of phishing – untargeted, spear phishing, and whaling. Untargeted phishing campaigns sends an email to multiple recipients to get as many victims as possible. Spear Phishing targets specific users and whaling targets senior members of a corporation.
2. Malware
This software is engineered to gain unauthorized access into networks or devices to inflict damage or extract sensitive information. Different types of cyber attacks are classified as malware. Some examples include trojan, worm, virus, spyware, rootkits, or adware.
Just like phishing, malware attacks are becoming more sophisticated – modern malware capabilities are equipped with technologies to bypass anti malware detection tools. With more non signature based malware entering the network, traditional tools are no longer effective in detecting and containing unknown threats.
3. Ransomware
It is the most common type of malware. Ransomware is used by malicious actors who break into a system, encrypt the data, and extort money by threatening to delete it.
Over the years, ransomware models have changed the way they used to function. Previously, ransomware was used only to make the victim pay to retrieve the data, now it is not uncommon for criminals to steal the data.
The use of ransomware as a Service (RaaS) model is the most recent development where hackers sell a pre-developed ransomware kit to malicious actors on a subscription basis.
4. Cryptojacking
Also known as crypto mines, it is a type of cyberattack where hackers inject JavaScript into a website to slow down the device of its visitors by consuming its processing power.
The success of this type of threat depends on time – the longer it is present in the victim’s device, the more profit it mines. Due to the profit it generates, cryptography has gained massive popularity among cybercriminals.
5. Botnets or DDos
Botnets are IoT or endpoint devices infected by malware which allows malicious actors to take control remotely. If it infects multiple systems, botnets can act as a force multiplier to inflict more damage compared to a single source. It is commonly used for phishing campaigns, crypto mining, DDoS attacks, and spying operations.
DDoS attacks make a service unavailable by flooding the system with traffic. Botnets are essentially the actor, and DDoS the action.
Check out more on cyber security challenges
6. Gen V attacks
Fifth-generation attacks are commonly known as Gen V attacks. They represent a more sophisticated and complicated cybersecurity threat that has emerged recently.
Gen V attacks are particularly concerning due to their ability to infiltrate diverse IT ecosystems. They spread rapidly across multiple environments and organizations.
These attacks can target cloud devices, mobile devices, networks, and endpoints all at once, making them difficult to detect and mitigate.
These attacks are either state-sponsored or carried out by organized cybercriminal crime groups with large resources. The sheer scale of these attacks often raises concerns about their aim, which could be economic or geopolitical manipulation.
7. Supply chain attacks
As the name suggests, supply chain is a form of cybersecurity threat that targets an organization’s vulnerabilities in its supply chain network. Cybercriminals infiltrate a third-party vendor or a supplier that has access to the target organization’s system or data. By compromising the weaker link in the supply chain, attackers leverage that access to breach the primary target’s defenses.
Attackers can insert malicious code into software updates distributed by the vendor, compromise hardware during manufacturing, or exploit shared network connections. Their goal is often to gain long-term and stealthy access to the target’s system.
How to implement a strong Cybersecurity?
Now that you know what the common security threats are, let us understand how to mitigate each.
Phishing
As phishing techniques become harder to detect, here are some measures to prevent you from becoming a victim:
- Block spam emails
- Use websites that trigger warnings while attempting to access scam URLs
- Use unique passwords for all sites using a password manager
Malware
To prevent new and previously encountered malware, make sure to:
- Keep anti-malware tools updated
- Use AI-based malware tools to mitigate both known and unknown threats
- Implement a privileged access-based system to prevent unauthorized access
Ransomware
Despite being a common threat across industries, it is easy to prevent ransomware using a few simple steps:
- Frequently backup important data crucial for business continuity
- Keep your anti-malware tools updated with the latest versions
- Use firewalls to block unauthorized traffic
Also check out: How to develop an incident response plan
Crypto jacking
While crypto jacking has a high success rate, you can circumvent it by:
- Checking if your browser offers protection against crypto jacking. A reliable website is crytojackingtest.com
- Install browser extensions that block crypto jacking
- Install browser extensions that block crypto JavaScript
- Use built-in ad blocking tools
Botnets and DDoS
To prevent Botnets and DDoS from infecting your system, take the following measures:
- Locate your servers across multiple data centers
- Use different internet providers
- Ensure that your service provider offers DDoS mitigating controls such as firewalls, load balancers, and monitoring and response capabilities.
Gen V attacks
To prevent Gen V attacks, you can adopt the following tactics:
- Implement advanced threat prevention technologies to detect and respond to threats in real-time across all networks, cloud environments, and endpoint devices.
- Ensure that threat intelligence can be shared across the entire IT infrastructure, as similar attacks can happen simultaneously.
Supply chain attacks
Here’s how you can mitigate the possibility of supply chain attacks
- Implement a software verification process that includes code signing and integrity checks.
- Adopt a zero-trust security model that provides an additional layer of protection. This means that no user system should be automatically trusted and that all access requests would require constant verification. This applies to external and internal user systems.
- Develop an incident response plan that addresses supply chain attacks.
Benefits of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is no longer optional – many businesses don’t consider adding it to their process till an incident occurs. But this should not be your approach; damage control is not easy and often proves to be fatal if not handled at the initial stages.
Here are the three benefits of cybersecurity:
Business continuity:
As discussed before, it takes 277 days to contain a breach. This would not make a significant impact for large organizations, but smaller organizations often don’t survive a setback of this magnitude. As startups and small businesses don’t chalk out a budget for cybersecurity, they are more likely to end up becoming a target.
A 2019 report by Verizon found that small businesses are the top target for cybercriminals. So would you focus on growth or deplete your resources to solve cyber crimes?
Privacy concerns:
Intellectual property theft is a serious issue that can throw SMBs out of the game. Malicious actors target trade secrets or intellectual property – your most valuable asset. For many businesses, their unique service secrets are the only thing keeping them up and running.
Selling data in the black market is a lucrative business. Hackers won’t leave any door unopened to gain access into your sensitive information – a disaster you can prevent using cybersecurity.
Business growth:
If you provide a service or product, security is perhaps the important investment you will make. The threat posed by poor security is not unknown to decision makers in a business. Many won’t even consider partnering with you without sufficient proof of strong security practices. So consider security tools as your key to unlock new projects.
Also read: A detailed list of best cybersecurity practices
Conclusion
When it comes to security, prevention is better than cure. As previously outlined, a holistic approach to strong cybersecurity can be achieved by involving people, processes, and technology in the right way. A smart way to integrate this into your system is through automation. Sprinto takes care of your security needs using a single solution that automates processes, trains people, and leverages technology to detect vulnerabilities.
If you snooze on cybersecurity, you lose on growth opportunities. Let’s simplify security. Talk to our experts about your needs.
FAQs
What are the 3 major principles of cyber security?
The three principles of cybersecurity are integrity, availability, and confidentiality.
What skills are needed for cyber security?
Top skills preferred for cybersecurity jobs are attention to detail, in-depth knowledge of how security works across systems, computer forensics skills, and ethical hacking abilities.
Who needs cyber security?
Individuals, businesses, and government organizations need cybersecurity. Security threats don’t target anyone in particular. So irrespective of the type and size of business, cyber security is crucial.
Anwita
Anwita is a cybersecurity enthusiast and veteran blogger all rolled into one. Her love for everything cybersecurity started her journey into the world compliance. With multiple certifications on cybersecurity under her belt, she aims to simplify complex security related topics for all audiences. She loves to read nonfiction, listen to progressive rock, and watches sitcoms on the weekends.
Explore more
research & insights curated to help you earn a seat at the table.





















