Risk Management Framework (RMF): Key Components and Best Practices
Meeba Gracy
Sep 19, 2024
“Risk Management lets you appreciate the risk while you let someone else shoulder all the worry.” – Anthony T. Hincks
Risk is a natural part of business and any projects you undertake. Whether it’s day-to-day operations or financial choices, risk is always present. But there’s a smart way to handle it: a Risk Management Framework. This approach allows you to understand risks while others handle the stress.
In this article, we’ll take you through how to create a Risk Management Framework, break down its key elements, and explore its importance. You’ll also find practical strategies and examples of risk management frameworks for businesses, helping you navigate risks effectively.
What is the Risk Management Framework?
A Risk Management Framework (RMF) is a structured approach organizations use to identify, assess, and mitigate risks. Originally developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the RMF was designed to secure the U.S. government’s information systems.
Beyond government applications, risk management frameworks for businesses help protect sensitive data, maintain a competitive edge, and avoid legal complications.

Originally, the RMF was meant for federal agencies to follow better regulations like the Privacy Act of 1974 and the Federal Information Security Modernization Act of 2014 (FISMA). Over time, these guidelines, crafted by NIST, have found usefulness beyond just federal agencies. Now, private organizations also see their value in managing risks effectively.
Comprehensive Risk Monitoring & Mitigation
Importance of risk management framework
The importance of a Risk Management Framework lies in its ability to uncover potential issues in your organization. It equips you to manage both existing and potential risks effectively.
For example, a company needs a better plan for cybersecurity risks. They store lots of valuable information, like customer data and financial records, on their computers. Without a risk management framework in place, you can fall victim to the following risks:
- Data Breach Risk
- Reputation Damage
- Legal Troubles
- Financial Loss
- Business Impact
So, having a risk management plan is like bringing that umbrella in case it rains unexpectedly. It keeps the company safe and helps it make smart choices. Also, if a company takes too many risks without a good plan, it can make others see it differently and even affect its money situation.
How to implement a risk management framework?
Implementing a risk management framework is undeniably critical in the risk management process. If implementation falls short, it could mean not using the carefully designed framework you’ve dedicated significant time and energy to build.
However, with Sprinto all these steps will fall easily into your plan. You don’t need to put in so much manual effort, which was a thing of the past. But what is Sprinto? Sprinto is a compliance automation platform that helps you get compliant in no time.
This is because 90% of the efforts inducing the implementation of a risk management framework for your company are automated with the help of Sprinto. To know how it works, just get in touch with our experts and take a demo call. Also, I will get a brownie point if you do 🙂
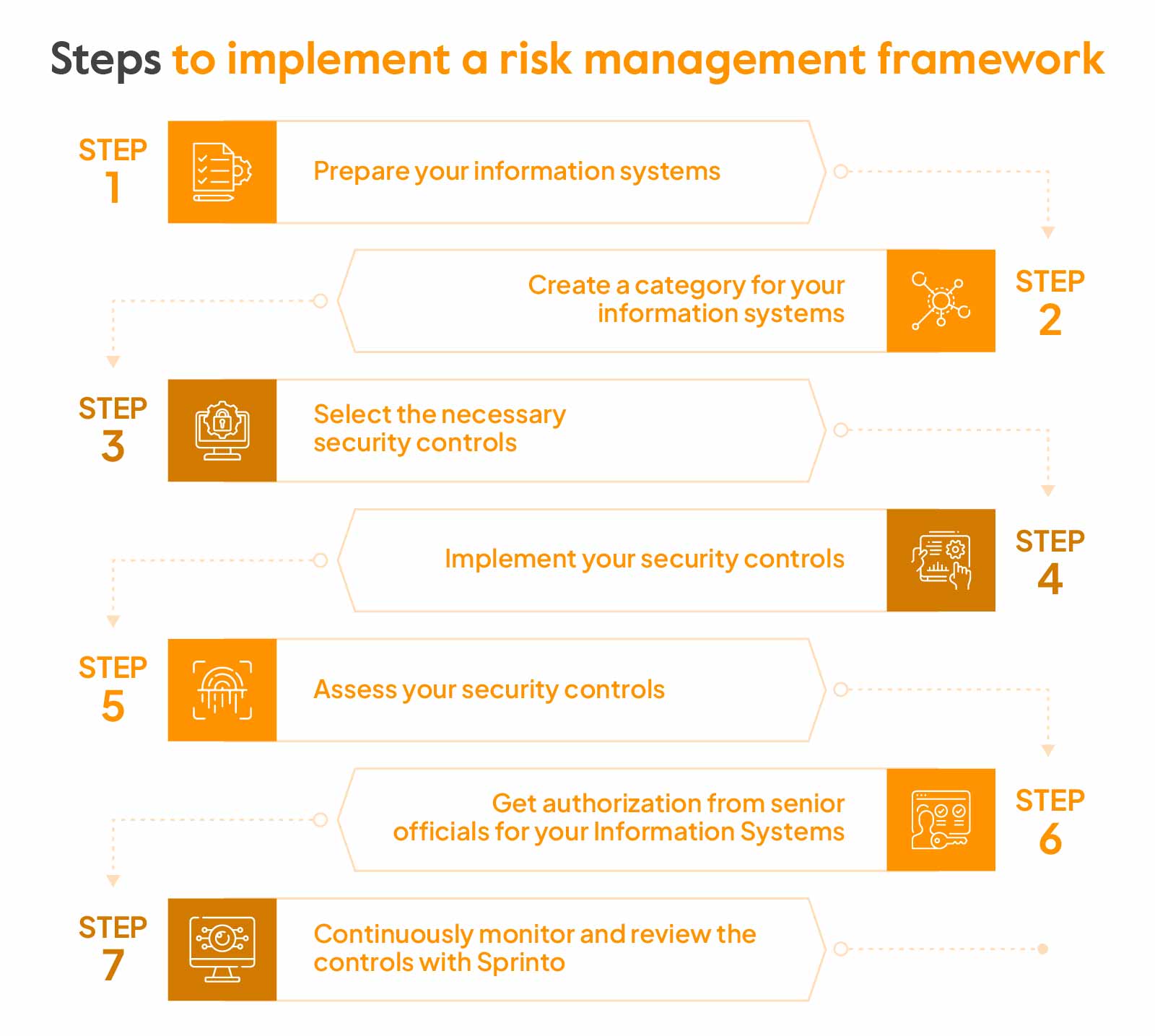
But first things first, here is how you can start:
Step 1: Prepare your information systems
This step supports all the other steps we will explore in the framework. It pulls together guidance from different NIST publications and incorporates requirements from the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) policy, or sometimes a mix of both.
Occasionally, your company might have already included some of the tasks from the Prepare step within your existing risk management program.
The main objectives of this step are to:
- Simplify the process of implementing your RMF
- Advance your IT modernization goals
- Save security and privacy resources
- Give utmost priority to protecting your most critical assets and systems
- Ensure the privacy of individuals
Step 2: Create a category for your information systems
To get the ball rolling, you need to organize your IT systems based on your company’s main goals, financial plans, and industry. To better understand security categories and potential risks, you need to follow the guidance provided by NIST in FIPS 199. This helps you determine which information and systems need the highest coverage against internal and external vulnerabilities.
Step 3: Select the necessary security controls
NIST has created a wide collection of security measures you can use for your systems worldwide. Choose the specific controls from this collection that match your security from your organization. Sprinto has control mapping to make it easier and will help you monitor these controls. It’s because these controls are important as they will mitigate cyber risks and safeguard the assets of your company.
Step 4: Implement your security controls
Once you’ve picked the appropriate security controls for your IT systems, it’s time to implement them. You can proceed to the next stage if these controls function as expected and meet all required regulatory standards.
Step 5: Assess your security controls
With the initial setup complete, evaluating how well your security controls are performing is now necessary. The aim is to ensure that they consistently meet the set standards. You can perform this evaluation on your own, or you can use tools like Sprinto (Compliance automation platform). This significantly reduces your manual effort, and you don’t need to assess it constantly!
Step 6: Get authorization from senior officials for your Information Systems
If the previous steps have produced positive outcomes, you’re ready to give the green light for the wider IT risk management framework implementation. If other people are involved in decision-making, like stakeholders and executives, make sure to get their approval as well.
Step 7: Continuously monitor and review the controls with Sprinto
The last step is to continuously monitor and assess your risk management plans. Things change – new risks pop up, old ones shift, some might disappear, and priorities can shift. This is why you must keep an eye on what’s already in place, spot any new issues, find trouble areas, and see if your current strategies are still doing the job.
But the manual process of checking every time is simply arduous. This is why you need a continuous compliance tool (like Sprinto). This is your time to transition to a compliance system that operates continuously and seamlessly integrates with your existing systems. (Just look at the screenshot below). Anytime something fails, you will get an alert, and you can navigate to Sprinto’s all-in-one dashboard to resolve the issue.
Sprinto gathers high-quality evidence for audits automatically, maintains your compliance status through ongoing monitoring, and sustains compliance progress by automating the resolution of issues and compliance-related tasks.
To understand more about continuous monitoring, read the following case study – Audit & Assurance firm Sensiba LLP on why ‘continuous readiness’ should be the goal of compliance programs!
Here’s the highlighted citation from the firm – “Managing compliance in one place makes visibility easy to achieve and helps everyone keep track of what’s happening,”
Also, check out the list of enterprise risk management software
Risk management framework examples
Here are some risk management framework examples:
Strategic risks
- Business vitality decrease from competition, healthcare changes, and pricing pressure
- Intellectual property and trade secrets loss
- Rising trade barriers due to protectionism and nationalism
- Challenges accessing affordable, quality healthcare due to limitations in healthcare systems
- Reputation damage and loss of public trust
Compliance risks
- Ensuring the safety of clinical trial subjects/patients
- Handling personal information following data privacy rules
- Prioritizing employee health and safety
- Adhering to rules in selling and promoting products, including healthcare compliance and global anti-corruption laws
- Meeting requirements for U.S. government contracts/programs
- Concerns regarding the quality, safety, and effectiveness of products
- Dealing with major legal proceedings, including product liability cases
Operational risks
- Disruption in the flow of goods and information within the organization, suppliers, and consumers
- Business continuity or resilience getting compromised
- Risks with procurement and suppliers, including human rights concerns
- Challenges in getting vital materials and labor
- Resources being used inefficiently and product costs rising
Financial risks
- Unfavorable financial outcomes or economic performance
- Shifts in tax regulations leading to possible extra tax responsibilities
- Instability in currency exchange rates, alongside inflation and currency devaluation
- Errors in financial reporting
- Exposure to credit-related risks
Environmental risks
- More frequent and intense severe weather events like storms and floods
- Rise in pollution because of insufficient waste management
- Incorporation of unsustainable materials in the product lifecycle
Cybersecurity risks
- Data breach or fraudulent activities
- Disruption to the availability of crucial information systems
- Security issues arising from critical third-party incidents that affect business operations
Risk management frameworks are the foundation of organisational resilience. They offer organised techniques to assist firms in efficiently navigating uncertainty, such as preserving sensitive data and connecting day-to-day operations with larger corporate objectives. These frameworks are critical for navigating risks with clarity and purpose.
Types of Risk Management Frameworks
Risk management frameworks vary across industries and objectives, offering tailored approaches to address specific needs. Here’s a closer look at the key types:
NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF)
The RMF, developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, is a six-step process intended primarily for US government organisations. It focusses on strong security measures, regulatory compliance, and constant monitoring, making it ideal for organisations that handle sensitive data or operate in highly regulated industries.
The reason it works: The NIST RMF provides a step-by-step framework for managing risks in information systems while balancing operational security and compliance.
COSO Framework
The Committee of Sponsoring Organisations created the COSO framework, which emphasises on enterprise risk management and internal control. It is often employed in corporate governance, emphasising transparency, accountability, and adherence to legislation.
Best suited for: Companies that prioritise regulatory compliance and strategic alignment in their operations.
ISO 31000
ISO 31000 is a widely established standard that outlines risk management principles and best practices for organisations of all sizes and sectors. This adaptable framework is based on risk identification, assessment, treatment, and monitoring, making it suitable for firms looking to establish a risk-aware culture.
Its versatility means it may be adjusted to a variety of industries, including manufacturing and healthcare.
ITIL Framework
The IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL) framework is intended to address risks in IT service management. It focusses on aligning IT services with overall business objectives and ensuring that risk mitigation promotes operational efficiency and customer happiness.
ITIL is particularly valuable for organisations that rely on sophisticated IT systems. It helps businesses manage cybersecurity, downtime, and service delivery concerns.
PMBOK Risk Framework
The Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) framework covers the risks inherent in project management. It includes procedures for recognizing, analysing, and responding to project risks, allowing teams to stay on track and within budget.
This framework is highly valued in the building, software development, and engineering sectors, where project delays or cost overruns can have serious effects.
Continuous Improvement with Sprinto
No matter your business’s industry, dealing with risks is inevitable. It’s just part of running a business. Yet, how you handle these risks can determine whether your business flourishes or falters.
Since risk management can be complex, it’s smart to rely on a seasoned expert like Sprinto. Integrate Sprinto seamlessly into your tech setup with ready-to-use connections and personalized APIs. Streamline and automate tasks like monitoring controls and gathering evidence. Attain a detailed perspective on your compliance status and access higher levels of efficiency, all in one place.
FAQs
What are the 4Ts of risk management?
The 4 Responses to Risks are Tolerate, Terminate, Treat, and Transfer. This is a concise and effective method to outline various approaches for handling enterprise risks.
What are the four 4 elements of risk management?
The 4 elements of risk management are:
- Risk Identification
- Risk Assessment
- Risk Action Management
- Risk Reporting and Monitoring
How much does risk assessment software cost?
The cost of risk assessment software varies based on the vendor you choose. If you choose Sprinto, you can get it done within a fraction of the cost. However, the platform cost starts from $5000, and more premium vendors charge up to $25k.
What are the benefits of a risk management framework?
- Stronger security: Helps safeguard critical information systems by identifying and addressing vulnerabilities before they become threats.
- Stronger compliance: Ensures your organization meets regulatory requirements like FISMA or HIPAA, avoiding fines and legal troubles.
- Clearer risk insights: Provides a structured way to spot and prioritize risks, so nothing important slips through the cracks.
- Always prepared: Continuous monitoring keeps your defenses up-to-date as new risks emerge.
- Simplifies processes: Makes it easier to integrate security controls into your operations without disrupting workflows.
- Flexible for all: Works well across industries, whether you’re in government, healthcare, or tech.


Use Sprinto to centralize security compliance management – so nothing
gets in the way of your moving up and winning big.


























