Cybersecurity Readiness Assessment: The First Move Toward Proactive Defense
Payal Wadhwa
Jan 28, 2025
The 2024 CISCO cyber readiness index revealed that only 3% of organizations worldwide have the security maturity and readiness to be resilient against emerging risks. However, strangely, 80% of organizations feel moderately to highly confident in their readiness capabilities. The report highlights how organizations today are ‘underprepared’ and ‘overconfident’ regarding cyber readiness.
But honestly, tell us. When did you last evaluate your security maturity and conduct a cybersecurity readiness assessment?
Whether you are strengthening your defenses, preparing for compliance audits, or building a strong cybersecurity posture, a cyber readiness assessment should be the first step in evaluating the stance of your key pillars and guiding you towards enhancements.
This blog will help you quickly assess your cybersecurity readiness and uncover best practices to ensure consistency over time.
TL;DR
| Cyber readiness is no longer a choice but necessary for organizations, given AI trends, evolving regulations, skill shortages, and threat sophistication. |
| To perform a readiness assessment, start by conducting an asset audit, reviewing existing policies, identifying threats, evaluating third-party risks, testing incident response plans, checking employee awareness, and creating improvement plans. |
| Best practices for cybersecurity readiness include adopting a proven framework, transitioning to proactive defense, regularly monitoring controls, ensuring regular security assessments, and minimizing attack surface area. |
What is cyber readiness?
Cyber readiness is a set of proactive measures, policies, and practices that enhance an organization’s ability to anticipate, respond to, and recover from threats and attacks. It is an ongoing process with compounding efforts that help the organization maintain resilience and adapt to the evolving landscape.
Cyber readiness requires a culture of preparedness, agility and awareness and must be embedded in daily business operations.
Why is cyber readiness crucial for organizations in 2025?
Attackers work challenging year after year to find new loopholes to exploit your business. As threat sophistication rises, legacy systems fail, and regulatory changes focus on cybersecurity, agility and proactiveness become increasingly important.
Here’s why cyber readiness should be your top priority in 2025:
Embracing AI is crucial
AI is a double-edged sword, and attackers have already started using it for advanced phishing and social engineering attacks. It’s time that organizations also embrace it for the good. Add AI-driven tools to your cyber readiness kit for 2025 for faster anomaly detection, incident response, and even predictive analytics. Since AI models need vast data to train, now is the best time to start.
The regulatory landscape will continue to evolve
The trends point to unified global data protection laws and increased adoption of AI innovation, leading to AI compliance laws and a stricter focus on cybersecurity maturity. Your incident response plans, third-party management, and overall security posture must be resilient to navigate the stringent laws.
Skill shortage will remain
According to a report by BCG, we have less than four qualified professionals to fill five cybersecurity jobs. The global shortfall is 2.8 million, and trends indicate that the gap will only increase. So, it’s imperative to invest in upskilling current staff and using automation for routine tasks to remain robust, both of which are key to cyber readiness.
Attacks will only get sophisticated
By 2025, ransomware attacks are expected to pose an even more significant threat, especially to critical infrastructure. With advanced AI, cybercriminals are also expected to get crafty when launching targeted attacks. Having a strong foundation with baseline security measures and gradually enhancing your cyber readiness is no longer a choice but a necessity.
Roll out a security compliance program in a few clicks
How to perform a cybersecurity readiness assessment?
A cybersecurity readiness assessment focuses on key pillars of security and compliance to evaluate an organization’s resilience and adaptation to the changing environment. It helps identify potential cyber risks, compliance gaps, and response capabilities to pinpoint areas for improvement.
Here are the steps to perform a cyber readiness assessment:
Pre-assessment tasks:
1. Define objectives and scope
Start by establishing the assessment’s objectives, such as evaluating current security maturity, checking compliance readiness, or identifying key organizational risks. Then, define which systems, networks, and data will be included in the assessment.
2. Appoint a team
Appoint a cyber readiness assessment team with clear roles and responsibilities to delineate the tasks and avoid org-wide ambiguity. The team may include CISOs, CROs, CCOs, security analysts, and leaders from other functions.
Assessment steps:
3. Conduct an inventory and data audit
You can use automated discovery tools to list all software, hardware, cloud resources, and network components and compile an asset inventory. Classify and prioritize the ones under scope based on criticality and business importance. Follow the same procedure to conduct a data audit and label it as public, confidential, internal, and restricted. You’ll also need a data flow diagram to understand how data moves across the organization.
Key question: What are the ‘crown jewels’ that can impact operations, competitive advantage, reputation, and compliance?
4. Review existing policies and procedures
Review current policies and procedures to identify gaps in coverage and enforcement. Evaluate if you have covered critical areas such as data security, identity and access management, incident response, business continuity, risk assessments, third-party management, and employee awareness. Also include compliance-specific policies and any internal code of conduct guidelines.
For a detailed review, include stakeholders from different teams, such as HR, IT, legal, and other departments. Highlight any missing policies, outdated references, and inconsistent documentation.
Key question: Do the current policies and SOPs address critical areas for security and compliance?
5. Understand threats and vulnerabilities
Conduct vulnerability assessments to identify unpatched software, misconfigurations, weak passwords, and other vulnerabilities. You can use automated scanners like Nessus or Qualys. Next, penetration testing is used to simulate real-world attacks and uncover weaknesses at a deeper level. You can also gather threat information through previous incident analysis, internal audit results, and external sources such as threat intelligence feeds.
Based on the risks associated with these threats and vulnerabilities, assess the likelihood and impact of each of these to prioritize remediation efforts.
Key question: What are the most likely and severe threats and vulnerabilities that could impact our systems and operations?
6. Evaluate third-party risks
Have a handy active vendor list and assess their level of access to systems and the type of data they handle. This will help you rate vendors based on risk profiles and prioritize due diligence and risk assessment efforts. You can also send security assessment questionnaires and request compliance certifications such as ISO 27001, PCI DSS, HIPAA, etc. Examine the contractual obligations and ensure that they discuss the minimum necessary safeguards.
Key question: Are service providers and vendors meeting security and compliance expectations?
7. Analyze existing controls
Identify whether you have the relevant preventive, detective, and corrective controls by benchmarking them against a standard or framework, such as NIST CSF or ISO 27001. Some basic measures include firewalls, encryption, intrusion detection systems, multi-factor authentication, incident response, audit logs, and backup and recovery procedures.
The next step is to map them against risks to determine implementation gaps. Finally, the effectiveness of controls can be assessed through automated control tests or manual methods. For example, is there a system for frequent patch management? Is the firewall effective in blocking unrequired traffic? Having a system to report control effectiveness on dashboards is also crucial to making well-informed decisions.
Key question: Can the existing controls effectively mitigate identified risks and stand firm against advanced cyber threats?
8. Test incident response plan
Evaluate the effectiveness of the incident response plan through tabletop exercises, red team/blue team exercises, and real-world simulations. Test incident detection speed, reporting by first respondents, the effectiveness of communication with third parties, and the efficiency of containment, mitigation, and recovery procedures. Take note of areas needing improvement and adjust the incident response plan or train the incident response team accordingly.
Key question: How well does the incident response plan perform in real-life scenarios?
10. Check employee awareness
The key areas to focus on for employee awareness include password management, phishing, secure storage and file sharing, software updates, incident response, and adherence to compliance requirements.
You may conduct surveys to assess knowledge of password hygiene or the importance of software updates and phishing tests to track how many employees fall for the tricks. You may also check activity logs to understand adherence to access management policies and record training completion rates to create a plan of action for employee awareness.
Key question: Are employees adequately trained on cyber hygiene and best practices?
11. Create an improvement plan
The above analysis will help you discover loopholes in your cybersecurity readiness. Based on the red flags identified, create a tactical mitigation and improvement plan and set short-term and long-term goals. The process is ongoing and gradual and requires a combination of robust policies, technical measures, behavioral changes, and continuous iterations.
Evaluate your cyber readiness with Sprinto
Best practices to achieve cybersecurity readiness
Achieving cybersecurity readiness requires a comprehensive strategy that aligns people, processes, and technology while consistently implementing best practices. It’s a gradual process where efforts compound over time to build organizational resilience.
Here are 6 best practices to achieve cybersecurity readiness:
1. Adopt a proven framework
Adopting a proven framework developed by experts helps you address critical cybersecurity requirements without creating a program from scratch. These frameworks provide a structured set of guidelines for security maturity and are regularly updated to keep up with the regulatory environment. The choice of framework will depend on your business context and requirements. For example, if your client base is mainly in Europe, you can choose ISO 27001, or if you are looking to take a more flexible and risk-based approach, you can adopt NIST CSF.
2. Transition to proactive and preemptive cyber defense
Given the threat sophistication and compliance complexities, another best practice is transitioning from a reactive stance to a proactive approach. It involves staying ahead of the threats and updates by continuously monitoring vulnerabilities and compliance gaps.
According to Gartner, 2025 will also be shaped by preemptive defense, which goes further than proactive defense. It aims to mitigate threats and attack vectors before they can cause harm, such as blocking a suspicious domain using predictive threat intelligence.
3. Implement multi-layered controls
Forward-looking organizations focus on defense in depth using multi-layered controls, making it harder for attackers to penetrate through a single point of failure. The idea is to create a safety net to protect your data and assets from exploitation. For example, using multi-factor authentication for system access and implementing role-based access control ensures that only the right people access sensitive information.
4. Regularly monitor and test controls
Establishing a continuous monitoring mechanism helps identify red flags early and creates a cycle of ongoing improvements. This gradually improves threat detection, compliance readiness, and operational efficiencies. Similarly, it is essential to set up automated control testing to evaluate whether they function as intended and can adapt to emerging risks.
GRC platforms like Sprinto can help you here. The automated control testing and continuous control monitoring help you track real-time status on the health dashboard. Sprint also sends notifications and alerts for deviations to eliminate blind spots and take proactive steps to mitigate threats.
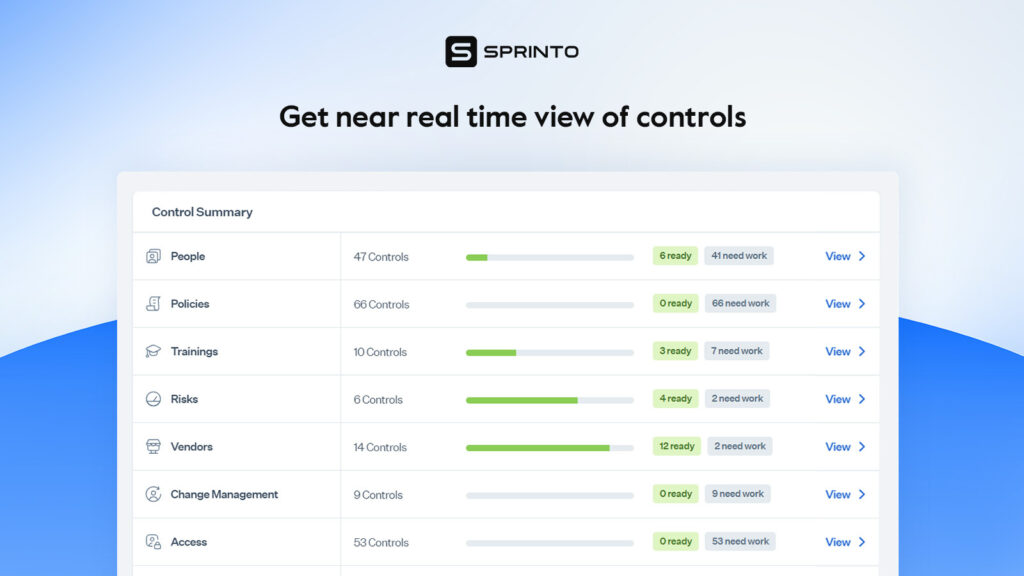
5. Ensure regular security assessments and internal audits
Establishing routine security assessments and internal audits enhances transparency about your security and compliance posture and helps you prioritize efforts better. They provide actionable insights on control effectiveness and help verify compliance, enabling organizations to make well-informed decisions. It also enhances stakeholder trust in the company’s security fabric and aligns with reputation management goals.
6. Minimize attack surface area
Minimizing attack surface area aims to limit the entry points of attack vectors to reduce the probability of attacks or minimize any damage. You can achieve this by:
- Segmenting networks that handle sensitive data
- Regularly updating software and patching vulnerabilities
- Using zero-trust always to verify identities and access and implementing the principle of least privilege
- Closing unnecessary ports
- Training your employees to reduce human errors
- Using strong encryption policies etc.
Achieve cyber readiness with Sprinto
A well-rounded cyber readiness strategy requires risk management, cybersecurity governance, and streamlined compliance management. Taking the manual route to achieve this only makes you realize its limitations later when employees complain of bandwidth issues, errors occur, and top management feels handicapped in decision-making due to a lack of real-time insights. You need automation to keep up with the complexities and accelerate the process. Enter Sprinto.
Sprinto is a next-gen GRC platform for cloud-first companies that seamlessly embeds with your tech stack to unlock efficiencies. The agile, responsive, and scalable platform helps you build a connected view of risks and controls through 200+ native integrations and Sprinto APIs. These APIs also help with granular-level monitoring, control testing, and evidence collection and are supported by time-bound and multi-channel alerts for gaps. The platform also allows you to track risks and compliance in real-time on health dashboards and offers comprehensive reports for senior management reviews.
The capability-rich and cost-efficient platform also allows you to demonstrate your cyber readiness and compliance posture through a complementary trust center. It allows you to create public and private profiles and attach the relevant documents and information to build market trust.
The platform features policy templates, training modules, vulnerability management, and role-based access controls to enhance the scope of security and compliance programs.
Check out the platform and take the first step to cyber readiness with us.
FAQs
What are the key components of cyber readiness?
The key components of cyber readiness are:
- Risk assessments
- Well-defined policies and procedures
- Security technology
- Continuous monitoring
- Incident response plan
- Employee training
- Governance and compliance
What tools can help the organization achieve cyber readiness?
To achieve cyber readiness, organizations can use risk management tools, Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools, GRC tools, endpoint detection and response tools, identity and access management (IAM) tools, and Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools.
What is the difference between cyber security and cyber readiness?
Cybersecurity aims to implement technical measures to protect networks, systems, and data from threats and attacks. On the other hand, cyber readiness is a broader concept that encompasses the right strategies and mindset for cybersecurity preparedness to defend against risks.
Can you share the cyber security readiness checklist?
Here’s a quick cyber security readiness checklist:
- Regular risk assessments
- Strong access controls and authentication
- Up-to-date software
- Backups
- Incident response plan
- Trained employees
- Continuous monitoring of logs
- Third-party risk management
- Testing of disaster recovery plans


Use Sprinto to centralize security compliance management – so nothing
gets in the way of your moving up and winning big.

























