Mastering NIS2: Critical controls, Proven Practices & ROI
Payal Wadhwa
Dec 15, 2024
Just when you thought GDPR was your most brutal compliance battle, NIS2 is raising the cybersecurity bar and putting organizations to the test again. For over 21 months, the European Commission has been answering questions and offering guidance to help member states adapt to the requirements. However, as of the publication of this blog, only a few countries, including Belgium, Croatia, and Italy, have successfully transposed the law. Many others are still working through drafts or preparing the necessary bills.
It’s said that GDPR is related to personal data, and NIS2 is related to cybersecurity—thanks to its stringent fines, personal liability for executives, and other security requirements. It’s no surprise that it’s the talk of the GRC world.
But don’t panic—this blog is here to help. We’ll walk you through the NIS2 directive, covering its scope, key measures, best practices, and ROI so that you can navigate it with confidence
TL;DR
| NIS2 replaces the previous NIS directive to strengthen cybersecurity across entities that provide critical services and meet a size and revenue threshold. |
| The key security measures under the directive revolve around governance, risk management, reporting to authorities, and requiring entities to use trust-qualified services. |
| NIST implementation can cost an increase of 12% – 22% budgets depending on whether or not you have been an NIS operator. |
A Closer Look at NIS 2
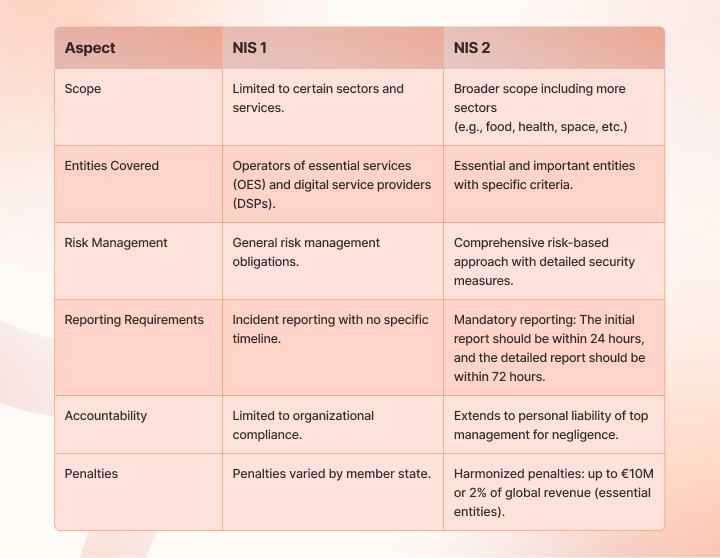
The NIS2 (Network and Information Security 2) Directive is a European Union law that replaces the original NIS Directive (2016) to enhance cybersecurity across the EU and address emerging threats.
Unlike the previous legislation, NIS2 expands its scope to include more sectors such as energy, transport, banking, healthcare, digital infrastructure, and public administration. It introduces consistent and more robust cybersecurity measures to address the increasing sophistication of threats, applying to organizations of all sizes regardless of their risk profiles.
NIS2 is legally binding and in effect (from 18 October 2024), and organizations within its scope must have policies and practices aligned with the law.

Over 100,000 new organizations have been impacted. Are you in scope?
The estimated 100,000 organizations are in addition to the number already under the NIS directive. The scope and applicability of NIS2 are now broader and defined by the criticality of service, headcount, and revenue threshold.
Check here if you are under the purview:
Applicability criteria:
- Size: NIS2 applies to medium and large organizations defined by the EU. A medium-sized company has at least 50 employees and a turnover or balance sheet of €10 million. A large enterprise, on the other hand, has at least 250 employees and a turnover of € 50 million or a balance sheet of € 43 million.
- Sector: The law identifies sectors as essential or important based on the criticality of services to the economy and society.
- Risk profile: Smaller organizations are only included if their services are critical to national security or the supply chain.
Following are the two types of entities under the directive:
Essential entities
- Energy (electricity, district heating and cooling, gas, oil, hydrogen)
- Transport (air, rail, water, road)
- Banking and Financial market
- Public Administration at national and regional levels
- Health (healthcare providers, research labs, pharmaceutical companies)
- Space
- Drinking Water
- Waste Water
- Digital Infrastructure (data centers, cloud providers, content delivery network providers, internet exchange points)
- ICT-Service Management B2B (Managed service providers, Managed security service providers)

Important entities
- Postal services
- Waste Management
- Manufacturing, Production, and Distribution of Chemicals
- Research
- Food
- Manufacturing (medical devices, computers, and electronics, transport equipment)
- Digital Providers (online marketplaces, search engines, social networking platforms)
- All sectors under essential that meet the size criteria under ‘important entities’
Exemptions
Micro and small organizations with less than 50 employees and turnover below € 10 million are excluded unless they provide a critical service.
Get compliant faster with automation
Key Security Measures under the NIS2 Directive
NIS2 suggests taking an all-hazards approach, which means organizations must implement risk-appropriate and proportionate measures to protect against risks. However, the law suggests some key focus areas and minimum security controls.
The main focus areas under the NIS2 directive are:
Management: Management is responsible for understanding the requirements, identifying cyber risks, overseeing employee training, and implementing appropriate measures.
Reporting to Authorities: Organizations must have stringent processes to report an incident within 24 hours of discovery and provide a detailed report within 72 hours.
Risk Management: Entities must take a risk-based approach to compliance and implement technical, operational, and organizational measures to minimize risks and impacts.
Business Continuity: Businesses should have a crisis management and business continuity plan, including system recovery, emergency procedures, and a dedicated team for crisis response.
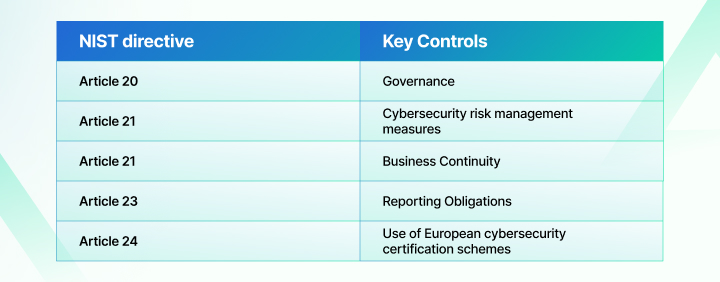
Member states can also require organizations to use ICT products, services, or processes that have been qualified under European cybersecurity certification schemes.
The minimum security measures to be implemented revolve around these focus areas include:
1. Policies and procedure documents around risk analysis, incident handling, access management, use of encryption and cryptography, and business continuity management
2. Policies and procedures to assess the effectiveness of cybersecurity risk management
3. Tailored supply chain security measures based on vulnerabilities of each direct supplier
4. Implementing multi-factor authentication or continuous authentication solutions
5. Arranging for workforce training on cybersecurity and cyber hygiene practices
6. Ensuring security throughout acquiring, developing, and maintaining network and information systems.
7. Ensuring human resource security measures and asset management.
How to build a Robust Control System? Some Best Practices
If you’ve determined NIS2 applicability and conducted a gap analysis as part of your preparatory work, the next step is to focus on control planning and implementation.
Here are some best practices to guide you through this phase:
1. Adopt a Proactive risk-based approach
A risk-based approach implies identifying all your organization’s risks and prioritizing the ones that truly matter. It requires you to embrace a forward-thinking mindset, not reacting to threats but prioritizing actions safeguarding critical assets. Embed regular risk assessments into the process, prioritize risks that truly matter, and stay adaptive to evolving threats, regulations, and third-party dependencies.
2. Strengthen Governance practices
The NIS2 holds the senior management directly accountable for cybersecurity initiatives, so strong governance forms the foundation of the directive. Set clear governance structures with well-defined roles, responsibilities, and reporting lines to involve all key stakeholders, including the board. Ensure that the risk assessments and internal audit reports regularly go through senior management reviews and well-informed decisions are made to stay on top of compliance.
3. Prioritize supply chain security
The NIS2 directive takes a layered approach to ensuring supply chain security and discusses three risk assessment types: coordinated, national, and internal risk assessments.
- Coordinated risk assessments happen at the EU level, which means a coordinated effort must be made to identify vulnerabilities that can impact the member states.
- National risk assessments allow expanding the directive’s scope to suppliers not initially covered by the directive to ensure national security.
- Internal risk assessments occur at the entity level as required under Article 21(2)(d)
The three mechanisms aim to evaluate vendors’ cybersecurity posture and help you identify high-, medium-, and low-risk vendors. It is also crucial to set minimum security requirements for vendors and suppliers and include these in contract clauses. Use monitoring tools to ensure visibility into third-party risks and breaches and mandate an incident response plan for suppliers.

4. Enhance incident detection and reporting
NIS2 requires businesses to report ‘significant’ incidents that cause financial loss, reputational damage, exfiltration of trade secrets, harm an individual, compromise information, or repeatedly occur with the exact root cause. The window for early warning is 24 hours, followed by a notification in 72 hours and a full report within a month.
The best practice for complying with the directive is to have a solid incident response plan with standardized procedures and a proper reporting structure. Automated tools are used for continuous monitoring, incident detection, and triage. Train the staff about incident detection through tabletop exercises and test the plan regularly. Conduct post-incident analysis and maintain proper documentation to work on improvements.
5. Adopt a zero-trust framework
Adopting a zero-trust framework aligns with NIS2’s risk management and resilience requirements. To adopt the framework, focus on verifying the security of every user, device, and application and mandate authorization and authentication mechanisms like MFA (multi-factor authentication) and SSO (Single sign-on). Apply the principle of least privilege to grant minimum necessary access to individuals based on job functions. Lastly, systems and processes should be designed with a mindset that breaches are inevitable, so measures like micro-segmentation of networks and data encryption should be implemented.
6. Promote a culture of cybersecurity
NIS2 holds leadership and employees accountable for maintaining cybersecurity, making a strong cybersecurity culture essential for better preparedness. The commitment must come from the top and be supported by soft and hard measures such as training programs, risk-adjusted rewards, and appraisals. Ensure the stakeholders understand the directive’s critical requirements and are trained on basic cyber hygiene practices.
7. Scale on existing certifications
Frameworks like ISO 27001 or NIST CSF cover baseline requirements such as risk management, incident response, and supply chain security. Use these to eliminate the need to create existing policies from scratch and minimize duplication of efforts when implementing controls. This will help you speed up the process and work with confidence.
Try cross-framework mapping with Sprinto
From Costs to Value: The NIS2 ROI equation
Implementation costs are often a significant concern for organizations, but presenting a clear ROI case can make securing budget approvals easier. Let’s break this down with a cost vs. ROI analysis:
Implementation Costs
- According to the European Commission, existing NIS operators can expect an increase of 12% in their information security budgets over the next three years following the directive, while those not affected by NIS1 can expect an increase of 22% in their budgets.
- According to a report by the Economic consultancy Frontier Economics, the direct costs of implementing NIS2 can be €31.2 billion per year and represent 0.31% of turnover on average.
The direct costs cover infrastructure upgrades, employee training, policy changes, and external consultations. Beyond these costs, the organization must also account for ongoing monitoring, reporting, audits, and compliance maintenance.
The Cost of Non-compliance
Non-compliance with NIS2 can lead to the following consequences:
Fines and penalties
- For essential entities, the fines can reach up to €10 million or 2% of global revenue, whichever is higher.
- For important entities, the maximum fine is €7 million or 1.4% of global revenue, whichever is higher.
Further enforcement actions
The other enforcement actions are non-monetary remedies or penalties and include consequences such as:
- Compliance orders
- Binding instructions
- Security audit implementation orders
- Threat notification orders to customers
In case of severe violations, operations may also be suspended partially or completely until compliance is achieved.
Criminal sanctions for management
The NIS2 directive also introduces personal liability for C-suite-level managers, such as executives and board members, if their actions constitute negligence and result in a cybersecurity incident. In such cases, the consequences are as follows:
- Organizations must publicly disclose compliance violations and identify the managers involved with details such as names and roles
- For essential entities, individual managers may be temporarily banned from holding authority positions in case of repeated violations
Costs of data breaches
The average data breach cost in 2024 was $4.88 million (€4.64 million).
For critical entities handling personal data, breaches may invoke GDPR fines, reaching €20 million or 4% of global turnover, whichever is higher.
This means that breaches could cost millions of euros—before factoring in reputational damage and customer loss.
Building the ROI case
Investing in NIS2 will not only save you from fines, penalties, and the costs of data breaches but also provide immense ROI from overall risk reduction. Beyond financial benefits, the reputational advantages of compliance are critical—non-compliance can damage credibility and drive away customers. Ultimately, non-compliance costs will always outweigh the investment required for compliance. Think long-term!
How much time can the implementation take?
NIS2 implementation can take anywhere from 9 months to over a year. Here’s a breakdown of the timeline:
- Assessment and planning (Identifying critical assets, reviewing current policies, and gap analysis): 1-3 months
- Implementation (implementing technical and organizational measures): 6-12 months
- Testing and observing the effectiveness of measures (security assessments, audits): 1-3 months
- Compliance Maintenance: Ongoing
Are you Future-Proofing?
NIS2 is just the beginning of regulatory change as the cybersecurity landscape evolves. We’ll see many more updates, especially as AI laws start coming in. Organizations should start thinking ahead and building flexible and adaptable frameworks that can evolve with changing requirements.
- Adopt a forward-thinking approach: The goal is to stay ahead and not panic when new updates or regulations come in. Build a solid foundation of measures to weave a strong security fabric, including risk assessments, encryption, incident response, access controls, continuous monitoring, and third-party risk management.
- Agility is key: It is crucial to continuously track vulnerabilities, stay informed on upcoming threats, and monitor regulatory changes. Connect with your peers and subscribe to cybersecurity newsletters that help you stay ready.
- Leverage automation: Use tools like Sprinto to minimize workload, launch audit-grade programs, and stay continuously on track.
Consider leveraging the BYOF (Bring-Your-Own-Framework) approach with NIS2 and Sprinto.
Sprinto helps you manage every framework under the sun under custom framework management. Just import your requirements and oversee the implementation on a centralized platform. We streamline critical tasks like monitoring, documentation, policy templates, evidence collection, incident management, vulnerability tracking, and reporting.
If you’re taking the ISMS route, i.e., using ISO 27001 as a baseline to move to NIS2, we can help with 1:1 guided implementation.
Additionally, out-of-the-box support for NIS2 is coming—our team is working to deliver this soon.
Sprinto’a agility is sure to impress you. Watch the platform in action today!
FAQs
What is the difference between NIST CSF and NIS2?
NIST CSF is a voluntary framework developed in the US to manage cybersecurity risks. It is non-binding and flexible and can be adopted globally by any organization that aims to identify, protect, detect, respond to, and recover from cyber incidents.
NIS2 is an EU directive that is legally binding on the member states. It aims to improve cybersecurity across essential entities in the EU and has specific requirements on risk management, supply chain security, and incident management.
What is the difference between GDPR and NIS2?
GDPR is a data protection law focused on safeguarding the privacy of individuals in the EU. It sets stringent rules for organizations processing personal data and holds data processors and controllers accountable for compliance. NIS2, on the other hand, focuses on strengthening cybersecurity for essential services. It requires covered entities to implement specific security measures, manage cyber risks, and ensure top management accountability for framework implementation. Legal obligations and penalties are imposed in cases of negligence.
What is the difference in the supervision of essential entities?
Essential entities under NIS2 are proactively supervised, and authorities ensure that are continuously meeting the framework requirements. On the other hand, important entities are monitored after an event, meaning that the authorities intervene only after cybersecurity incidents or evidence of non-compliance.


Use Sprinto to centralize security compliance management – so nothing
gets in the way of your moving up and winning big.





















