Complete Guide To Data Governance Roles And Responsibilities
Meeba Gracy
Jul 23, 2024
Organizations must comply with various regulations and standards governing data usage, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and others. This is why you need to understand the roles and responsibilities in data governance to help ensure compliance.
No one puts the definition of data governance more aptly than Mike Ferguson, Intelligent Business Strategies –
“Data governance is the orchestration of people, processes, policies, and technology to formally define, discover, assess, clean, integrate, and protect structured and unstructured data assets through their lifecycle to guarantee commonly understood, trusted, and secure data throughout the enterprise.”
However, clearly data governance responsibilities are central to a successful data governance strategy. Without these, even the best strategies and technologies can falter.
In this guide, we’ll explore the key data governance roles and responsibilities, providing a comprehensive understanding of who does what and why it matters for your organization.
| TL;DR |
| A data governance team has various roles essential for a data-centric culture, starting from Data Governance Office to Operational Data Stewards. |
| The Data Governance Council educates on data governance, approves policies, promotes practices, and advises on governance to risk management and compliance. |
| Assigning responsibilities involves defining roles, matching skills and experience, and establishing accountability. |
What are the Roles and Responsibilities for Data Governance?
The roles and responsibilities for data governance typically consist of a dedicated governance team, a steering committee acting as the governing body, and a team of data stewards. Data stewards play an important role in overseeing data quality and suitability within an organization.
Their responsibilities include managing and improving the organization’s data assets, offering specialized expertise, and supporting the development and implementation of data strategies. They also contribute to refining the data governance process to enhance overall effectiveness. The next section will discuss all the roles and responsibilities in detail.
Fastrack your Data governance efforts through automation
Various data governance roles and their responsibilities
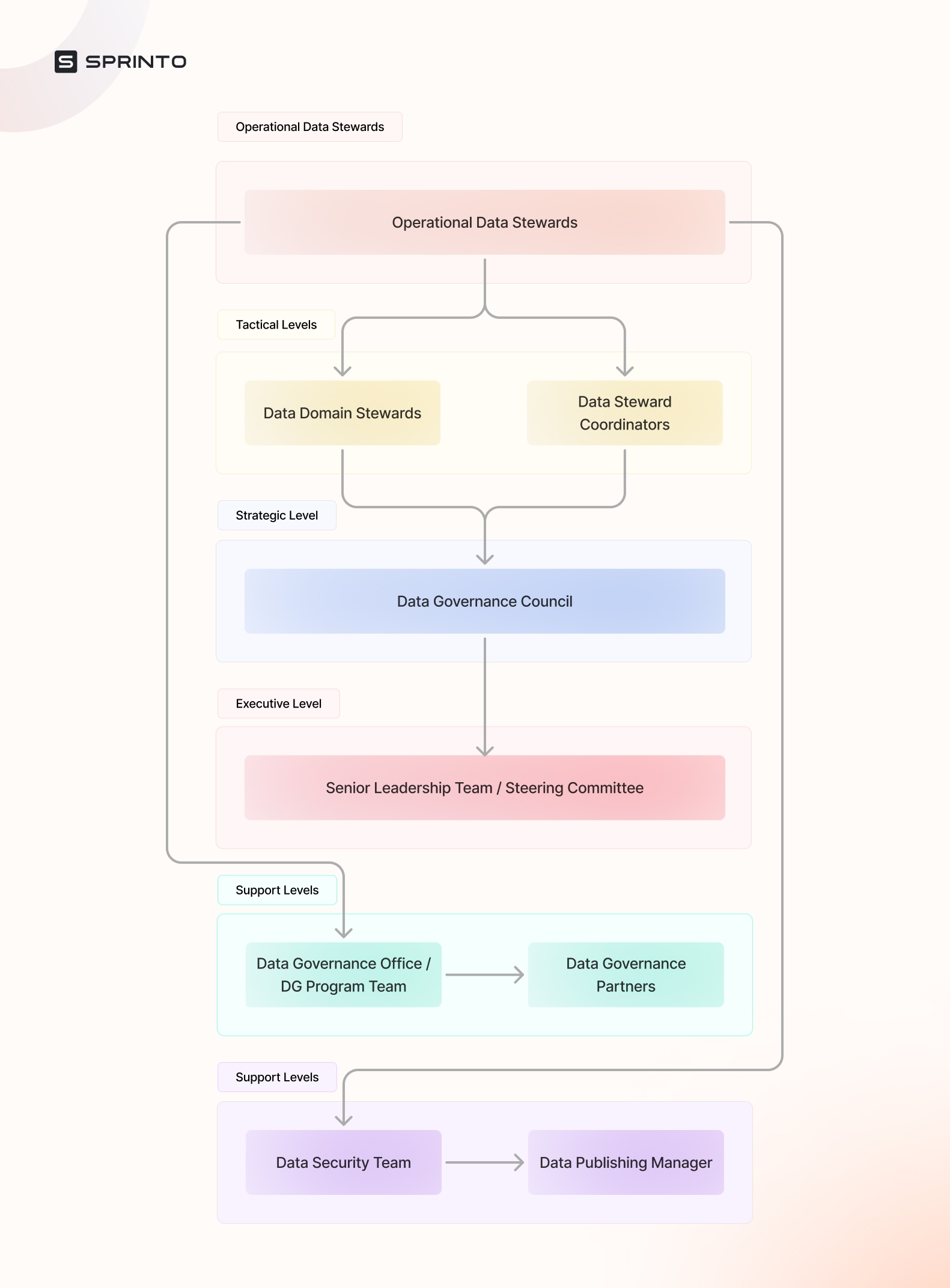
A data governance team comprises various roles, each important for creating a data-centric culture in your organization. Data governance responsibilities can differ between organizations, but the following is a general guide.
| Data Governance Role | Responsibilities |
| Support Levels | Data Governance Office / DG Program Team: Oversee enterprise data governance program developmentAdminister the program and architect solutionsFacilitate council meetings, provide agendasDevelop educational materials and ensure quality assuranceEstablish and review policies and define data quality metricsConduct audits |
| Data Governance Partners (IT) | Information Technology (Data SMEs and System SMEs): Ensure consistent data protection/classificationSecure IT infrastructureProtect sensitive dataIntegrate data governance in projectsModel and define strategic dataProvide technical support for data quality and governance |
| Operational Level | Operational Data Stewards: Define, produce, use, and manage organizational dataCreate and approve data definitionsMaintain data integrity and quality, classify data access levelsDocument regulatory/legal issuesSupport other stewardsCommunicate new requirements Address data concerns/issues. |
| Tactical Levels | Data Domain Stewards: Ensure data quality in domains, act across business unitsFacilitate issue resolutionEscalate issues, document and communicate rulesParticipate in tactical groups for specific issues/projects. Data Steward CoordinatorsDistribute rules and regulationsDocument and communicate issuesIdentify operational stewardsWork on tactical teamsManage data stewardship |
| Strategic Level | Data Governance Council: Educate on data governanceApprove policies and frameworksPromote data governance practicesMake strategic decisionsIdentify pivotal rolesAdvise on governance to risk management and compliance |
| Executive Level | Senior Leadership Team / Steering Committee: Sponsor and approve strategic plansCommunicate data governance expectationsIdentify and prioritize data quality initiatives |
| Others | Date Security Team:Responsible and accountable for data access security and data privacy policy enforcement. Data Publishing Manager:Responsible and accountable for quality assurance checking and publishing of newly created trusted. |
Now, these are the most common data governance lead roles and responsibilities, so let’s dive deeper.
1. Chief Data Officer (CDO)
A Chief Data Officer plays an important role in using data, arguably your organization’s most valuable asset. The CDO, a senior executive, is in charge of data utilization and governance across the entire organization.
The responsibilities of a CDO include the following:
- Governance: Advising on, monitoring, and governing enterprise data.
- Operations: Ensuring data is usable, available, and efficient.
- Innovation: Driving digital transformation, reducing costs, and generating revenue.
- Analytics: Supporting analytics and reporting on products, customers, operations, and markets.
2. Data Admin
Data administrators are the behind-the-scenes heroes of your data governance program. In executing their core data governance functions, they closely supervise its implementation and act as the first point of call for subject matter consultants regarding data issues.
Right-skilled and primarily technical, their job entails guaranteeing that your data systems operate optimally and comply with governance expectations.
Responsibilities of a Data Admin
- Overall, be responsible for project managing the entire process of data governance.
- Act as the referee grounds for handling all matters concerning data.
- Ascertain data systems’ smooth running and compliance with the governance standards.
- Supervise data conversions, assess data movement, and construct data architectures.
- Establish, embark on, and maintain data storage infrastructure which encompasses databases, warehouses)
- Include data analytics for decision-making and management of training and onboarding for the user group.
- Ensure the record of data’s credibility to ensure the reliability, relevance, and relevancy of data.
3. Data Steward
A data steward oversees the use and protection of an organization’s data while also translating technical issues between technology and business processes. They put into practice data governance solutions that help organizations to obtain and maintain proper data management.
Responsibilities of a Data Steward
- Address the user community data requirements
- Accumulate, assemble, and assess issues and problems by facts
- It is advisable to delegate stewardship duties in relation to the subject matter or line of business.
- Align stewardship roles along Key Data Entities (KDE) boundaries in cases of Master Data Management (MDM).
- It is also important to report prominent concerns to the respective people who may be affected.
- Standardize data definitions, rules, and descriptions to provide context to data assets.
- Ensure data quality and standards are assessed, controlled, and checked all over the business.
- Adopt best practices of data security governance to integrate with governance objectives, policies, norms, and regulations.
- Identify and classify data access levels, ensuring the right business users can access necessary data.
4. Data Custodian
A data custodian data modeler, or ETL developer, is responsible for maintaining the organization’s databases, making them available, and protecting them. Their responsibilities include:
Responsibilities of a Data custodian include:
- Authorizing and controlling access to data
- Determination of the data steward for each data type
- Maintaining the discursive processes so that data is sustained
- Collaboration with data stewards to handle data quality issues
- Implementing technical controls to safeguard data
- Verification of Data Consistency with the help of a common data model
- Maintaining backups of Master data, as well as documenting the process of updates.
- Considering the implementation of the change management process in the maintenance of the database
5. Data Governance Committee
The data governance committee is responsible for ensuring that the data needs, demands or concerns of organizations and its related activities are coherent across several life cycles. Typically, organizations have two data governance board responsibilities within this committee: The first is known as Strategic Data Management, while the second one is considered Tactical Data Management.
The Strategic Data Management board includes the roles of Chief Data Officer (CDO), Data Governance Council, and Senior Leadership Team / Steering Committee.
Tactical Data Management includes the Data Governance Office / DG Program Team rules, Data Governance Partners, Operational Data Stewards, and Data Domain Stewards: Ensure data quality across business units, facilitate issue resolution, and participate in tactical groups.
Responsibilities of a Data governance committee include:
- Addressing data governance policies, standards, processes, and other requirements
- Control and enforcement of data governance standards
- Providing a framework for effective communication and collaboration between the IT department and business units
- Supervising various kinds of data management policies or strategies that address approval processes
- Suggestions and recommendations on data quality activities
- Aligning data requirements, priorities, and issues across different entities
- Resolving disputes related to data governance
- Amending policies as needed
- Coordinating general and detailed issues related to data strategy
How Do You Assign Responsibilities to the Data Governance Team?
Assigning responsibilities to your data governance team is important to ensure everyone knows what they’re supposed to do. It helps keep things organized and ensures that data is managed well.
However, assigning responsibilities to a data governance team involves several key steps to ensure clarity and effectiveness:
1. Define Roles
Roles within data governance lay the groundwork for effective management of data assets and activities across an organization. Each role specifies responsibilities, ensuring clear accountability, consultation with stakeholders, and keeping all parties informed about pertinent data-related tasks.
In a small tech startup, roles in data governance might look like this:
- Data Steward: Responsible for maintaining data quality in customer databases and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
- Data Administrator: Manages database infrastructure, ensuring data accessibility and security for the development team.
- CDO: Oversees overall data strategy, aligning data initiatives with business goals to drive growth and innovation.
2. Identify Responsibilities
Next up is assigning responsibilities to these roles. Typically, the Chief Data Officer (CDO) takes the lead in overseeing data governance efforts. The CDO’s primary responsibility is to ensure that data policies support the organization’s strategic objectives.
This involves defining clear tasks and duties for each role to ensure they contribute effectively to achieving data governance goals.
3. Match Skills and Experience
The next step after identifying responsibilities is to match them with the right skills and experience. For example, someone skilled in data quality management would focus on ensuring data accuracy across the organization.
This way, each team member can handle tasks they’re best equipped to manage, and your data governance will proceed well.
4. Establish Accountability
This step clearly defines who is responsible for each specific task or area of data management. For example, the Chief Data Officer might be accountable for overall data strategy and compliance with data policies in a company’s data governance team.
Meanwhile, a Data Steward could be accountable for ensuring the quality and integrity of customer data used in marketing campaigns.
Can you see the clarity here? This ensures that every aspect of your data governance has a dedicated owner who can be held responsible for its success and outcomes.
A GRC tool like Sprinto helps you project manage governance more effectively by allowing you to see all governance tasks and understand their impacts. Sprinto enables you to assign clear owners for each task and follow up based on passing and failing checks. This ensures that all aspects of data governance are monitored and managed in the best possible manner.
Overall, with Sprinto you can maintain high data standards with less effort.
5. Provide Training
To ensure your data governance team understands their roles and responsibilities effectively, provide training and resources.
For example, a financial services company implements a program where the Chief Data Officer ensures data stewards receive data quality and compliance training. They attend workshops and gain certifications.
You need to offer ongoing support with updated guidelines, regular training sessions, and mentorship. This way, your data governance team can maintain high data standards.
Sprinto Advantage: Sprinto’s built-in security training modules and the ability to launch custom training campaigns as needed make achieving and maintaining compliance effortless and far less chaotic.
Save 80% of man hours spent on data governance
How Can Sprinto Help?
Creating a data-driven culture requires a robust data governance program to oversee data quality, security, and compliance. However, building such a program demands a skilled team with diverse roles and responsibilities. Even with capable team members, managing everything manually can be overwhelming.
That’s where Sprinto – the GRC automation platform comes in. It’s your solution to straighten out the processes and automate repetitive tasks, reducing the burden on your team. Sprinto monitors your system for policy violations, automates actions to address risks in the cloud, and provides alerts for non-compliance issues.
It’s a sophisticated and automated tool designed to lighten your workload.
Still hard to believe? See How HackerRank streamlined security due diligence and regained 20% of engineering time.
Sprinto manages policies and leaves no stone unturned. It accurately identifies and mitigates risks and triggers alerts for compliance deviations. Moreover, it offers a training module to educate employees on data governance, which is one of the most important parts of governance in general—all without manual intervention.
If you’re looking to implement top-tier data access governance for your data ecosystem while promoting data democratization, consider giving Sprinto a try.
FAQs
How does data governance enhance organizational decision-making?
Data governance frameworks play an important role in improving organizational decision-making. They ensure that the data used in decision-making processes is accurate, reliable, and secure.
What challenges do organizations face in implementing data governance?
Implementing a data governance framework comes with its share of challenges. Organizations often struggle with establishing clear policies, creating collaboration across departments, and effectively managing ongoing data governance practices.
How does data governance relate to regulatory compliance?
Data governance is closely tied to regulatory compliance. It involves creating and implementing policies and procedures that ensure an organization’s data handling practices comply with legal standards and regulations.


Use Sprinto to centralize security compliance management – so nothing
gets in the way of your moving up and winning big.


























