
Every 39 seconds, the U.S. faces a cybersecurity attack, impacting one in three Americans and countless companies each year. As a CISO, neglecting security can place you in that unfortunate statistic.
The Secure Controls Framework (SCF) is your solution.
This solution should be your go-to because it is created to empower companies in guiding the creation, implementation, and management of cybersecurity and privacy principles, which we will discuss in detail below. It goes beyond mere compliance.
Now, what’s in it for you in this article? We’ll explore the Secure Controls Framework (SCF), its meaning, and its importance. By the end of this article, you’ll have the knowledge plus a control bundle that you need to safeguard your digital assets from harm’s way.
What is a Secure Controls Framework (SCF)?
The Secure Controls Framework (SCF) serves as a catalog of controls with the primary aim of facilitating the development, construction, and upkeep of secure processes, systems, and applications within companies.
Security control framework mapping achieves this by baking in cybersecurity and privacy considerations at every level, whether strategic, operational, or tactical.
Be mindful that the essence of the SCF lies in its role as a meta framework or a “framework of frameworks.” It is designed in such a way as to provide a holistic approach to address the fundamental elements of controls, which revolve around People, Processes, Technology, and Data, which is also called PPTD.
For example, let’s say you are a healthcare organization handling sensitive data of cancer patients for research purposes.
So, when you use SCF across different levels, this is how it looks like:
- Strategically, you need to identify the need to safeguard patient data (Data)
- Establish access controls (Processes)
- Train staff on cybersecurity (People)
- Invest in encryption (Technology)
This is how security control framework mapping can assist you in strategic planning and help you chart your overarching security and privacy goals while offering practical, tactical guidance.
What is the purpose of the Secure Controls Framework?
The fundamental purpose of SCF is to get a repository of controls designed to support companies in creating, maintaining, and perpetuating secure procedures, systems, and applications.
Remember here that the SCF is not just a short-term solution; it’s a long-term tool you will need to keep security, privacy, and compliance. This framework drills down the demands of cybersecurity and privacy into practical, organization-specific expectations, including:

- Legal obligations
- Regulatory requirements
- Contractual commitments
- Industry best practices
Get A Real Time View Of Security Controls
3 Types of Secure Controls
Security controls play a role in implementing the secure controls framework mapping, designed to actively prevent, detect, counteract, or reduce security risks to a range of assets, including physical property, information, computer systems, and more.
The three types of secure controls are:
Preventive Controls
Preventive controls reduce the likelihood of errors and fraud before they occur, with a primary focus on separating duties.
These safeguards actively thwart security incidents by preventing unauthorized access, for example, through mechanisms like lockouts.
Detective Controls
Detective controls actively have the purpose of identifying errors or issues after the transaction has taken place. They hold significance because they furnish evidence of the effective operation of preventive controls and offer a post-transaction opportunity to uncover irregularities.
These controls actively work during a security incident to identify and characterize the ongoing event. For example, they may actively trigger alarms, alert security personnel, or notify the authorities.
Corrective Controls
Corrective controls actively aim to rectify errors or irregularities that have been identified. In contrast, preventive controls are actively designed to prevent errors and irregularities from occurring initially. These controls can take on various forms, whether automated, manual, or a combination of both.
After a security incident, these corrective controls limit the extent of damage and efficiently restore the organization to normal working conditions.
List of SCF Domains
SCF domains serve different purposes. In the table we’ve created below, we have listed the different types with explanations. Please do have a look.
| SCF Domains | Cybersecurity Principles |
| Cybersecurity & Data Privacy Governance | Implement a documented, risk-based program that aligns with business goals. This program should incorporate cybersecurity and data privacy principles and address relevant statutory, regulatory, and contractual obligations. |
| Asset Management | Manage all technology assets, both physical and virtual, from purchase to disposition, ensuring their secure use, regardless of their location. |
| Business Continuity & Disaster Recovery | Maintain the capability to sustain critical business functions and effectively respond to incidents through well-documented and exercised processes. |
| Artificial and Autonomous Technology | Ensure trustworthy and resilient Artificial Intelligence (AI) and autonomous technologies, which inform, advise, or simplify tasks while minimizing unintended consequences. |
| Change Management | Manage change sustainably with active participation from technology and business stakeholders to ensure only authorized changes occur. |
| Capacity & Performance Planning | Govern technology assets’ current and future capacities and performance. |
| Continuous Monitoring | Maintain situational awareness by centrally collecting and analyzing event logs from systems, applications, and services. |
| Cryptographic Protections | Utilize cryptographic solutions and key management practices to protect sensitive data at rest and in transit. |
| Configuration Management | Enforce secure configurations for systems, applications, and services based on industry-recognized practices. |
| Compliance | Oversee the execution of cybersecurity and data privacy controls to ensure evidence of due care and due diligence for compliance with statutory, regulatory, and contractual obligations. |
| Cloud Security | Govern cloud instances with security protections equal to or greater than those of internal cybersecurity controls. |
| Endpoint Security | Harden endpoint devices to protect data against threats. |
| Embedded Technology | Scrutinize embedded technology to reduce risks associated with malicious use. |
| Data Classification & Handling | Enforce standardized data classification to determine data sensitivity and handling requirements. |
| Human Resources Security | Cultivate a cybersecurity and privacy-minded workforce through sound hiring practices and ongoing personnel management. |
| Information Assurance | Validate the existence and functionality of cybersecurity and privacy controls before production use. |
| Identification & Authentication | Enforce “least privilege” consistently across systems, applications, and services. |
| Incident Response | Maintain a viable incident response capability, training personnel to recognize and report suspicious activities. |
| Mobile Device Management | Implement measures to restrict mobile device connectivity with critical infrastructure and sensitive data. |
| Network Security | Architect and implement a secure and resilient defense-in-depth methodology. |
| Maintenance | Maintain tech assets |
| Physical & Environmental Security | Protect physical environments through physical security and environmental controls. |
| Data Privacy | Align your data privacy practices with recognized principles |
| Secure Engineering & Architecture | Use secure engineering and architecture principles |
| Project & Resource Management | Achieve your cybersecurity and privacy objectives as key stakeholders within project management practices. |
| Security Awareness & Training | Create a cybersecurity and privacy-minded workforce through awareness |
| Third-Party Management | Implement Supply Chain Risk Management (SCRM) practices to use trustworthy third parties. |
| Vulnerability & Patch Management | Strengthen system, application, and service security and resilience against evolving threats using industry-recognized practices. |
| Web Security | Ensure the security and resilience of Internet-facing technologies through secure configuration and monitoring for anomalous activity. |
| Threat Management | Identify and assess technology-related threats to determine risk and necessary corrective action. |
| Technology Development & Acquisition | Develop systems, applications, and services using a Secure Software Development Framework (SSDF). |
| Security Operations | Deliver cybersecurity and privacy operations to provide secure systems and services meeting business needs. |
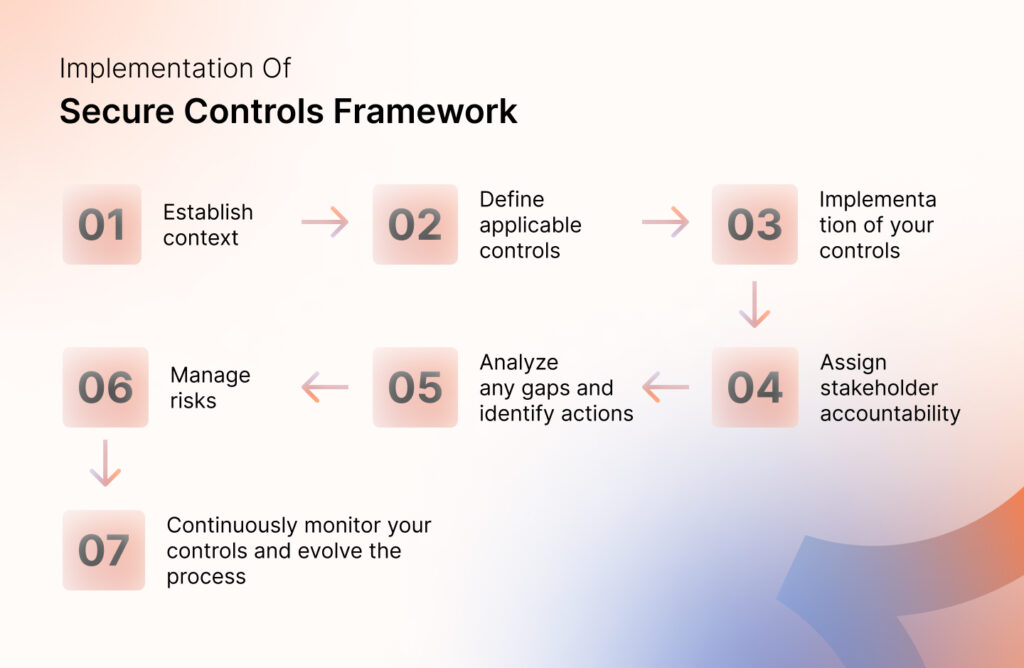
How to Implement Secure Controls Framework?
Implementing the SCF framework is not straightforward. But with a bit of research and your security team’s help, you can implement it in no time. That being said,
Here are the steps for implementing secure controls framework mapping:
Establish context
The first thing you need to do before starting the implementation of a secure control framework is set goals and context regarding the objectives of your data security.
- What level of risk are you comfortable with?
- Which areas of your asset need the most safekeeping?
These kinds of questions will not come up when you create a scope of your security control efforts.
Define applicable controls
You must carefully consider various factors to define the right controls for your information systems. Here, controls refer to various measures or actions, including policies, procedures, technologies, and training.
For example, if vulnerability management is a critical control and HRMS for people management is also a critical control.
List all the controls and choose the ones that match your risk level, align with your business needs, and fit your budget.
You can refer to established standards and guidelines like ISO 27001, NIST SP 800-53, or CIS Controls to assist in this selection process.
Implementation of your controls
This phase involves putting your carefully planned controls into action. Here’s what you need to do:
- Ensure Proper Installation and Configuration: Your controls should be configurable to work effectively.
- Testing: Test your controls to verify that they perform as intended.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation for your controls, including how they work and any configurations made.
- Roles and responsibilities: Assign roles for the management and upkeep of your controls.
- Communication and training: It’s crucial to communicate with and train your staff and stakeholders to use and adhere to your controls.
- Monitor and measure: Continuously assess and measure the performance and effectiveness of your controls to ensure they meet your security objectives.
Here’s how we can help
We (Sprinto) are a compliance automation platform that automates 90% of your compliance efforts. This will give you ample time to focus on achieving your core business objectives. Here’s how we help:
- First, you can easily set up the controls on all your cloud apps with the help of 100+ integrations Sprinto supports
- Sprinto’s intuitive, all-in-one dashboard will help you see if your controls are running as they should be
- If there is any anomaly (like an employee missing a security training), Sprinto will immediately send alerts to the admin, who can then address the issue
- Sprinto helps you continually monitor and measure all your controls 24*7 with more than a million checks a month running in the background
Assign stakeholder accountability
We mentioned this briefly in the implementation of the controls step above, but we will double-click on it here, too.
One person managing many controls at a time will cause chaos, and you don’t want that piling up. For this reason, it is smart to assign stakeholder responsibility to different people for different controls.
For example, assign a person for access management and assign change management to someone else in the security team.
This way, the responsible stakeholder will immediately address any issue that arises.
Analyze any gaps and identify actions
A critical part of the process involves conducting a security gap analysis. This helps organizations identify weaknesses in their network security controls to ensure a robust and effective network.
When you compare your current practices to industry best practices, this analysis reveals where improvements are needed and how your organization can implement the right structure and controls.
After identifying these gaps with SCF maps, take prompt action to address them. This might involve implementing new controls, revising procedures, or enhancing existing security measures to close the vulnerabilities and fortify your network.
Manage risks
The next step is to examine risks and their potential impacts on your company. So, don’t forget to create an effective plan to manage risks that you may encounter in the future.
Sprinto assists in risk management so effectively. Drawing from various sources helps you identify and prioritize the most relevant risks. It reduces the need for manual control oversight by automating the detection of weaknesses in your security controls.
With Sprinto, you don’t need to rely solely on patchwork solutions since you are continually minimizing your dependencies on manual processes.
The deeper an organization understands these risks, the better equipped it is to implement proactive measures.
Continuously monitor your controls and evolve the process
After implementing your controls, the next step should be about facilitating ongoing monitoring. Risks are constantly changing, and so should your approach to security.
With continuous monitoring, you are constantly aware of the minute changes in the threat landscape and have the intel required to tweak your security posture to offer the best defense against a breach attempt.
How Sprinto facilitates continuous monitoring:
Sprinto simplifies the task of continuous monitoring by handling all compliance-related responsibilities. It monitors your controls, promptly notifying you of any omissions or irregularities.
Also, it provides real-time tracking of your controls and offers a comprehensive overview of your compliance and security status. This real-time data empowers you to make well-informed decisions to enhance security posture.
Which frameworks can be integrated into the Secure Controls Framework?
The SCF maps can easily be integrated into your broader security framework because it align with guidelines like NIST CSF and ISO/IEC 27001:2013.
You can integrate it with frameworks like:
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX)
- Generally Accepted Privacy Principles (GAPP)
- UK – Data Protection Act (DPA)
- European Union General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR)
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
- Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA)
- Service Organization Control (SOC)
And many more based on your requirements..
Benefits of Implementing Secure Controls Framework
The key benefits of implementing the secure controls framework help you adopt a detailed approach to safeguarding the Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability, and Safety (CIAS) of your data, systems, applications, and processes. The main thing to note here is that it simplifies everything by breaking them into clear expectations.
Here are some of the benefits:
Simplified compliance
A comprehensive analysis of over 100 statutory, regulatory, and contractual frameworks was conducted when implementing the SCF.
This extensive review uncovered commonalities, enabling the SCF to address several thousand unique controls.
For example, the necessity of maintaining strong passwords is a shared requirement across many laws and regulations.
The SCF streamlines this complexity with well-crafted controls, emphasizing simplicity and sustainability.
Breaks down silos
The design of the SCF has been drawn up so that it can impede efficiency and lead to subpar security due to communication gaps and incorrect assumptions. The SCF also provides valuable guidance on tools and solutions to address controls.
Also, it incorporates maturity criteria to assist companies in planning for and evaluating controls based on a target maturity level.
Tailored to your needs
The SCF may be perceived as overly complex if your company has 1-2 compliance requirements.
However, for companies with 3 or more compliance obligations, including ISO 27002, SOC 2, PCI DSS, and GDPR, the SCF becomes a powerful tool to streamline the management of cybersecurity and privacy controls.
Automate Security Controls by Sprinto
What’s Next?
Now that you know that the SCF is a premium catalog of all controls, you may think implementing it will solve all the problems. Instead of implementing the controls individually, understanding the SCF framework gives a one-pass way to get them in a bundle. However, it is not a solution that works alone.
The SCF is not:
- Not a substitute for due diligence
- Not a complete solution
- Not infallible
Overall, the main purpose of implementing controls is to prevent, detect, and respond to security incidents or breaches in real-time. This minimizes potential damages and safeguards the security of your system. Manually doing this is a huge pain, so you need a compliance automation platform like Sprinto.
Do note that Sprinto’s continuous monitoring feature can show the status of assets and security controls in real-time. Also, the automated responses can address low-level issues instantly, reserving human intervention for more severe problems.
To know more about the SCF, connect with our compliance experts, who will point you in the right direction.
FAQs
What is an example of a security control framework?
Security control frameworks are like organized plans that help protect a company’s data. They include rules and best practices to guard against cyber threats and risks.
How does SCF relate to other frameworks?
The SCF acts as a ‘Rosetta Stone’ for cybersecurity controls, translating and connecting controls from different best practice frameworks and various legal or contractual requirements.
What is the SCF standard of security?
The SCF centers its attention on internal controls as a main thing. These controls include cybersecurity and privacy-related policies, standards, procedures, and processes. Their primary aim is to offer reasonable assurance that business objectives will be met and that any unwanted events will be either thwarted, identified, or rectified.
Meeba Gracy
Meeba, an ISC2-certified cybersecurity specialist, passionately decodes and delivers impactful content on compliance and complex digital security matters. Adept at transforming intricate concepts into accessible insights, she’s committed to enlightening readers. Off the clock, she can be found with her nose in the latest thriller novel or exploring new haunts in the city.
Explore more
research & insights curated to help you earn a seat at the table.
















