
Willie Sutton, the infamous twentieth-century U.S. criminal, was allegedly known to rob banks because “that’s where the money is.” In this digital age, organizations are exposed to financial fraud due to their lax security- leaving sensitive consumer data stolen and misused.
To protect against this, PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) was set up by the PCI Security Standards Council (PCI SSC). A PCI DSS audit ensures that businesses comply with the standard and are well-equipped to safeguard cardholder data.
In this article, we will discuss how you can better prepare for an upcoming PCI DSS audit.
What is a PCI Audit?
A PCI audit assesses an organization’s compliance with the 12 requirements of the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and its security measures to ensure the safe and secure handling of credit card information throughout its lifecycle.
This comprehensive evaluation:
- Highlights areas of non-compliance
- Offers recommendations for improvement
- Presents evidence of compliance
The audit thoroughly tests essential elements such as:
- Application processing capabilities
- Storage encryption practices
- Router security
This process ensures secure credit card transactions and safeguards sensitive authentication data (e.g., PAN, CVV) throughout the entire payment processing cycle.
How does PCI DSS Audit Work?
Once the organization is ready to get it’s PCI DSS itscontrols reviewed, it must select a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) for the audit. You can find QSA’s qualified by the PCI Security Standards Council on the website.
The Qualified Security Assessors (QSA) look at the PCI scope to understand the systems and processes in scope. The assessor then verifies and maps your systems and security practices against the PCI Compliance requirements.
These professionals analyze various parts of your business’s environment and provide an in-depth risk assessment, enabling you to determine how you stack up on sensitive cardholder data management standards. They offer guidance on the gaps identified and provide a detailed report on findings along with recommendations for improvement.
The QSA issues an Attestation of Compliance (AoC) after validating that the remediation measures have been implemented.
How to prepare yourself for the PCI DSS audit?
The PCI DSS requirements are extensive, but many of them can be addressed through common security measures. For example, implementing strong access control measures and limiting access to cardholder data will help reduce the risk of a data breach.
So, as a next step, we’ve listed down the measures you can take on how to perform PCI DSS audit internally before the official one begins
Here are the 7 key steps to prepare for the PCI DSS audit:
- Conduct gap analysis and remediation
- Document all the activities
- Monitor the security controls
- Track and monitor all access to network resources
- Maintain accurate network diagrams
- Risk Assessment
- Examine your internal infrastructure
- Consult with a third-party auditor
Conduct gap analysis and remediation
If you already have an information security program in place make sure it adheres to the latest PCI DSS 4.0 version. Conduct a gap assessment to identify areas where you fall short and the threats to the cardholder environment because of these compliance gaps.
Based on the findings, create a tactical remediation strategy to minimize each threat. Arrange for security awareness training for your workforce and build a pipeline of controls such as firewalls, anti-virus software, encryption etc. for air-tight security.
This is the preparation stage. Once you are done with this start gathering everything needed for the audit process.
Document all the activities
Ensuring security of customer data is paramount and comprehensive documentation is essential to securing card data. You must document all encryption protocols, key management processes, analytics, and procedures for storing information – records show your auditors that you meet various compliance requirements and document your findings every step of the way.
Any changes to your business policies or card data environment need to be documented, as they could affect your PCI compliance status.
Monitor the security controls
An effective continuous monitoring strategy starts with the development of processes for performing periodic reviews of all security controls relevant to the organization.
- Keep your goals in line with the organization’s business and security objectives
- Make sure to cover all relevant places, such as stores, data centers, and back-office locations
- Make sure that you establish and follow PCI DSS requirements
- Make sure staff members continue to follow the correct security protocols
- Anytime changes to the organization, operating environment, or technologies are being used, you will need to provide concrete evidence that security requirements are still being met
Regular evaluations of the implemented security controls should be conducted to measure performance and ensure maximum protection. This strategy allows organizations to document implementation, view the impact, and assess status to guarantee appropriate daily safeguarding from potential threats.
Track and monitor all access to network resources
Logging mechanisms are crucial tools for forensics and vulnerability management. Audit trails can be used to trace any activity on the system back to its user, ensuring that malicious actors can be identified if something goes wrong.
System logs give invaluable access to system activity and are essential for determining the cause of a security breach. With effective logging, it would be much easier for administrators to accurately track user activities and prevent subsequent attacks from taking place. Logs thus play a vital role in both forensic investigations and cybersecurity defenses.
Maintain accurate network diagrams
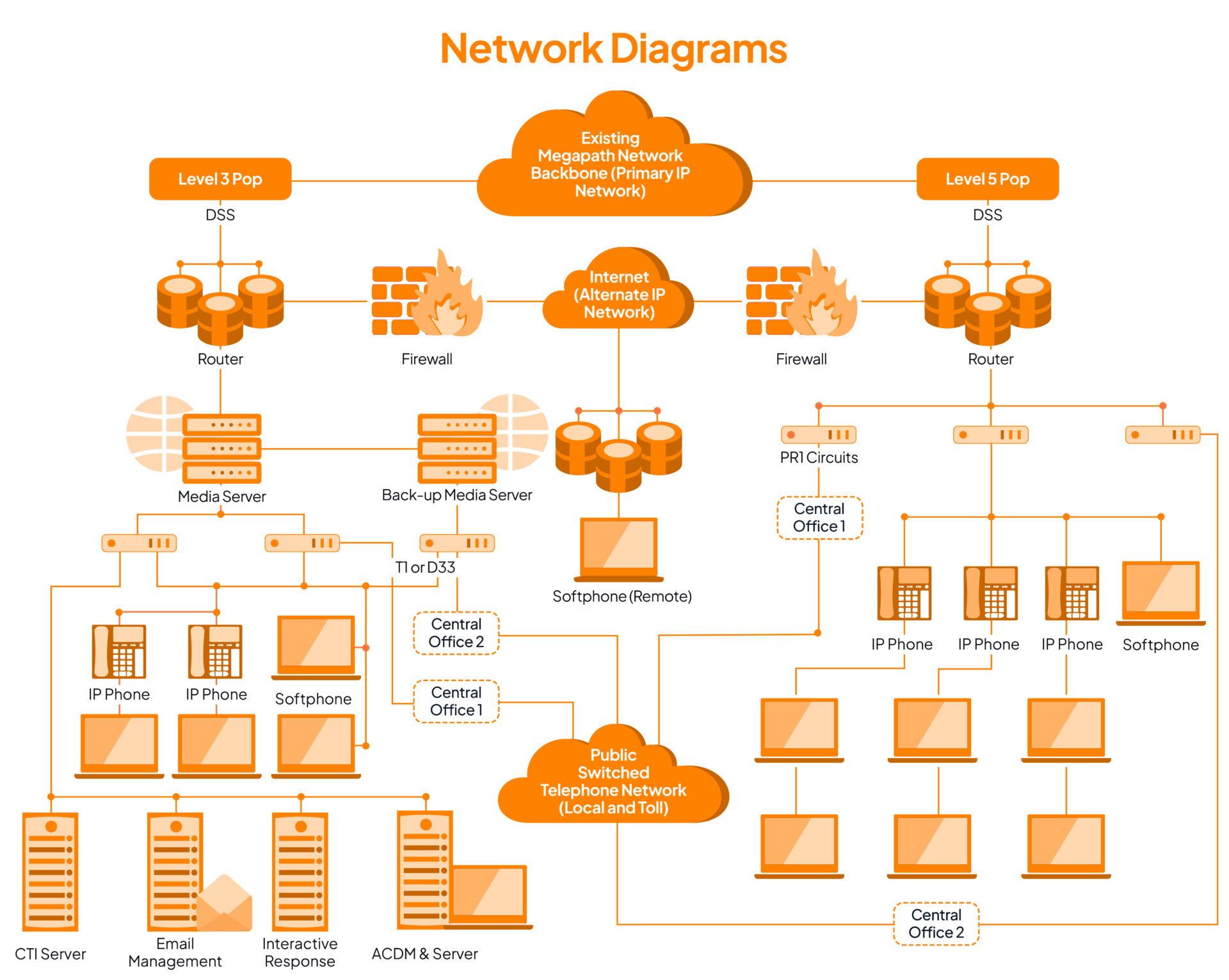
Network architecture diagrams refer to the documentation that identifies the flow of data within an organization. In simple terms, it pertains to data flow across telecommunication hardware.
When it comes to PCI compliance, maintaining accurate network diagrams is an essential step for any merchant that handles card data. Without these diagrams, it can be difficult to safeguard systems, as it is unclear how individual systems interact and which are used for storing, processing, or transmitting card data.
Unfortunately, many companies employ a flat network model with just an edge firewall in place. This makes it difficult to meet the requirements of PCI DSS certification rules as everything inside the network is considered in assessment scope—which highlights the importance of having up-to-date and correct diagrams.
For example, mapping out the steps taken for transmission of cardholder data is a great way to ensure that data flows quickly and securely. You should map out each card flow your network has – many companies have multiple systems that their payment cards can pass through (so make sure they’re all accounted for!).
Creating accurate diagrams of your data movement not only enables efficient processing but also helps protect the trustworthiness of your systems. Examining your network is an important step in constructing a secure card-processing environment and to maintain PCI DSS compliance. Ask yourself these questions:
- How is my network constructed?
- Is there one firewall at the edge for defense?
- Is there segmentation between networks to secure them from each other?
- Is a multi-interface firewall enabled?
- And are there multiple firewalls available?
Answering these questions gives perspective on how prepared your network is and if adjustments are needed. For example, if you find that only one firewall exists at the edge, then a second should be added or existing hardware upgraded. Knowing your network architecture lets you ensure everything is in order and well-defended against potential vulnerabilities.
Risk Assessment
Requirement 12.2 of the PCI DSS entails that every company yearly assesses security risks inherent to their organization, particularly their cardholder data environment (CDA). This stipulation helps businesses identify and prevent potential information safety hazards.
This provides an opportunity for you to analyze the security of your CDE and identify any potential security vulnerabilities. For example, these actions include patching systems upfront or revising user access controls over critical assets.
By reducing the window of compromise – the time available to attackers before they can harm the system – it is possible to maximize prevention against serious security incidents. Thus, risk assessments should be regularly conducted in order to prioritize vulnerabilities and stay one step ahead of malicious actors.
While some vulnerabilities may appear harmless at first, remember that not all are what they seem. For example, a seemingly minor misconfiguration could be so complexly interconnected to other system components that an attack would require far too long and intricate preconditions to be met for it to be viable.
In these cases, assessing the vulnerability is not enough – you need to understand risk levels to make informed decisions on how best to protect your IT systems from malicious actors.
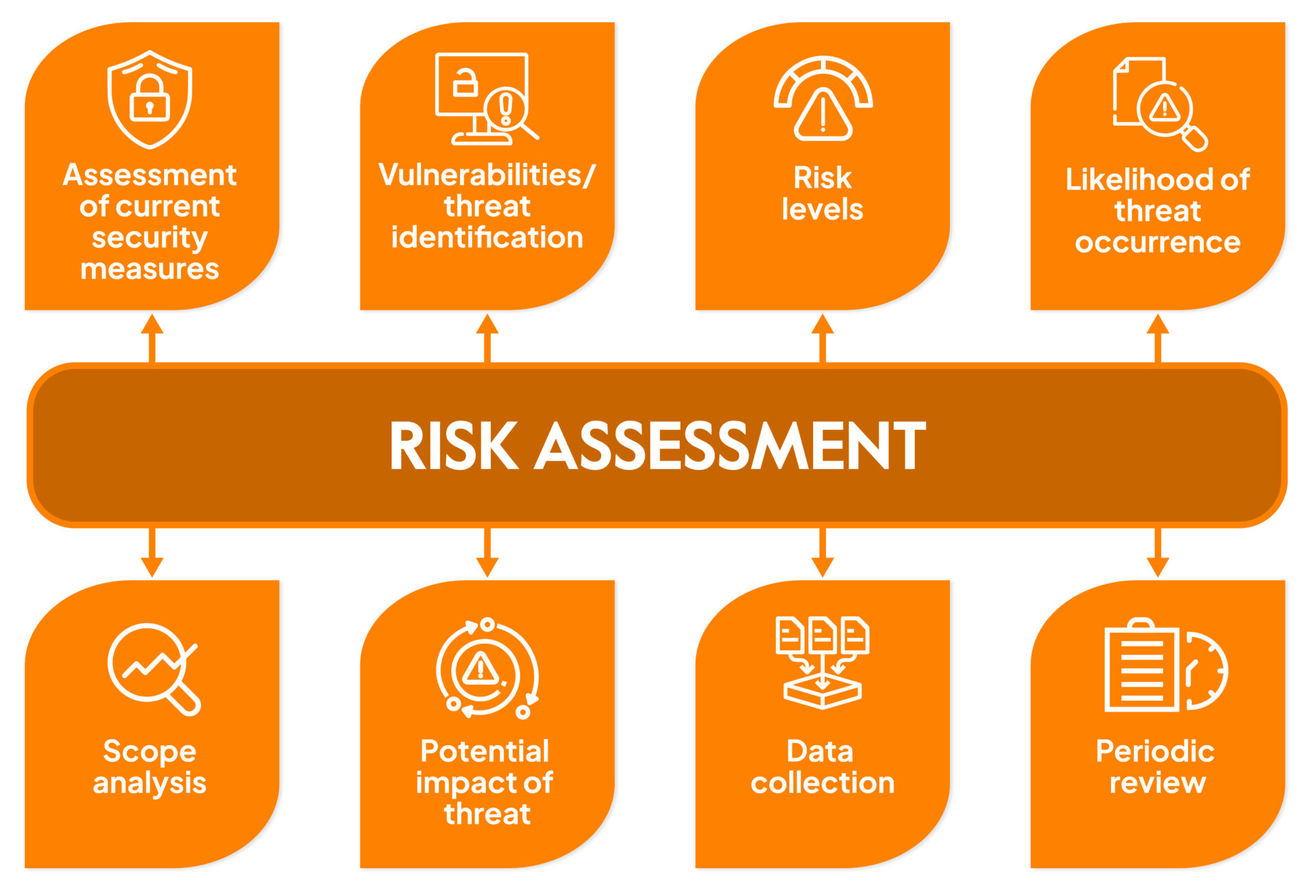
In your risk assessment, make sure to include the following information:
- Assessment of current security measures
- Threat identification
- Risk levels
- Likelihood of threat occurrence
- Scope analysis
- Potential impact of threat
- Data collection
- Periodic review
With that being said, beginning a risk assessment starts with scanning your environment for potential problems. You must ask yourself:
- What vulnerabilities exist that could leave your system or process exposed?
- What kind of external or internal threats exist in relation to those vulnerabilities, and how likely are they to take advantage?
Suppose an organization with sensitive information on paper has stored it in an unsecured file cabinet. In this case, there is a risk that confidential documents could be accessed without authorization.
The assessment requires you to consider these scenarios to ensure the security and integrity of your operations. The risk levels associated with each vulnerability and associated threat are vital – failure to consider the gravity of the issue could lead to irreversible consequences.
For example, vulnerabilities classified as being of ‘high’ risk should be addressed first, followed closely by those in which the risk level is deemed ‘medium.’ The act of an initial assessment and documenting this information can give you a detailed, prioritized list of your underlying security issues.
Examine your internal infrastructure
Examining an security infrastructure annually is crucial to maintaining PCI DSS controls and assessing security posture. However, it’s a task that cannot be done in isolation.
Instabilities can arise in the course of the year that can directly affect PCI DSS compliance – changes in the threat landscape, deploying new applications, personnel adjustments, and revised regulations are examples of potential events that could cause issues. To ensure your website’s success, perform the following tests and adopt the necessary measures to ensure the protection of cardholder data:
- Web application tests – To comply with PCI DSS Requirement 6.6, annual web application testing is required.
- Vulnerability scans – To adhere to PCI DSS Requirement 11.2, an authorized scanning provider should assess your external network systems quarterly.
- Local network vulnerability scans – You should perform quarterly local vulnerability scans to identify weaknesses in your system.
- Penetration tests – To stay up-to-date with PCI DSS Requirement 11.3, you must carry out an annual penetration test.
This emphasizes the importance of retaining PCI DSS compliance over the course of a year to ensure one’s internal infrastructure stays secure and compliant.
In the same way that brushing and flossing your teeth can help prevent a more painful trip to the dentist, monitoring and testing internal staff processes and systems year round can help preserve ongoing compliance without having to pay an expensive penalty during annual PCI DSS assessments.
Consult with a third-party auditor
Consulting with a third-party auditor is invaluable when preparing for a PCI DSS audit. They can offer expertise and clarification on expectations and processes and can help proactively identify potential issues before the actual audit.
Additionally, engaging a third-party auditor helps ensure that organizations remain compliant throughout their entire PCI environment, not just at the time of an audit. This kind of support allows you to have peace of mind knowing that you are meeting all standards regarding safely and securely protecting cardholder data.
The consultation of a third-party auditor is helpful as they will help you adhere to the PCI DSS standard. The auditor will:
- Firstly, they will verify all technical information given by the organization.
- Use their judgment when approving whether or not the supplied standard has been met.
- Guide the compliance process.
- Validate any scope of assessment and evaluate compensating controls as applicable before producing a final report.
Staying in contact with your QSA throughout the year can be valuable for any business, allowing them to get ahead of their upcoming audit. Throughout the year, businesses tend to expand, card data environments evolve, and PCI DSS regulations become updated- making staying informed on the current changes essential.
For this to work, establishing a relationship with your QSA will also serve as a way to plan for the audit in advance and gives you more time to address any potential issues that could pop up during this process.
But to make this more efficient, the Sprinto way is easier. Sprinto is a compliance software designed to help you get compliant with minimal error and zero-touch audits. With Sprinto, you can automate repeatable tasks, remove the scope for error, and continuously (24×7, real-time) monitor your compliance stance.
Also check out: Guide on PCI DSS compliance checklist
Continuously monitor to stay compliant
Although the PCI audit is a point-in-time assessment, maintaining the compliance requires ongoing efforts. The organization must continue with quarterly scans, ongoing monitoring of controls, training and awareness and policy updates to accommodate any changes. This ensures continuous compliance for the organization and makes it easier to pass the annual audit.
Tools like Sprinto help you with real-time monitoring of controls to contain any compliance drift on time and ensure that you stay ever-vigilant.
How much will it cost to get PCI DSS audited?
The PCI DSS costs for audits can vary drastically. Take, for example, a prominent business processing countless payments each year – they may have to shell out anywhere from $50-200k for their Report on Compliance (RoC). But small enterprises need not fret as much – an Attestation of Compliance or Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) will cost them no more than $20k annually.
Want to understand how much will PCI DSS compliance cost for your business? Try Sprinto’s cost calculator
You can download the SAQ eligibility checklist below:
Download Your PCI DSS SAQ Eligibility Checklist
Who must go through a PCI DSS audit?
PCI DSS audits are a necessary evil for many service providers and merchants across the globe. All companies with access to debit card or credit card information must comply with PCI DSS regulations, which usually involve implementing an information security system following 281 directives and 12 core requirements.
For example, a company that processes payments over the internet must go through such an audit to remain compliant with PCI DSS. In this way, companies – and their customers – remain protected from potential threats related to the mismanagement of important financial details.
Find out how Sprinto can help you prepare for PCI DSS audit
Understanding the complexities and implementing practices for PCI DSS can be time-consuming. Luckily, it doesn’t have to be. With Sprinto, you can access automated compliance solutions that remove the manual effort from the equation.
Our centralized dashboard helps streamline tasks associated with PCI DSS:
- It helps you with the scoping exercise to define people processes and technology falling under the audit scope
- Sprinto helps you identify gaps in security parameters and apply technical and tactical measures to enable secure payment processing
- Sprinto helps you continuously monitor controls and enable quarterly vulnerability scans and penetration testing through its vetted VAPT partner network
- Sprinto also helps you fill out the Self-assessment Questionnaire and connect with an auditor for testing of controls
You get in-built policy templates, training modules, automated evidence collection, role-based access controls and more to expand the scope of the information security framework.
Talk to us now and fast-track your PCI DSS journey.
FAQs
What are PCI DSS audit requirements?
PCI DSS audit requirements include implementing all applicable controls and safeguards, documenting all processes and policies, working with an auditor, and continuously improving to stay compliant post audit.
Do you need to go through PCI audits?
PCI auditing is a necessity for those who run businesses that process a high volume of payment card transactions. Even if your organization processes one transaction annually, you must be PCI compliant.
Who performs PCI DSS audit?
A qualified security assessor conducts a PCI compliance audit. This professional evaluates point-of-sale systems and other components of a business IT architecture to determine whether internal operations meet cardholder information security standards.
What is the penalty for any data breach found during the audit?
A data breach can be a huge financial and reputational cost to your business, so it is important to determine the corresponding penalties if any such breach is found during an audit. For example, suppose compromised cardholder data is identified during an audit.
In that case, the payment processors and banks involved may issue fines ranging from $50 to $90 per cardholder whose data was accessed in the breach. In addition, those entities may terminate their relationship with your business if a data breach occurs.
How often are PCI DSS audits required?
Level 1 businesses must complete a PCI validation form annually and undergo an annual audit conducted by a qualified auditor. This requirement is mandated by the PCI DSS and applies regardless of how card data is accepted – in-person, online, or mobile.
Meeba Gracy
Meeba, an ISC2-certified cybersecurity specialist, passionately decodes and delivers impactful content on compliance and complex digital security matters. Adept at transforming intricate concepts into accessible insights, she’s committed to enlightening readers. Off the clock, she can be found with her nose in the latest thriller novel or exploring new haunts in the city.
Explore more
research & insights curated to help you earn a seat at the table.





















