TL;DR
- GDPR uses a stricter opt-in model and applies to anyone processing EU data, while CCPA applies only to California residents and focuses on opt-out rights for data sharing and selling.
- GDPR has broader data definitions and higher penalties, whereas CCPA is narrower in scope with lighter fines.
Understanding how CCPA and GDPR differ is essential for any business handling personal data across geographies. While both laws are designed to protect consumer privacy, they vary in scope, enforcement, definitions, and compliance expectations. These differences often lead to confusion—especially for companies operating globally or managing data from both California residents and EU citizens.
This guide compares the CCPA and GDPR standards side-by-side, explains what each law requires, and helps you understand how to stay compliant with both.
Sprinto centralizes GDPR + CCPA seamlessly.
👉 Book a demo →
CCPA and GDPR – Introduction
Before diving into the differences between CCPA and GDPR, let’s first understand what each of these privacy frameworks entails and to whom they apply.
What is CCPA
The CCPA is a California state data privacy law that gives California residents specific rights over their personal information — including the right to know, access, delete, and opt out of its sale. It applies to any business that collects or processes the data of California residents, regardless of where the business is located.
The CCPA imposes rules on businesses the “covered entities” that handle sensitive information. It also grants consumers new privacy rights and protections. The CCPA enhances consumer privacy rights in several ways:
- CCPA Requires greater transparency.
- CCPA gives consumers broad access to their personal information.
- CCPA provides consumers with the right to opt-out of data collection.
- CCPA imposes new restrictions on how covered entities collect, share, and sell consumers’ personal information.
Verify if CCPA applies to your business with this CCPA compliance guide
Both CCPA and GDPR focus on obtaining GDPR cookie consent from users. But the way they do it is significantly different.
CCPA was rolled out in July 2020, and on August 14, 2020, the CCPA regulations were in effect.
CCPA extends their data users the right to request businesses to delete their personal information or opt out from selling their personal information to third parties.
What is GDPR
The GDPR is a European Union data protection law that regulates how organizations collect, process, and store the personal data of individuals in the EU and EEA. It emphasizes consent, transparency, and accountability to protect individual privacy rights.
The GDPR became effective in May 2018 across the 27 member states of the European Union.
GDPR dictates how businesses, through their website and mobile applications, should handle customer information. Attributes like name, email ID, location, data from wearables, IP address, and more are categorized as personal information under GDPR.

Under GDPR, the Data Subject (user) is given controlling power to decide how businesses use their personal information. As a business, you are responsible for collecting user consent before collecting any personal information of a Data Subject.
Here’s an example of a general GDPR consent form.

CCPA vs GDPR: 5 key differences
Here’s a quick side-by-side look at how CCPA and GDPR differ across the key areas.
| Aspect | GDPR | CCPA |
| Who they cover | Applies to anyone processing data of people in the EU, regardless of where the business is located | Applies to California residents and businesses meeting revenue, data volume, or data-sale thresholds. |
| Type of data protected | Covers all personal data and requires opt-in consent. | Protects the personal information of CA residents and uses opt-out consent. |
| Data collection & processing | Any action performed on personal data (collecting, storing, sharing, deleting, profiling). | Focuses on three actions: collecting data, using it for business purposes, and selling or sharing it with another entity. |
| Information given to users | Users must be told how their data is used, stored, shared, and for how long. Strong rights like deletion and withdrawal. | Users get a summary of how their data was collected, used, and sold in the last 12 months. Must be notified when data is sold. |
| Penalties | High global fines | Lower fixed fines |
Let’s now talk about the key differences between CCPA and GDPR in detail:
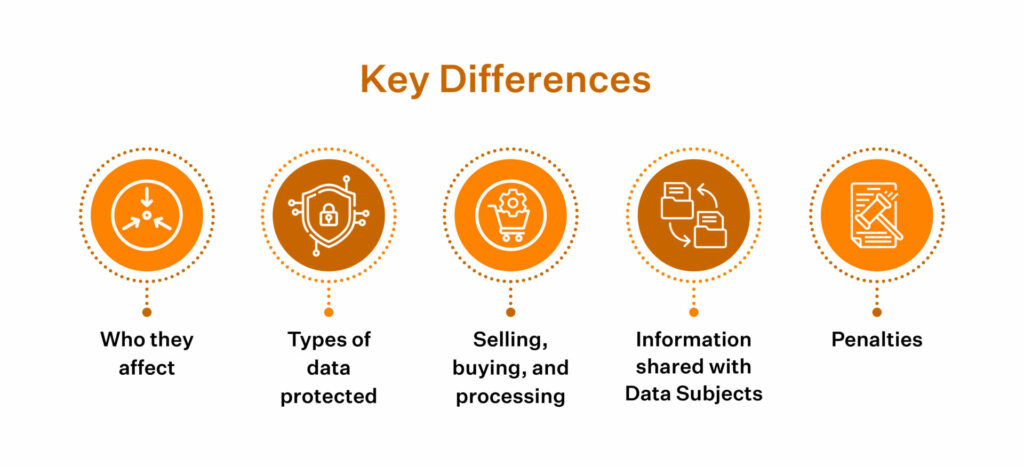
1. Who They Affect:
GDPR
All businesses and their entities (website and mobile application) that personally process data of people in the European Union(EU) must comply with the GDPR law. This includes non-profit businesses and e-commerce companies.
GDPR compliance also applies to every Data Subject (user) in the EU regardless of their citizenship, residence nature, and more.
CCPA
CCPA is only applicable to legal residents of the California region.
CCPA only applies to businesses that meet at least one of the three listed criteria:
- Businesses whose gross annual revenue is greater than $25 million
- Collects, buy, or share data of more than 50,000 users
- Half (50%) of the revenue is generated from selling said user data
While these are the conditional qualifiers, for businesses to fall under the scope of CCPA regulation, they must also qualify for two additional criteria.
- They operate in the California Region
- They collect data from users in California and have stated the purpose and means for their data processing operations.
2. Types of data protected
GDPR is stricter when compared to the CCPA, and this reflects in what they consider protected data and its exemptions.
GDPR covers all kinds of data processing regardless of the intent and process of processing. The only two exceptions are:
- When the data is processed in a non-automated manner(no electronic methods are used)
- When individuals process data for their interests
Also check: Sensitive Personal Data – Special Category under the GDPR Article 9
The scope of CCPA, however, is not that broad. For instance, under GDPR, users are required to ‘Opt-in’ if they wish to have their data processed, while CCPA only stresses the ‘opt-out’ feature. With ‘Opt-out’, users can choose not to share their information for processing or data sharing/selling.
CCPA does not apply to:
- Any user data that is already made available
- Medical information protected by HIPAA certification and CMIA
- User data that is covered by CCPA’s DPPA (Department of Public Policy and Administration)
- Other data sets protected by supervisory authorities
The route to compliance with CCPA is a little tricky. That said, if you are following the best practices for GDPR, you will likely comply with CCPA as well. The policies and procedures required to become GDPR compliant can be used for CCPA as well. Overall, there is an 80-90% similarity in controls and policies.
3. What is considered data collection, sale, and processing?
Both frameworks consider personal data as information that can be used to identify a person.
GDPR
The term processing in GDPR applies to activities like taking consent for data processing, informing the users about the intent for collection and how it will be processed, informing users about their data rights, and the removal/erasure of data.
CCPA
CCPA has defined its stages of data collection and processing in three segments.
- Collection refers to collecting data from users, vendors, and third-party data providers.
- Processing is when the business acquired the data and has started working with the data for gains.
- Selling is when the collected data is transferred to another business entity
4. Information Shared with Data Subjects:
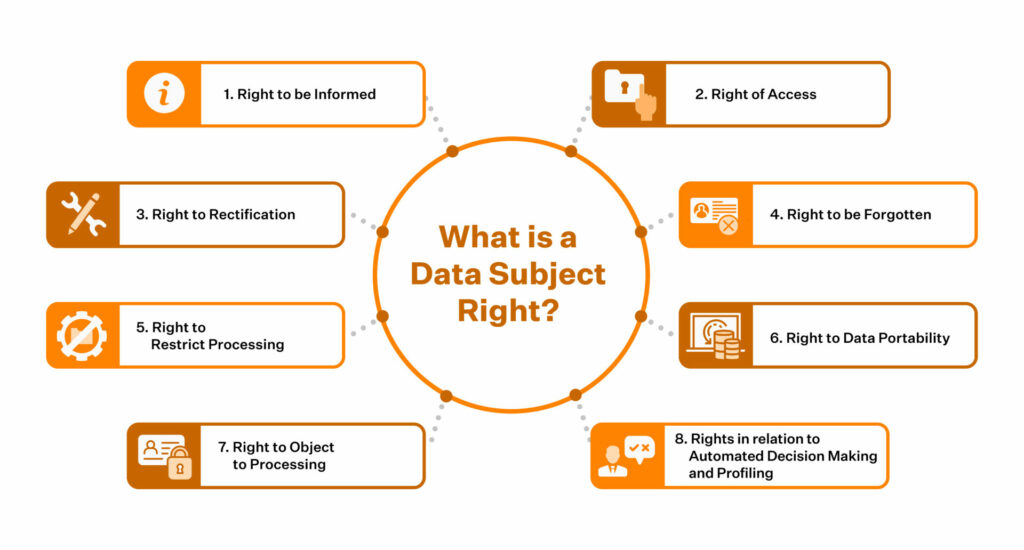
GDPR – Rights of data subjects
Individuals have a relatively higher degree of control over what happens to their data under GDPR as compared to CCPA.
In GDPR, the Data Subject is when their data is collected directly from them or when their information is acquired from another source.
- Businesses must inform users how long their data will be stored with them and how they intend to process it.
- Businesses are also required to give detailed information on reasons for profiling and inform the users about their data rights, specifically the right to erasure. This right empowers them to withdraw their consent to data processing at any point in time.
In CCPA, businesses are required to send Data Subjects a report of how their data was collected, how it was processed, and to who it was sold after 12 months from the date of data acquisition.
- Individuals must also be notified when their information is sold to third parties and if the third-party business sells it to another third-party entity.
5. Penalties
In the CCPA vs GDPR comparison, GDPR’s administrative fines are definitely on the higher side.
If a business is non-compliant with GDPR, it could be levied with a fine of $20 million or 4% of its annual turnover, whichever is higher. Here’s a breakdown:
| GDPR breach type | Penalty |
| Less serious violations | €10 million or 2% of worldwide annual turnover |
| Serious violations | €20 million or 4% of worldwide annual turnover |
| Additional remedial powers (orders to stop processing, corrective orders, bans, etc.) | + regulatory enforcement beyond fines (not directly monetary) |
The penalties of CCPA are on the lighter side as the maximum fines for violations are relatively much less. Here’s the breakdown:
| CCPA violation | Penalty |
| Unintentional | $2500 |
| Intentional | $7500 |
| Damages in civil court | $100-750 |
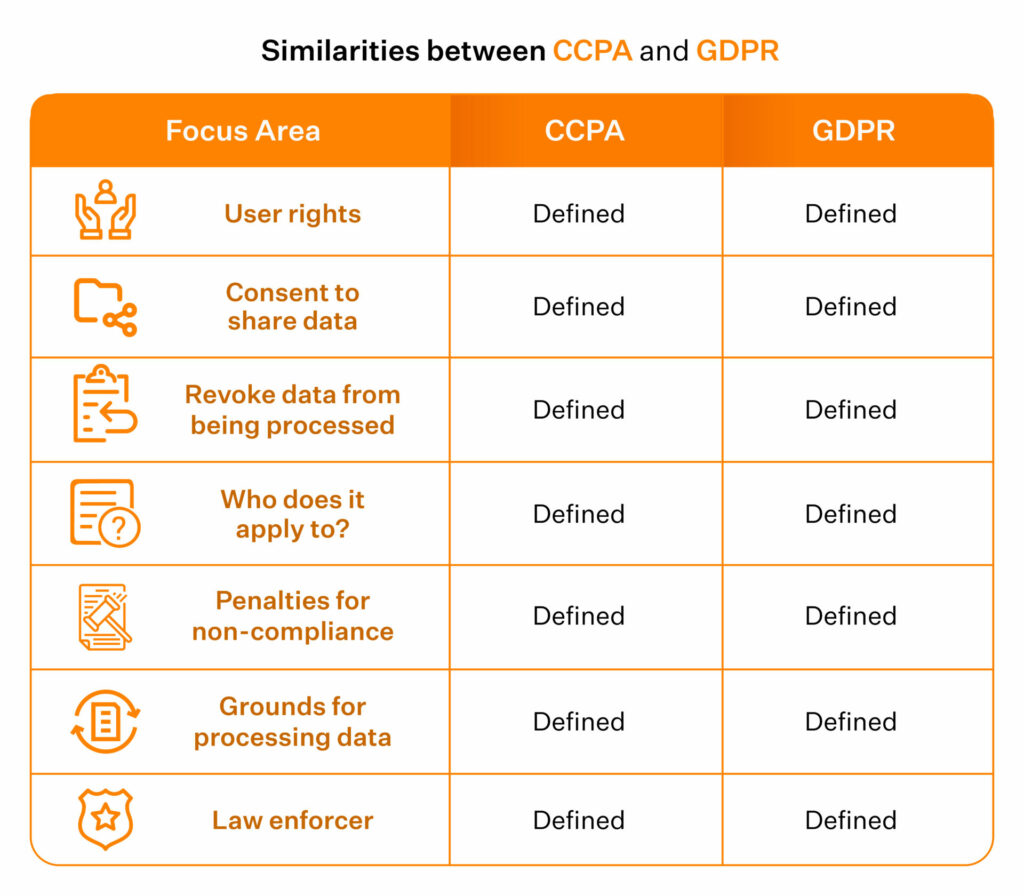
CCPA vs GDPR: Key similarities
Now that we have understood the differences between CCPA and GDPR, let us look at how they are similar to each other.
Both laws are built to strengthen user privacy and give individuals control over their personal information. They clearly define user rights, set rules for consent, and allow people to revoke how their data is used. CCPA and GDPR also apply based on whose data is being processed rather than where the business is located, making both extraterritorial in nature.
They outline valid grounds for processing data, specify penalties for non-compliance, and assign regulatory bodies to enforce the rules, which creates a structured and comparable compliance framework for organizations.
So, here’s a quick summary of the similarities.
Smart mapping, DSAR automation, and risk alerts built-in.
👉 Talk to experts →
CCPA vs GDPR Compliance – Who do the laws apply to?
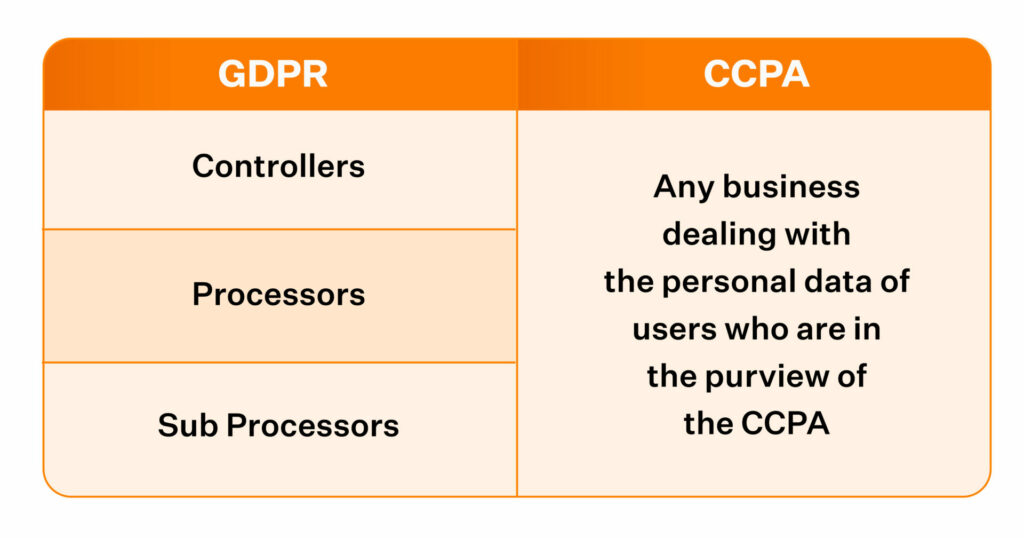
CCPA vs GDPR: Scope
GDPR protects any Data Subject in the European Union.
For example: If a tourist from Asia is travelling in the EU and their data is processed during their stay, they are protected by the GDPR law.
If companies out of Asia are processing the tourist’s data, they would need to comply with GDPR to avoid any hefty administrative fines.
The definition of an individual is restricted and defined under CCPA.
An individual is in the State for other than a temporary or transitory purpose” or an individual “who is domiciled in the State who is outside the State for a temporary or transitory purpose.”
Extraterritorial scope
Both CCPA and GDPR present extraterritorial scope in their framework
Any business around the world will need to be CCPA compliant if they are processing data of more than 50,000 Californians annually.
GDPR also requires businesses to comply with the law if they offer goods or services to users in the EU region. But, again, this is regardless of where they are conducting their processing activities.
CCPA does and leaves no scope for entities to be non-compliant.
Also check out: Best CCPA compliance tools
Business vs Data Controller (Terminology Explained)
Businesses and Controllers
Business is common jargon in CCPA. According to CCPA, a business is an entity that is for-profit and exhibits one of three conditions mentioned below:
- Whose gross annual revenue is greater than $25 million
- Collects, buys, or shares data of more than 50,000 users
- If half (50%) of your revenue is generated from selling said user data
Controller or Data Controller is GDPR jargon for an entity that collects data and processes data in the EU.
GDPR’s scope for categorizing an entity that processes data is broad as it does not qualify them like CCPA does and leaves no scope for entities to be non-compliant.
What rights are given to people by CCPA and GDPR laws?
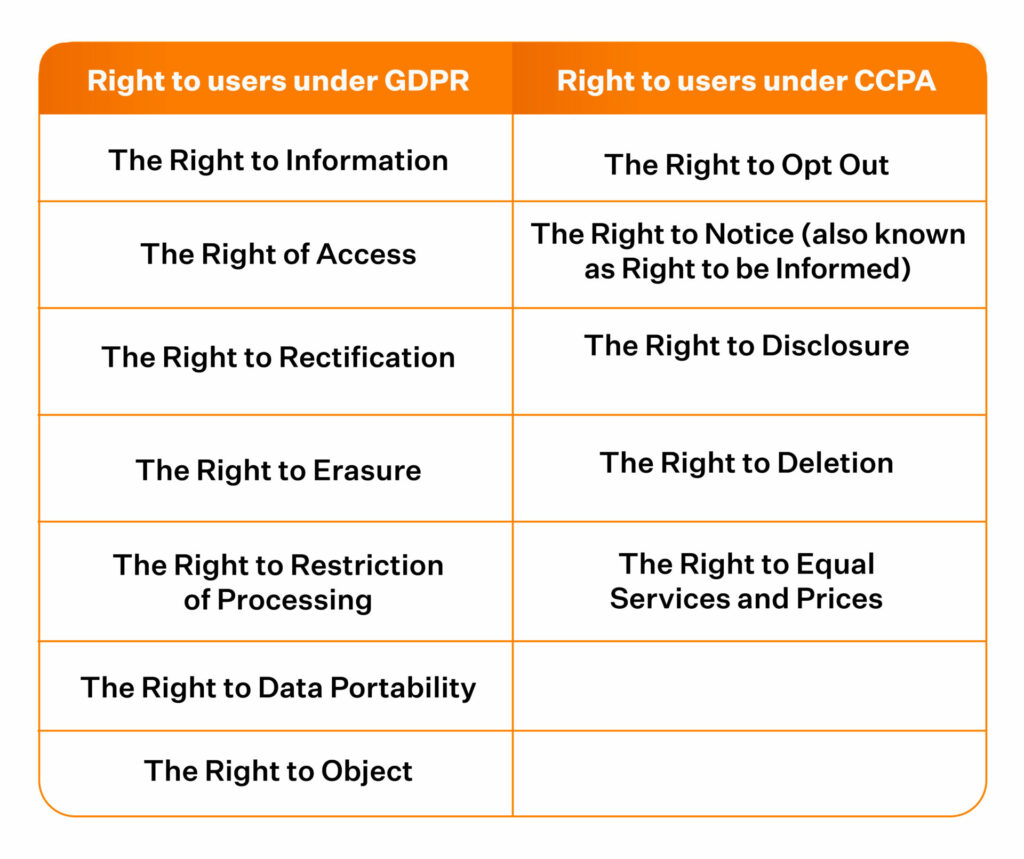
The table here gives you an insight on the rights each compliance law empowers its users with; it is noticeable that there is a significant overlap between the two.
In this section of the CCPA vs GDPR comparison, we dive deep into the rights data users/individuals are entitled to. Both CCPA and GDPR extend these rights:
- Right to Knowledge:
Organizations must make it clear to the user(s) how their data is collected and what it would be used for - Right to Access:
Users can request to receive a copy of their data - The right to Opt-out:
Users can request businesses to remove their data from any processing activities - Right to Portability:
Users can request organizations to send them a copy or another business a copy of their data in a structured and machine-readable format. - Right to Data Erasure:
Under exceptional circumstances, users can ask an organization to delete any information they hold about them. $100-750 in damages in civil court
Automato CCPA and GDPR compliance with Sprinto
Sprinto helps you streamline compliance for both CCPA and GDPR by centralizing your controls, eliminating repetitive tasks, and giving you complete visibility into how data moves across your systems.
With Sprinto AI, you get an intelligent layer that actively monitors risk signals, keeps controls aligned, and reduces the effort it takes to stay compliant every day.
With Sprinto, you get:
- AI-powered data mapping and personal data discovery across tools, systems, and environments.
- Automated policy, control, and workflow setup tailored to GDPR and CCPA expectations.
- Real-time compliance monitoring with personalized, hyper-contextual signals.
- Self-healing controls that adjust automatically as risks, gaps, or system configurations change.
- Embedded compliance that integrates with your everyday tools to keep workflows smooth.
- Continuous audit readiness with audit-friendly evidence captured automatically.
FAQs
The main difference is that GDPR applies to organizations handling the personal data of EU and EEA residents, whereas CCPA applies to businesses that collect or process the personal information of California residents. GDPR focuses on data protection and consent, while CCPA emphasizes consumer rights and data transparency.
The best way to manage GDPR and CCPA compliance in a SaaS business is to build a unified privacy program that covers data mapping, consent management, user rights handling, vendor monitoring, and continuous security controls. Automating these workflows with a compliance platform helps reduce manual effort, avoid gaps, and stay audit-ready. Tools like Sprinto streamline personal data discovery, map data flows, automate controls, handle DSARs, and monitor compliance in real time, making it easier for SaaS companies to stay aligned with both GDPR and CCPA requirements.
GDPR applies to anyone processing EU data and uses an opt-in consent model, while CCPA applies only to California residents and focuses on an opt-out model for data sharing or selling. GDPR has broader data definitions, stricter processing rules, and higher penalties compared to CCPA.
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a state-level data privacy law that gives California residents the right to know, access, delete, and control how businesses collect and use their personal information. It applies to any organization that processes the personal data of California residents, regardless of where the business is based.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a European Union (EU) law that governs how organizations collect, process, and store the personal data of individuals in the EU and EEA. It emphasizes consent, transparency, and accountability to protect individual privacy rights.
Yes. Businesses that operate globally or serve customers in both the European Union and California must comply with both CCPA and GDPR, as each has its own requirements and penalties.
Vimal Mohan
Vimal is a Content Lead at Sprinto who masterfully simplifies the world of compliance for every day folks. When not decoding complex framework requirements and compliance speak, you can find him at the local MMA dojo, exploring trails on his cycle, or hiking. He blends regulatory wisdom with an adventurous spirit, navigating both worlds with effortless expertise
Explore more
research & insights curated to help you earn a seat at the table.





























