What Is Risk Control: Types, Example & Identification
Pansy
Jan 16, 2025
Risk control is important for any kind of business. It safeguards your company’s assets while maintaining sustainable growth. But how effectively are you managing risks in your business? Are you following the essential control measures to eliminate and manage your cyber threats and vulnerabilities?
The current threat landscape is volatile, and mastering how your risk control function works can decide if your business thrives or survives. This article discusses the controls to enhance your risk management plan with an example and detailed insights.
| TL;DR Risk control is a set of measures for mitigating risks in any business. It forms a part of the risk management process. Measures for risk control function include elimination, substitution, isolation, using engineering and admin controls, and enforcing PPE. The risk and control matrix (RACM) provides a unified view of your business’s risks, categorized according to their priority and impact. |
What is risk control?
Risk control is a set of processes and strategies for reducing, mitigating, or eliminating different types of risks that businesses face. It limits the probability of certain risks occurring and their associated consequences.
The main goal of a risk control strategy is to reduce or remove threats caused by risks like financial losses, data breaches, legal liabilities, etc.
Risk control safety is integral to enterprise risk management (ERM) strategy and provides preventive or proactive measures to avoid future risks. It enhances decision-making, boosts stakeholder confidence, and fosters a resilient culture capable of adapting to unexpected challenges.
How does risk control and risk management differ?
Risk control focuses on implementing measures to reduce or eliminate specific risks. In contrast, risk management includes the wider process of identifying, analyzing, and prioritizing risks, followed by planning and executing strategies to mitigate them.
Risk control is a component of the overall risk management strategy. However, it differs from it in other key aspects, such as:
| Aspect | Risk Control | Risk Management |
| Scope | It is specific to particular risks, depending on the scenario | Encompasses all types of risks. |
| Focus | Preventing and mitigating risks | Includes risk strategy planning and overall risk handling. |
| Approach | Reactive | Proactive and strategic |
| Goal | Reducing impact or probability of potential hazards/risks | Building organizational risk resilience |
| Timing | During or after risks have been identified | Continuous and ongoing process |
Six types of risk control
The various types of risk control measures can be applied to specific situations after evaluating the associated vulnerabilities or threats. For example, conducting employee awareness training is a measure that can prepare employees for adverse events to reduce further risks.

According to the Health and Safety Authority of Ireland, there are six key types of risk control:
1. Risk elimination
Eliminating or removing a risk is the first line of defense against cyber threats. This can be done by periodically scanning for vulnerabilities and detecting threats to eliminate risks even before they surface.
Examples include:
- You can deactivate endpoints with outdated third-party software.
- Closing unused network ports and services to reduce the threat surface.
- You can also implement strict access controls and authentication protocols to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
2. Risk substitution
Not all risks can be eliminated or completely removed. For example, you cannot ensure that your company will not be exposed to insider threats at all. However, what you can do is substitute high-impact risks with low-impact risks.
For example, to mitigate internal threats, you could restrict access to sensitive information based on job roles and responsibilities. This should be done by continuously monitoring employee activities and using encryption to protect data even if access is unauthorized.
3. Risk isolation
Sometimes, cyber threats move laterally inside a network, going from one point to another. To avoid this, businesses should adopt cyber risk isolation techniques such as:
Data isolation
This involves segregating sensitive data from the rest of the network to limit access and reduce the impact of potential threats.
Browser isolation
Browser isolation contains web browsing within a separate environment, like a virtual machine, either done locally or on a remote server.
Sandboxing
Suspicious files or programs are executed in a controlled, isolated environment to observe their behavior without risking the main system.
4. Engineering controls for risk
To use engineering controls to mitigate risk, you should integrate risk controls in your digital systems to create barriers between your users and the threats. This can be done using
network segmentation, implementing firewalls, using intrusion detection systems, and updating software regularly for patches.
The GDPR framework establishes the use of engineering controls for risk, effectively using its privacy by design and default strategy. To know more about its requirements, consider downloading the full GDPR checklist:
Download Your GDPR Audit Checklist
5. Administrative controls
Administrative controls include using standard operating procedures with proper instructions and guidelines. In cybersecurity, this occurs in the form of governance frameworks with policies and following regulatory standards.
Enforcing a security policy is the baseline here. Businesses can further enhance their cyber security posture by getting certified with common industry standards like ISO 27001, SOC 2, NIST, etc.
6. PPE (Personal Protective Equipment)
Personal protective equipment, or PPE, is like wearing gloves, earmuffs, and aprons to protect yourself from physical hazards. In the cyber world, this can be done using technology and automation software to mitigate and reduce risks.
A wide range of tools like risk management software, SIEM (security incident and event management) software, and GRC (Governance, risk, and compliance) software allow you to enforce PPE into your system.
For example, Sprinto is a GRC automation platform that gives you real-time visibility into your risks by continuously testing controls set to limit them. It ensures constant governance of your system’s cyber security measures and triggers alerts in the event of an anomaly. Using such a tool will allow you to automate certain risk control measures while ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Risk and Control Matrix (RACM) in risk management
A risk and control matrix (RACM) allows you to identify, prioritize, and execute controls to manage risks. It provides you with a list of the risks threatening your organization’s operations and the controls in place to mitigate those risks.
RACM gives insight into your risk profile and displays how well-prepared you are to prevent negative events from happening. Within the tool, risks will be either inherent or residual.
Inherent risk is the level of risk present before any risk management controls are applied to mitigate the risk, while residual risk is the level of risk remaining after controls have been implemented.
Ideally, if you’ve integrated a risk management tool or a GRC tool with your cloud environment, the RACM containing both inherent and residual risks should look like this.
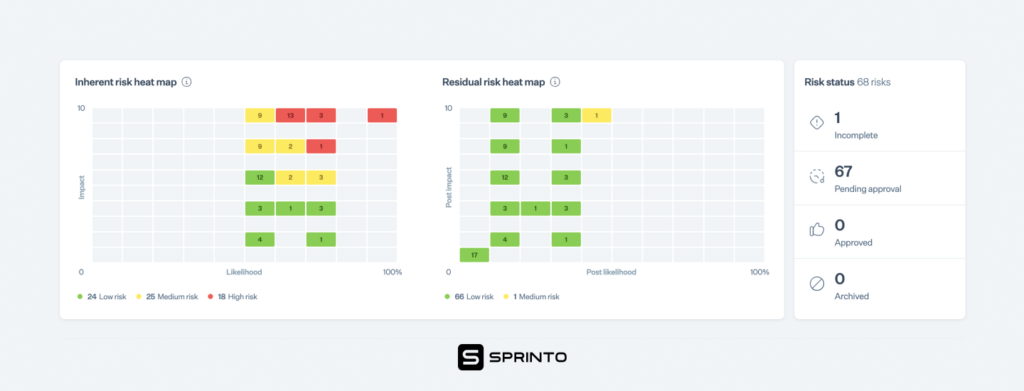
The tool should prioritize your risks into low, medium, and high-risk categories with their likelihood of occurrence on the X-axis and impact on the Y-axis.
Get A Real Time View Of Risk
A practical example of risk control

In 2017, there was a global cyber assault when the WannaCry ransomware cryptoworm targeted operating systems with MS Windows worldwide. It encrypted users’ data and demanded ransom payments in Bitcoin.
“Businesses lost hundreds of records, and hospitals reported surgery cancellations due to erased patient files. Even more terrifying: Ambulances reportedly rerouted due to the attack, as it affected stored GPS information, possibly resulting in lost lives.” – Case study by Marlese Lessing.
Although the attack was carried out for four days, Windows released patches to fix the vulnerabilities one day after the attack itself. However, this control couldn’t help the already infected devices.
After further research, the risk of being affected by the attack was controlled by retrieving the RSA key from the malware files, which effectively stopped the attacks. Combined with the Windows patches, these measures controlled the risk and ended WannaCry’s spread within a few days.
Read more: 11 types of cyber attacks you should be aware of in 2024
How do you identify emerging risks?
Emerging cyber risk identification is vital for businesses to protect their digital assets and plan appropriate risk control measures. However, this task is not easy as the threat landscape evolves constantly. A combination of several strategies can help achieve this:
- Stay updated on advancements in cybersecurity technology and potential vulnerabilities in new tech.
- Attend cybersecurity conferences and workshops to learn from experts and network with peers.
- Conduct simulations of cyber attacks to evaluate the company’s defenses and response strategies.
- Form dedicated GRC teams to monitor, report, and mitigate cyber risks.
- Adhere to industry standards like NIST, ISO 27001, SOC 2, and others for the best practices.
After the risks are identified, risk control measures can be implemented as per the following steps:
- Prioritize risks: Classify risks by their impact and likelihood. Focus on critical ones first.
- Develop controls: Mitigate risks using elimination, substitution, isolation, engineering, administrative measures, and cybersecurity tools.
- Deploy measures: Implement controls systematically and leverage risk management platforms for automation efficiency.
- Monitor and review: Continuously track control effectiveness and adjust as needed.
- Refine controls: Use feedback and compliance checks to update and improve risk management strategies.
Consistent monitoring of risk management controls
Implementing risk controls of elimination, substitution, isolation, engineering, administration, and PPE is inadequate if their proper functioning is not monitored correctly. You should have an integrated view of all the risks your organization faces in a single hub.
Since risk control function is reactive in nature, there should also be a notification system in place to alert you in case of any incidents or breaches. This, coupled with periodic risk assessment, will safeguard your business from potential cyber-attacks and fix vulnerabilities as and when they surface.
The best way to go forward with risk management controls is to use a software solution like Sprinto. It not only streamlines risk assessments and vulnerability scanning but also provides a holistic risk report so that you do not have to go back and forth with multiple departments.
Girish Redekar, Co-Founder at Sprinto says
“Risk is something which is common sense and we do it every day. It is also core to frameworks like ISO. If you find a good system that helps you translate that risk into the way your business runs, then you can do well as a risk function.”
Sprinto’s risk report contains summaries from across assets in relation to risk rating, identification, potential impact, mitigation, treatment, last risk assessment, and pending risk management tasks.
To know more about how the platform helps with risk management, watch the following video or simply get in touch with us.
Frequently asked questions
1. What is risk landscape?
A risk landscape assesses the risk exposure of a business’s assets. It is done based on the threat landscape that identifies potential cybersecurity threats. It considers the impact of these threats and includes measures to mitigate them.
2. What are the types of different risks?
The different types of risks include:
- Financial risk
- Operational risk
- Strategic risk
- Compliance risk
- Reputational risk
- Cybersecurity risk
- Market risk
- Credit risk
3. What are examples of potential losses from risks?
Potential losses from risks can include:
- Data breaches
- Financial theft
- Operational downtime
- Intellectual property loss
- Reputational damage
- Regulatory fines
- Ransomware payments
4. What are some common risk management practices?
Some of the most common risk management practices include:
- Risk assessment and analysis
- Implementing internal controls
- Developing and testing incident response plans
- Maintaining up-to-date software and systems
- Access control and authentication measures
- Data encryption and backup strategies
5. What is the inherent risk environment?
The inherent risk environment refers to the natural level of risk present in an organization’s operations and activities before any cyber risk controls or mitigation measures are applied. It includes all the potential threats and vulnerabilities that could impact the organization under normal conditions.


Use Sprinto to centralize security compliance management – so nothing
gets in the way of your moving up and winning big.























