How nice would your cybersecurity program drive predictable outcomes and preempt threats that matter most to the business, pinpoint areas that need attention, align stakeholders, win customer trust, and inform organization-wide security strategy? Well, that is precisely what cybersecurity reports help you establish.
Cybersecurity reports are more than hygiene documents—they are fundamental pieces of information that inform security decisions at every step, the glue that binds stakeholder aspirations and evidence that wins auditor and customer trust.
Every business needs cybersecurity reports to streamline its security operations. In this blog, we will discuss what a cybersecurity report contains, its key findings, and all the other aspects that make a comprehensive cybersecurity report.
So, let’s dive in…
TL;DR
| A cybersecurity report provides a snapshot of security posture, covering threats, control effectiveness, residual risks, vendor risks, and incidents to pinpoint vulnerabilities and necessary actions. |
| It includes key sections like executive summaries, security risk assessments, audit readiness reports, vendor risk evaluations, penetration testing results, and incident response summaries. |
| Modern cybersecurity reports leverage automation and real-time monitoring to track compliance, visualize security gaps, and streamline remediation efforts. |
What does a cybersecurity report cover?
A cybersecurity report is a snapshot of an organization’s security posture. The report covers an in-depth assessment of identified threats, effectiveness of control performance, residual risks, an overview of vendor risks, and incidents that occurred. Typically, it helps organizations measure residual risk and pinpoint areas of cyber risk that need further remedial actions. On top of it, some cybersecurity reports may adopt a forward-looking approach by analyzing the threat and security landscape and assessing readiness for future threats and security challenges.
It can be further detailed into sections:
- Executive summary
- Threat assessment and summary of risk profile
- Incident reports
- Vendor risk assessments
- Audit and compliance posture reports
Let’s discuss this one by one:
1) Executive summary of the cybersecurity report
Consider this report a high-level assessment of the entire posture. It’s usually helpful when you want to present progress toward KPIs and key factors impacting your organization’s resilience to the board succinctly.
It will cover a summary of key findings, security challenges, actions taken, and a recommended action plan to improve security posture.
To understand it better, let’s look at this cybersecurity executive summary example and template:
| Section | Description | Example |
| Key findings | This section summarizes critical findings of the cybersecurity incidents, quantifying vulnerabilities and control performance. | Our organization prevented X amount of cyber threats and incidents from turning into a breach; Y% of them were phishing attacksKey technical controls like MFA cover 80% of our digital assets, up from 70% last year. Our preparedness for the upcoming ISO 27001 audit is 90%, up from 70% in the last quarter. |
| Current challenges | This section of a cybersecurity report’s executive summary summarizes the critical threats that need to be tackled in the coming quarters. | 20% of our systems operate on legacy hardware, raising 15 necessary vulnerabilities. Only X amount of assets are protected with access controls, jeopardizing assets worth Y$ Updates in compliance regulations such as CCPA require policy changes to be implemented in X months. Expanded use of the cloud requires action to patch misconfiguration to maintain compliance with NIST and ISO 27001 |
| Actions taken | This quantifies the actions the security team has taken to bolster the resilience and compliance posture of the company. | “We mitigated X vulnerability, reducing our impact from $X to $Y.””We’ve cut recovery time from X hrs to Y, saving us $X in costs and potential lost revenue.”Implemented X policies and controls to bolster compliance with GDPR. |
| Recommendation | Propose specific actions or changes to enhance the organization’s cybersecurity posture. | Implement comprehensive endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems across all devices to meet and exceed the endpoint protection controls required by NIST SP 800-53.Upgrade encryption protocols for data at rest and in transit, ensuring compliance with GDPR’s privacy by design and default principles.Conduct regular internal and third-party audits to ensure continuous compliance with evolving standards like HIPAA for healthcare data and PCI DSS for payment security. |
2) Security risk assessment report sample
These reports visualize the organization’s and digital assets’ current risk level, detailing where the critical vulnerabilities are leaving sensitive information and networks exposed, which threats are adequately mitigated, and which attack vectors are most likely to impact business. They usually include recommendations for mitigating risks.
Here’s a sample of the cybersecurity threat summary:
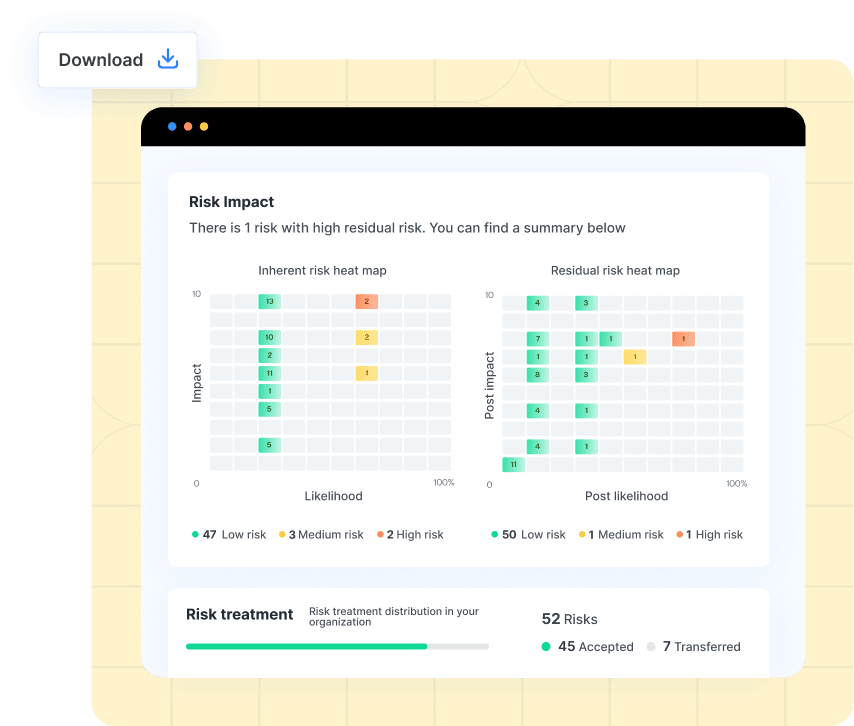
This risk report encapsulates the entire security posture of your organization, highlighting the total number of cyber threats relevant to your business and where they rank in terms of residual risks post-mitigation actions. In Sprinto, security teams like yours can get an overview of all your risks and control performance on a single window like this:
However, a risk report also contains a granular picture of a significant group of risks or individual vulnerabilities. The report clearly visualizes the category of risks, the assigned risk owner responsible for mitigating it, and the potential impact and likelihood of occurrence for your business. It also reveals the residual risk potential after implementing controls.
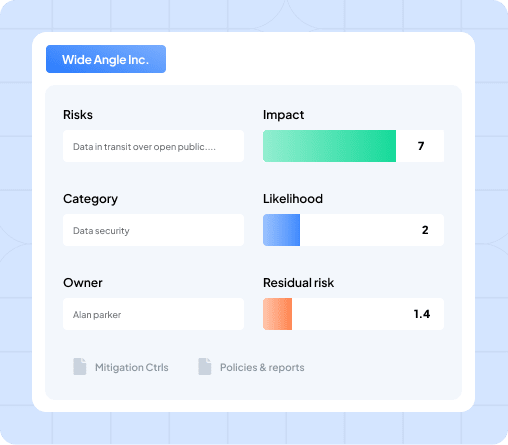
However, if your organization has a real-time control monitoring tool, these reports would also visualize the status of checks and controls and how they fare against different cybersecurity compliance standards.
Here’s how risk assessments against particular compliance standards look like:

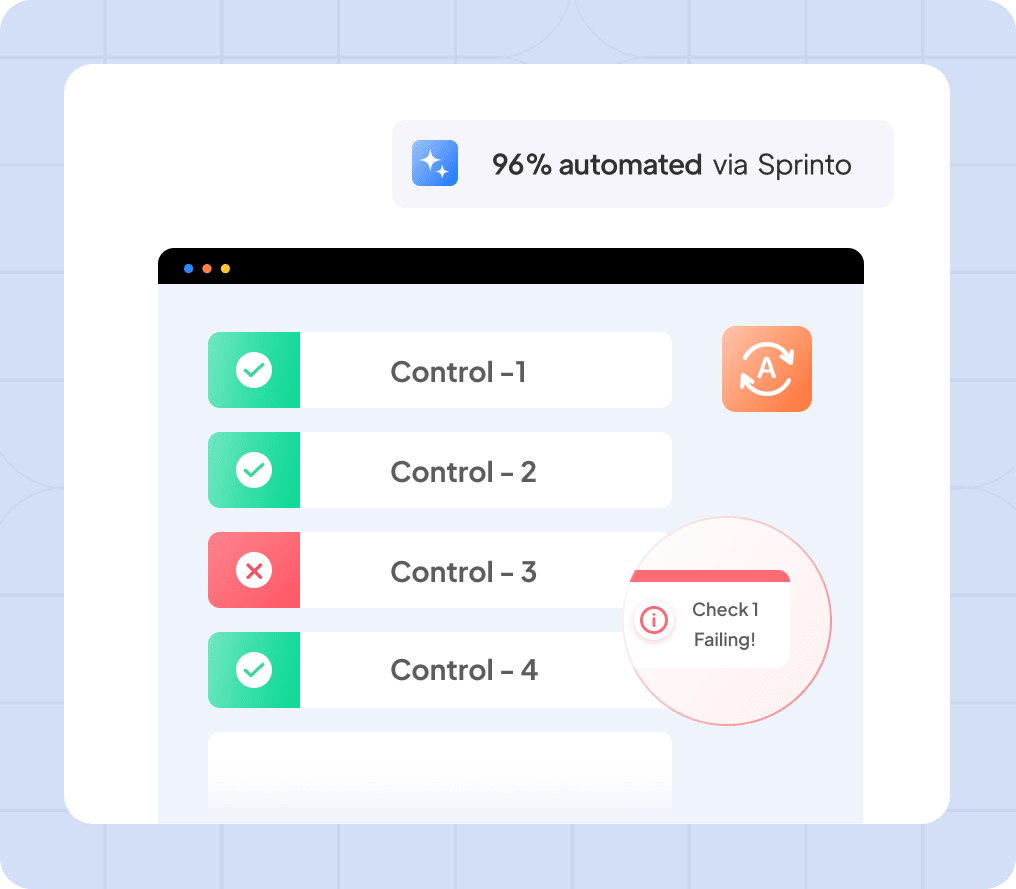
Lastly, a security risk monitoring report also records the real-time status of controls. This visualizes which controls are working as expected and which need attention to launch remediation workflows.
Your control monitoring report looks like this:
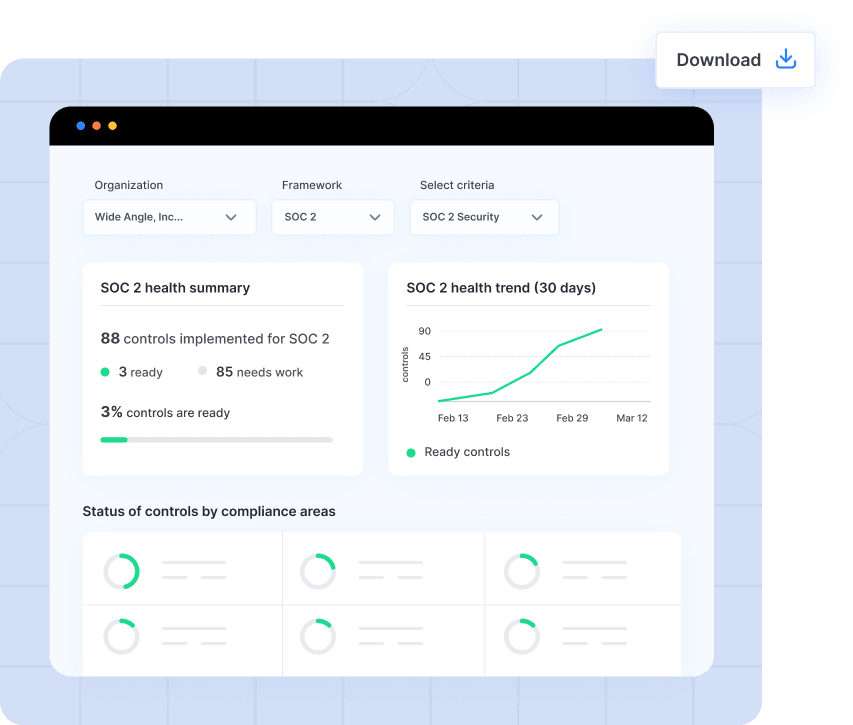
3) Cybersecurity audit readiness report example
These assess the adequacy of an organization’s cybersecurity policies and controls towards the requirement of a particular cybersecurity standard. These reports highlight areas of noncompliance and inform your compliance programs to fix deficiencies in policies, mitigation controls, or quality of evidence.
For instance, the compliance health report can provide an overview of real-time accounts of controls mapped to a particular security framework. In this example of a cybersecurity audit report, the report displays the number of controls that are implemented as per SOC 2 criteria, how their health has fared as the month progressed, which controls performed adequately to build a clear audit trail of evidence, and an overview of areas and their overall health.
4) Vendor risk assessment report example
Every organization would have third-party vendors in their software or material supply chain. From HRMS to raw materials, every vendor that partners with an organization gets access to some of the organization’s information. This data is sensitive and needs to be protected.
Vendor risk assessment reports assess the level of risks new vendors and partnerships bring in for the business via threat vectors. In a vendor risk assessment report for cybersecurity, you get an overview of the vendor’s security practices, compliance status with relevant frameworks, and the potential impact of risks on your business.
The report can be divided into two essential parts for your security program— a high-level vendor risk report and a granular vendor assessment.
High-level vendor risk report
A high-level vendor risk report factors in different control and criteria requirements for all the cybersecurity standards that your business complies with. It then aggregates the posture of your vendors against the requirements stated under those frameworks. It gives you a high-level view revealing whether your vendor risk posture is passing these requirements or not.
Here’s an example of a high-level vendor risk report.
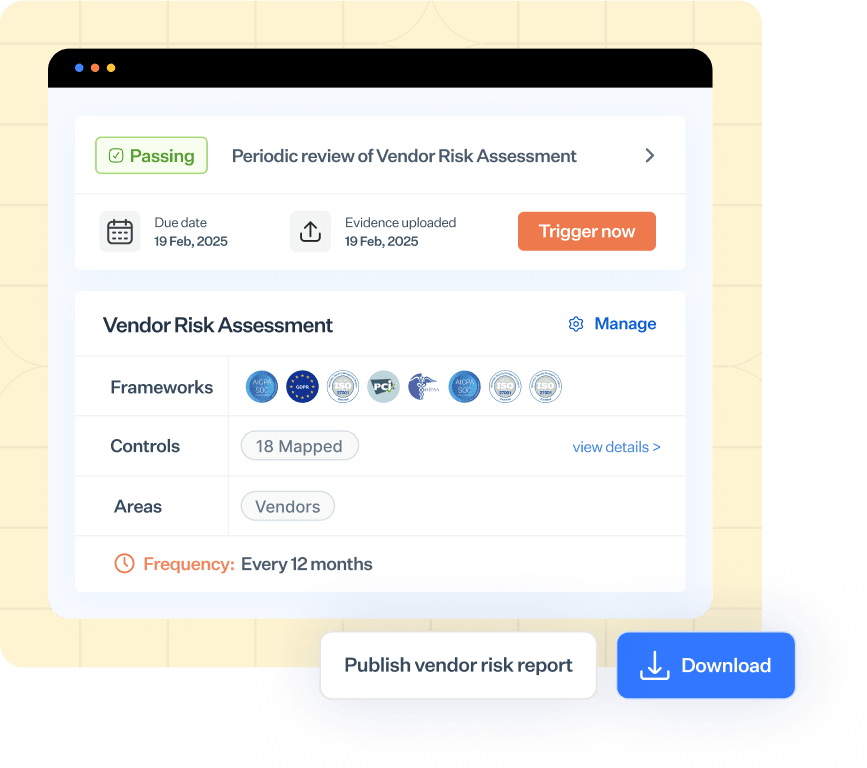
Granular vendor assessment report
This report provides a detailed assessment of each vendor’s compliance with security standards. It identifies specific vendors that are non-compliant, detailing the reasons for their failure, and facilitates the initiation of targeted remediation workflows to address these risks. Here’s an example of such a cybersecurity report:

Other components of the cybersecurity report
In addition to evaluating overall security posture, audit readiness, and vendor risks, a cybersecurity report also details the outcomes of penetration testing and summarizes incident response effectiveness.
Penetration testing summary:
These detail the findings from simulated cyber attacks (pen-tests) aimed at discovering and exploiting vulnerabilities in the organization’s systems and networks. The report outlines the severity of vulnerabilities discovered during penetration testing and their probable impact on business assets. The report also evaluates how existing policies and protocols align with the business context and demonstrate due diligence against the cybersecurity standards.
For example:
| Key findings | Vulnerability Example |
| Critical Vulnerabilities: Found SQL injection flaws in three web applications, allowing unauthorized access to sensitive customer data. | SQL Injection Flaws |
| High-Risk Vulnerabilities: Identified four instances of inadequate password storage practices, making several user accounts susceptible to brute-force attacks. | Inadequate Password Storage Practices |
| Medium and Low-Risk Issues: Detected various misconfigurations and outdated software components that, while not immediately exploitable, could lead to security risks if not addressed. | An FTP server is configured to allow anonymous access, potentially letting unauthorized users download sensitive files. |
Incident report summary:
These types of impactful cybersecurity reports are generated after the incident, outlining the specifics that led to the event and the mitigation actions to contain it. The report also includes recommendations to prevent such incidents from repeating and lessons learned from the overall event.
Here’s an example of an incident report summary:
| Field | Details |
| Incident ID | IR20250115 (Threat vector name) |
| Date/Time | January 15, 2025, 9:32 AM |
| Reported By | ABC name, IT Security Analyst |
| Type of Incident | Ransomware Attack |
| Systems Affected | Accounting, Payroll |
| Initial Detection | Anomalies detected by network monitoring tools in the payroll system. |
| Incident Description | Malware was introduced via a phishing email, encrypting critical files and demanding a ransom for their release. |
| Response Actions | – Immediate isolation of affected systems.- Activation of the incident response team.- Notification to legal and compliance departments.- An external cybersecurity firm was consulted for forensic analysis. |
| Impact Assessment | – Encrypted files on two main servers.- Temporary halt of payroll processing.- No evidence of data exfiltration. |
| Root Cause | An employee clicked a malicious link in a phishing email, bypassing the email filtering solution. |
| Lessons Learned | – Need to enhance email filtering capabilities.- Additional training required for employees on cybersecurity awareness. |
| Recovery Actions | – Restored data from backups.- Systems fully operational within 48 hours of the incident. |
| Preventive Measures | – Upgrade email security gateway.- Quarterly cybersecurity training for all staff.- Regularly review and update incident response protocols. |
| Status | Closed |
| Follow-Up Actions | – Follow-up training session scheduled for February 2025.- Review of all security protocols in the Q1 2025 review meeting. |
Get real-time compliance and cybersecurity reports with Sprinto
Sprinto transforms the daunting task of compliance and security reporting into a streamlined, clear process designed to bring the C-suite and other key stakeholders up to speed on your compliance status with minimal effort. Our platform generates out-of-the-box reports directly from your dashboard that are comprehensive and easy to digest, ensuring that decision-makers can quickly grasp the essentials without getting overwhelmed.
Overview your entire security posture from one dashboard, whether compliance health against different standards, audit readiness, vendor risks, or a detailed picture of your organization’s risk assessment.
Moreover, Sprinto reports are accurate and offer near real-time relevance. Our platform automatically captures the full spectrum of your organization’s posture, precisely detailing risks, controls, and ongoing tasks. This eliminates the guesswork in what to include, providing a detailed yet digestible summary of your compliance and risk landscape. Whether you’re looking to present progress to the board or diving deep to gauge the areas that need to be prioritized, our dashboards will help you and your board make more informed security decisions.
Furthermore, Sprinto enhances compliance reports with advanced analytics that convert complex data into clear, actionable insights through rich visualizations such as graphs, gauges, and pie charts. This not only simplifies the interpretation of your compliance status but also makes it easier to identify patterns, prioritize actions, and swiftly drive necessary adjustments.
Get a real-time view of your security posture
FAQ
A cybersecurity compliance report should include a comprehensive overview of the organization’s security posture, detailing compliance status against relevant standards and regulations. It should cover areas such as risk assessments, security controls, management of vulnerabilities, incident response capabilities, and any findings from recent audits for the senior management and executive team. The goal is to provide a clear picture of the organization’s strengths, weaknesses, and areas requiring attention to maintain compliance.
The frequency of generating and reviewing cybersecurity reports can vary depending on the organization’s regulatory requirements, the sensitivity of the information it handles, and the changing threat landscape. Typically, generating and reviewing these reports at least quarterly is advisable to ensure that all information is up-to-date and to adapt quickly to new cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities. However, monthly or even more frequent reviews might be necessary for environments with high-risk or rapidly changing conditions.
Cybersecurity compliance reports should be reviewed by key stakeholders across the organization, including the C-suite (such as the CEO and CFO), the board of directors, IT and cybersecurity teams, and compliance officers. In some cases, it might also be beneficial to share these reports with external stakeholders such as regulators, auditors, or cybersecurity insurance providers, depending on the organization’s industry, size, and regulatory environment. This ensures all relevant parties are informed of the cybersecurity status and can contribute to strategic decisions regarding risk management and compliance efforts.
Virgil
Virgil is a marketer at Sprinto who combines his media savvy with his cybersecurity expertise to craft content that truly resonates. Known for simplifying complex cybersecurity and GRC topics, he brings technical depth and a storyteller’s touch to his work. When he’s not busy writing, he’s likely exploring the latest in cybersecurity trends, debating geopolitics, or unwinding with a good cup of coffee.
Explore more
research & insights curated to help you earn a seat at the table.






















