Security models offer a blueprint for how security should be applied within organizations to ensure data confidentiality for both them and their consumers.
In this article, we will take a deep dive into the security models and their various types.
What are security models?
Information security models are systems that specify which people should have access to data, and the operation of the operating system, which enables management to organize access control. The models offer a mathematical mapping of theoretical goals, strengthening the chosen implementation.
A security model may have no theoretical underpinnings, or it can be based on a formal computing model, a distributed computation model, an access rights model, or even a model of distributed computation.
What is the objective of a security model?
The core aim of any security model is to maintain the goals of Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability of data. It can achieve these goals by:
- Allowing admins to choose the resources to that users are allowed access.
- Verifying user identities with authentication mechanisms that incorporate password strength and other variables.
- Allowing users who have been permitted to access resources provisioned and defined by authorization systems.
- Regulating which functions and rights are given to accounts and users.
- Giving admins access to a user’s list of activities on a request or assignment basis.
- Safeguarding private data, such as account characteristics or user lists.
Discover security models: Strengthen defenses, protect data
Types of security model
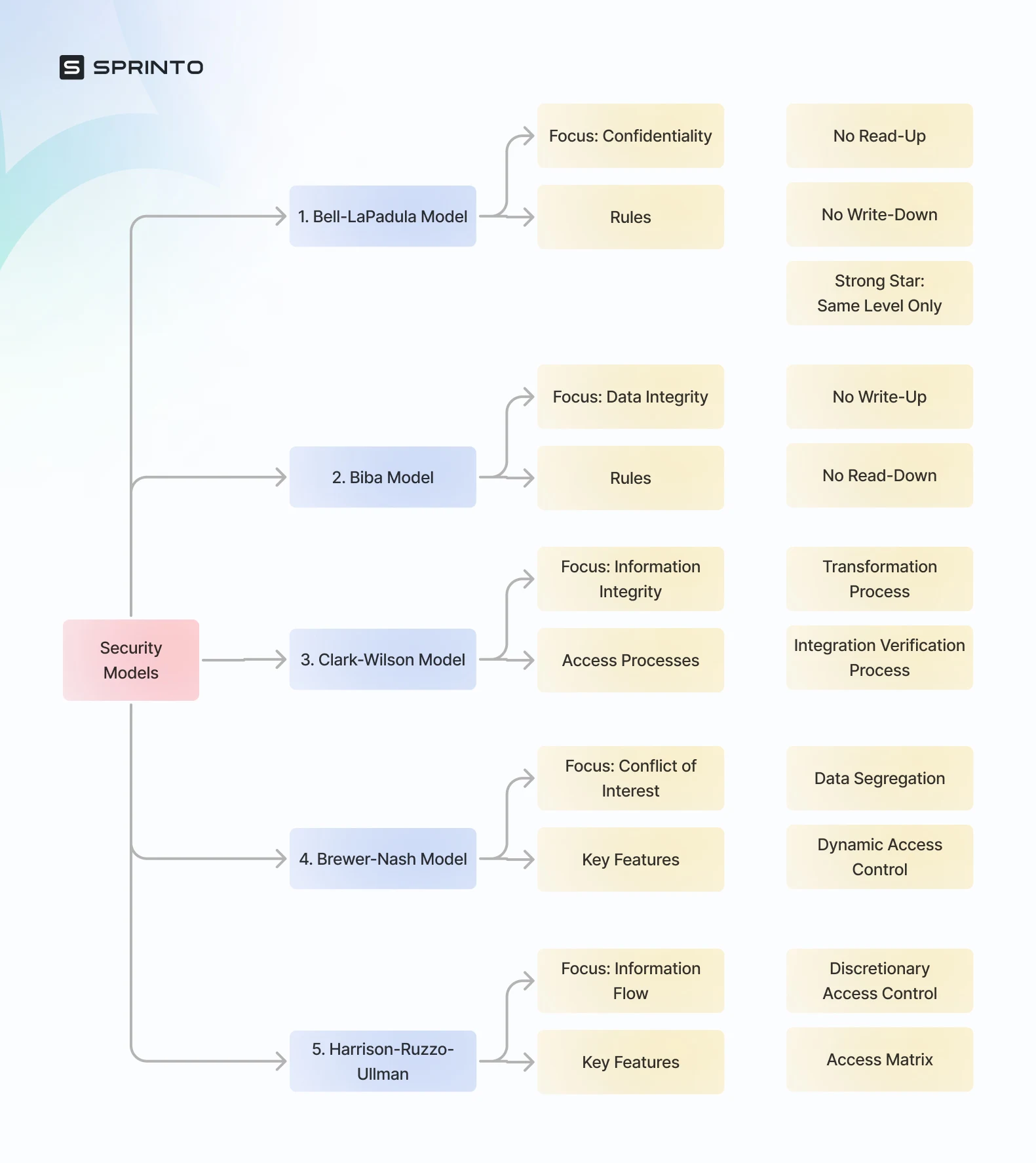
Since network and cyber security are continuously evolving domains, there have been numerous security models proposed in the history of time. However, there are three classic security models which serve as the foundation of many other models. Let’s have a look at them in detail:
1. Bell-LaPadula
David Bell and Leonard LaPadula, pioneers in computer security, created the Bell-LaPadula model, a lattice-based security concept, in the 1970s. The Bell-LaPadula model is a multilevel security system. It establishes a set of access rules and security levels (such as Top Secret, Secret, and Confidential) that specify how individuals may access objects at various security levels.
Bell-LaPadula only allows users at or above their own security level to create content. However, users are limited to seeing anything that is at or below their own security level.
When sensitive information has to be shielded from unwanted access, military and government institutions commonly employ the Bell-LaPadula model. It is sometimes employed in civil organizations, such as banks and hospitals, where a robust cyber security architecture and data protection are vital.
Rules of the Bell-LaPadula model:
SIMPLE Confidentiality Rule
Simple Confidentiality Rule specifies that the Subject may only read documents protected by the same layer of secrecy and the lower layer of secrecy, but not the upper layer of secrecy. For this reason, we refer to this rule as NO READ-UP.
STAR Confidentiality Rule
According to the Star Confidentiality Rule, the Subject may only write files on the same layer of secrecy and the upper layer of secrecy, but not the lower layer of secrecy. For this reason, the rule is known as NO WRITE-DOWN.
STRONG STAR Confidentiality Rule
The Strong Star Confidentiality Rule is the strongest and most secure, stating that the Subject may only read and write files on the same layer of secrecy and not on an upper or lower layer of secrecy. Because of this, the rule is known as NO READ WRITE-UP OR DOWN.
Significance of the Bell-LaPadula Security Model
Being among the earliest modern security models to be created, the Bell-LaPadula model is important. This model has influenced the creation of many security models. The lattice-based security model structure of the Bell-LaPadula model has additional relevance because it was unique when it was first developed.
The Bell-LaPadula model is a key security tool that fulfills several functions. The concept initially sets several security layers to protect information from unauthorized access. The model gives a technique for controlling access to information at multiple security levels by offering a set of access rules that govern how subjects can access objects at different degrees of security. The methodology may also be used to audit information access and ensure that no unauthorized access occurs.
Also, read: Data Privacy Week in 2025
2. Biba model
The Bell-LaPadula Model’s shortcomings inspired the development of the Biba Model. Data integrity is not addressed by the Bell-LaPadula paradigm; only data confidentiality is.
The Biba Model, which articulates a set of access control rules for maintaining data integrity, is a formal state transition system for data security regulations. Data and subjects are organized or categorized according to how reliable they are. Biba aims to prevent data corruption at levels rated higher than the topic and minimize data corruption at levels rated lower than the subject.
Rules of the Biba Model:
No Write-Up (Integrity Axiom)
According to this rule, no one is permitted to add to or change data that has a lower integrity level. This guards against low-quality sources, tainting information of high quality.
No Read Down (Simple Security Property)
A user cannot read an item with a higher integrity level, as per this rule. This suggests that the data you are allowed to access is not more important than the data you are not allowed to see or read. For example, in a school, a student would never need access to the principal’s file.
Importance of the BIBA model
The Biba Model is a collection of rules for a computer system that aids in maintaining valid and secure data. The name comes from Kenneth J. Biba’s proposal in 1977. The Biba Model’s main goal is to prevent people without the necessary authorization from tampering with data.
The model implements stringent integrity-based access restrictions. While users are prevented from downgrading data integrity, they are also prevented from accessing data from higher integrity levels. This ensures data isolation and confidentiality.
3. Clark-Wilson model
The Clark-Wilson security model is built upon protecting information integrity from hostile data-altering attempts. The security model states that the system should maintain consistency between internal and external data and that only authorized users should be able to generate and alter data—unauthorized users should not be able to do so at all.
The primary goal of this model is to formalize the idea of information integrity by preventing data corruption in a system due to errors or malicious intent. An integrity policy specifies how the system’s data items should behave to maintain their validity when they change from one system state to another. The model outlines certification and enforcement procedures as well as the capabilities of the principals deployed inside the system.
The Clark-Wilson security concept prohibits direct access to constrained data objects. You can use these two processes to access constrained data objects:
1. Transformation process
Constrained data items can be requested by the user and managed by the transformation process. This process is intended to ensure that data changes maintain data integrity and follow the prescribed certification standards. It is transformed into authorization by the procedure before being sent to the integration verification procedure.
2. Integration verification process
It carries out authentication and permission. The user is granted access to the restricted data items if this verification is successful.
4. Brewer and Nash Model
The Brewer and Nash model, also known as the ‘Chinese Wall Model’ is built to establish a set of rules to minimize conflict of interest. It aims to prevent access to any sensitive information that could lead to significant consequences because of personal interest conflict.
The model advocates for data segregation and dynamic access controls. Dynamic acces controls are decided based on the user’s previous interaction with the critical information. The model is however not as widely used as other models.
5. Harrison Ruzzo Ullman Model
The Harrison Ruzzo Ullman Model (HRU) is established to address security concerns related to information flow . Unlike the BLP model which is based on mandatory access control, the HRU model adopts discretionary access control. It utilizes an access matrix to understand permissible actions that subjects (such as users) can perform on objects (such as files).
Learn about different security models, Make your data safer.
Benefits of a security model
Implementing an extensive security model has several advantages. Let’s look into the top six advantages that a security model can provide you:
Accurate infrastructure inventory
A security model demands administrators to understand which people, devices, data, apps, and services are part of the business infrastructure and where they are located. In addition to assisting with security-related issues, a precise infrastructure inventory is useful for long-term performance planning.
Better alerts and monitoring
When security concerns arise, a robust security model’s features, like SIEM (Types of SIEM Tools) , security orchestration, automation, and network detection and response, employ a mix of log and event analysis to identify them and then offer recommendations for how to fix them. This enables security operations center administrators to notice and respond to cybersecurity attacks more quickly.
3. Easier security policy creation
Modern security models ease the development of security policies since they allow for the creation of a single, universal policy that can be applied throughout the organization end to end. SSO is an excellent example of this, as it controls authentication for all network resources. The possibility for security vulnerabilities or gaps in some sections of the infrastructure also becomes much less likely, making the deployment and administration of security policies from the administrator’s perspective straightforward.
4. Flexibility when transferring applications, data, and services
The requirements for the technology needed to support business shift along with the business objectives. As a result, applications, data, and information technology services are frequently relocated inside the corporate infrastructure. A modern security model is advantageous in this regard as it creates a central rule system for the management of app and data security. It also necessitates the use of automation tools to move these security and micro-segmentation policies to the necessary locations.
Security is always going to cost you more if you delay things and try to do it later. The cost is not only from the money perspective but also from time and resource perspective
Ayman Elsawah, vCISO, Sprinto
The Sprinto way to better security
As the SaaS era continues to bloom, applications and third-party vendor integrations have become an attractive attack surface for malicious actors. Organizations are, therefore taking a proactive approach to managing SaaS risks by integrating modern security models into their incident response strategy.
Sprinto facilitates this journey by becoming a comprehensive security and compliance solution. Sprinto lets you achieve a high degree of security compliance posture by implementing a advanced security models. It includes features such as role-based access control, rapid control detection, and continuous monitoring. Sprinto helps clients achieve a higher verifiable level of security when compared to doing it manually by automating compliance processes. Sprinto oversees cloud compliance risks and ensures compliance across various regulatory standards such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, and GDPR. The platform greatly enhances incident preparedness and response capabilities with automated compliance checks and actions, enabling faster remediation.
Talk to our experts to know more about how to implement advanced security models using Sprinto.
FAQ’s
What is the role of a security model in ensuring information security?
Security models offer an organized and methodical approach to information protection, guaranteeing the privacy, accuracy, and accessibility of data, which helps to boost information assurance.
In terms of security paradigms, what distinguishes authorization from authentication?
Verifying the identity of a person, system, or other entity is the process of authentication. On the other hand, authorization entails approving or rejecting access to resources in accordance with the verified identification and the permissions that go along with it.
Do security models remain constant or change throughout time?
To adapt to new threats, technology, and legislative changes, security models must change over time. Maintaining good security requires ongoing evaluation and changes.
Payal Wadhwa
Payal is your friendly neighborhood compliance whiz who is also ISC2 certified! She turns perplexing compliance lingo into actionable advice about keeping your digital business safe and savvy. When she isn’t saving virtual worlds, she’s penning down poetic musings or lighting up local open mics. Cyber savvy by day, poet by night!
Explore more
research & insights curated to help you earn a seat at the table.























