
Every business choice you make has some inherent risk to it—some very small, such as setting your password policy right, while others are much bigger, like entering a new market. Just think about it—what if the supplier doesn’t deliver? Or what if the compliance requirements in a new geography are vastly different from what you have in place?
That’s where enterprise risk management comes in. ERM checks all sides of those risks for you to make sure your business stays resilient no matter what challenges arise.
| TL;DR ERM enhances decision-making, improves operational efficiency, supports business continuity, and promotes a risk-aware culture within the organization. Implementing ERM can be costly, but combining it with compliance automation tools can reduce costs while providing real-time insights. Widely used frameworks such as ISO 31000, COBIT 2019, COSO 2017, and NIST RMF help organizations structure and manage risks effectively. |
What is Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)?
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is a structured approach to managing all kinds of risks that can potentially disrupt an organization’s ability to achieve its objectives. It includes identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring risks across various business units.
James Lam, in his book about ERM (From Incentives to Control), defined it as:
“ERM is a comprehensive and integrated framework for managing key risks in order to achieve business objectives, minimize unexpected earnings volatility, and maximize firm value.”
Unlike traditional risk management, which often addresses risks in isolation, ERM takes a holistic view. It integrates the risk management practices across all departments and levels of your organization and aligns risk tolerance and strategic goals.
Here’s a table highlighting the different types of risks addressed by ERM:
| Type of Risk | Description |
| Operational Risks | Risks due to internal processes, systems, and human errors. |
Financial Risks | Risks affecting financial performance, including market and credit risks. |
| Compliance Risks | Legal or regulatory risks that may lead to penalties for non-compliance with laws and regulations. |
| Strategic Risks | Risks associated with the organization’s failure to achieve strategic objectives. |
| Reputational Risks | Risks that harm the organization’s reputation and stakeholder confidence. |
Cyber Risks | Risks involving digital security, information breaches, and technology failures. |
| Environmental Risks | Risks related to environmental issues that could impact operations or reputation. |
How important is ERM for your business?
Enterprise risk management lets your stakeholders have a holistic view of all the battles your business is going through or will go through in the future. It acts as a proactive approach to being prepared to navigate uncertainties.
On a similar note, here are four more reasons why ERM is absolutely essential for your business:
- It enhances decision-making: By understanding potential risks, leadership can make more informed decisions and allocate resources effectively.
- It Improves operational efficiency: Risk identification and mitigation would lead to smooth processes with minimal waste.
- It supports business continuity: ERM helps keep people, finances, and physical assets safe and ensures the organization can withstand any calamity and remain sustainable.
- It promotes a risk-aware culture: A well-implemented ERM framework fosters an organizational culture that encourages employees to recognize and report risks.
If you’re still unconvinced, here are more benefits as stated by James Lam in his book.
Key components of Enterprise Risk Management as per COSO
In 2004, the COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission) published an Enterprise Risk Management— Integrated Framework. It was updated in 2017 with some of the key elements of ERM. Aligning with it, here are the five key components of ERM:
1. Governance and culture
Governance and culture are the foundational elements of enterprise risk management. Governance sets the tone in your organization as to why risk management matters and defines clear responsibilities and roles.
Culture, on the other hand, shows up in your decision-making and how your team approaches risks daily.
2. Strategy and objective-setting
When you start evaluating your business environment, you’ll know that risk management is a key part of your strategic decisions. It affects the internal and external factos that impact risk and helps you set your risk appetite according to your business goals.
3. Performance
ERM directly affects the performance of your business operations. You identify and evaluate the risks that could impact your ability to achieve your goals. Post that, you decide how you can respond to specific risks according to your risk appetite.
Furthermore, If there is ever a hiccup in the industry, regular monitoring (a key part of ERM) lets you adapt to the situation.
4. Review and revision
Reviewing your risk management processes and performance regularly against your goals will help you understand how well these efforts are adding value to your business. It’s also a chance to adapt and ensure that your approach remains effective, especially when you’re facing significant changes.
5. Information, communication, and reporting
Knowledge flow or information management is key to an enterprise risk management program. Not only does it facilitate better decisions, it also enable you to manage data efficiently and perform accurate reporting.
How can an effective enterprise risk management program be implemented?
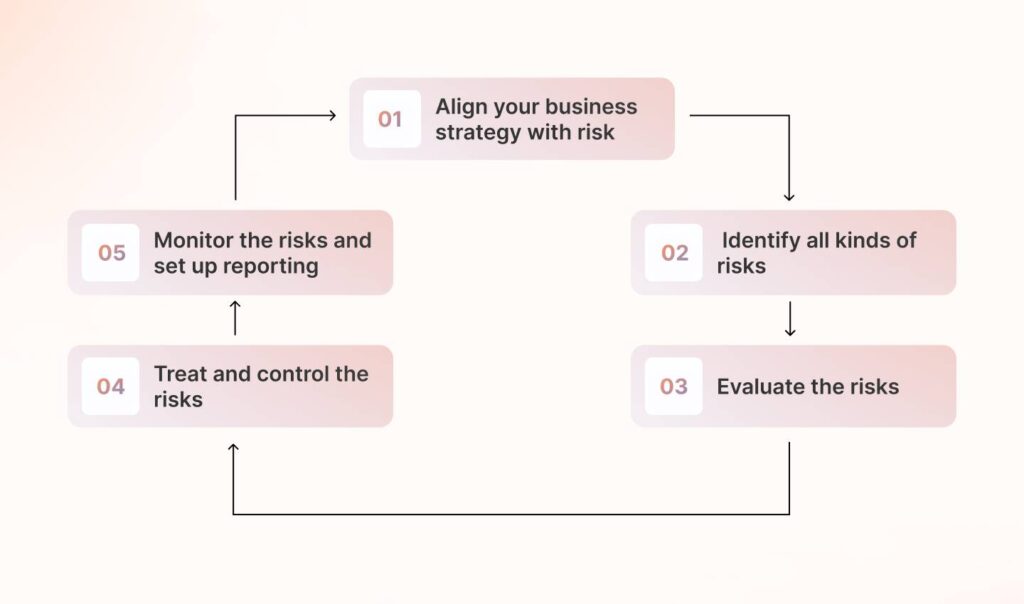
1. Align your business strategy with risk
The foundation of ERM starts with clarity around your strategy and objectives. Without a clear understanding of what your business is trying to achieve, it’s impossible to identify the risks that could derail you.
Ask yourself: Are your objectives well-defined and understood by everyone involved? If employees don’t see how their day-to-day work ties into broader goals, risks can go unnoticed or unmanaged.
This process should include all your team members and board members to ensure a strong starting point. It’s not just about managing risks but also about turning them into potential advantages.
2. Identify all kinds of risks
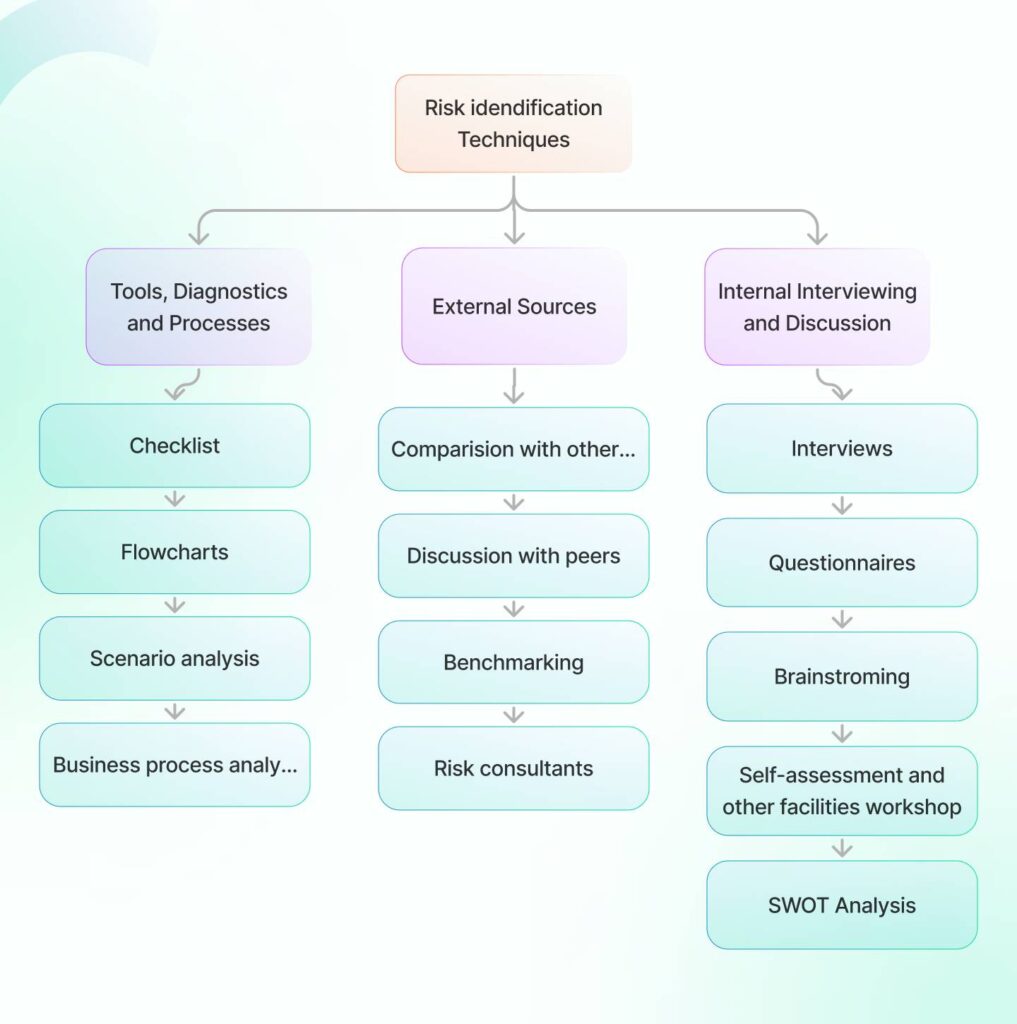
You can use the above techniques to identify the list of top risks facing your organization. If the complexity of risks is high, you can also use multiple techniques to make sure nothing important is missed.
You can either start from scratch (brainstorming inherent risks) or you can have a predefined risk universe to guide the whole process. Often, a mix of these methods works best to capture a full picture.
3. Evaluate the risks
Once risks are identified, the next step is risk assessment. It involves understanding two key factors:
- Which risks can you control?
- Which risks can be measured?
Risks can be assessed both qualitatively and quantitatively. For instance,
- You can rank risks on a scale (e.g., 1–3) based on importance. This allows your risk team to focus on the highest-ranked risks.
- Risks can also be categorized as low, medium, or high impact or measured by strategic risk factors, such as expected losses.
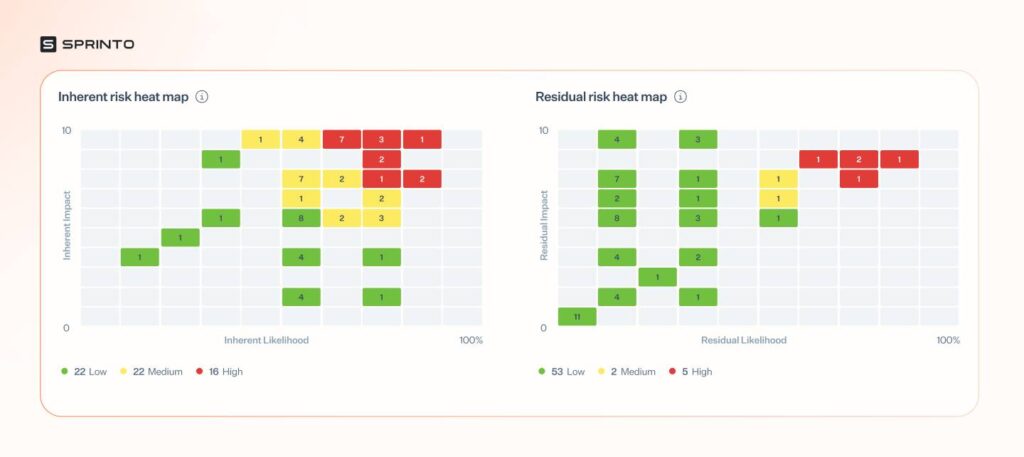
Assessing both the impact (e.g., financial loss) and the probability (likelihood) of a risk provides you with a clearer picture. With such granular data, you can create risk maps or risk registers. Here’s a visual:
4. Treat and control the risks
After all the risks are identified and assessed, you must determine how to respond to them. A key goal of ERM is to make intentional, informed decisions about handling risks. Common risk control methods include:
- Avoidance: Eliminating the risk entirely.
- Reduction: Minimizing the risk’s impact or likelihood.
- Sharing: Transferring the risk to another party (e.g., insurance).
- Acceptance: Acknowledging the risk and choosing to bear it.
The decision largely depends on the risk’s likelihood, potential impact, the cost-benefit analysis of the chosen response and ultimately your business’s risk appetite.
The following image highlights some common risk treatment strategies.
However, the type of treatment plan you use depends mostly on your stakeholders’ expectations, broader business strategy, and the industry in which you operate.
5. Monitor the risks and set up reporting
Organizations constantly take on risks to achieve their goals. ERM doesn’t aim to avoid risks but to encourage proactive, informed decisions at every level. This means taking risks intentionally, guided by clear risk indicators.
When monitoring risks, you need open communication—across teams and up to leadership. You can use KPIs and KRIs to track risks continuously, along with ERM to help you assign ownership and accountability.
Sprinto can make this easier. Here’s how:
How much does ERM implementation cost?
The implementation of an enterprise risk management program will cost you around $20k-100k/month depending on several factors like:
- Size and complexity of your business: Larger organizations often require more comprehensive ERM systems, increasing costs.
- Existing infrastructure: If the organization has existing risk management processes or systems, costs may be lower because there is less need for overhaul.
- Technology and tools you use: The choice of technological solutions (software for risk assessment, reporting, etc.) can significantly affect overall costs.
- Consultation and training: Engaging external consultants for expertise and training employees can add to the budget.
| Alternative: Implementing ERM with regulatory compliance If you don’t want to break the bank, consider pairing ERM with compliance workflows. Tools like Sprinto simplify this process by automating compliance while providing real-time insights into risks. Get your custom pricing. |
What are some common risk management frameworks?
Enterprise risk management frameworks help organizations identify, assess, and manage risks in a structured way. The standards mentioned here provide certain guidelines that you can implement to ensure that uncertainty in risks is handled effectively and assets are protected.
Here are some of the most widely used risk management frameworks:
1. ISO 31000: Risk Management
ISO 31000 is a comprehensive international standard for risk management. It provides a principle-based approach that can be applied to any type of risk in any organization of any size. Key principles of ISO 31000 include:
- Leadership commitment: Top-level support is crucial for effective risk management.
- Risk awareness: Understanding the organization’s risk context and culture.
- Risk assessment: Identifying, analyzing, and evaluating risks.
- Risk treatment: Developing and implementing appropriate risk treatments.
- Risk monitoring and review: Continuously monitoring and reviewing risk management processes.
2. COBIT 2019
COBIT 2019 is a framework for governing and managing enterprise IT. While focusing on IT, it incorporates risk management as a critical component. COBIT 2019 provides guidance on identifying, assessing, and mitigating IT-related risks. It emphasizes the importance of aligning IT with business objectives and managing risk effectively.
3. COSO 2017
COSO 2017 is a framework for enterprise risk management (ERM). It provides a comprehensive approach to managing risk across the entire organization. COSO 2017 outlines five components of ERM:
- Governance and culture: Setting the tone at the top and establishing a risk-aware culture.
- Strategy and objective-setting: Identifying and analyzing strategic risks.
- Performance: Implementing controls to manage operational risks.
- Review and revision: Monitoring and assessing the effectiveness of ERM.
- Communication and reporting: Effectively communicating risk information to stakeholders.
4. NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF)
The NIST RMF is a cybersecurity framework developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). It provides a structured approach to managing cybersecurity risk. The RMF consists of six phases:
- Categorize Information Systems: Assessing the impact of a system’s compromise.
- Select Security Controls: Choosing appropriate security controls to mitigate risks.
- Implement Security Controls: Deploying and activating security controls.
- Assess Security Controls: Evaluating the effectiveness of security controls.
- Authorize Information Systems: Making a formal decision to operate a system.
- Monitor Security Controls: Continuously monitoring and assessing security controls.
What challenges can you expect to face while implementing ERM?
- Cultural resistance: Employees or management may resist changing existing processes or adopting an ERM mindset
- Resource allocation: Limited resources (time, budget, personnel) can hinder the implementation and sustainability of an ERM program
- Complexity of risk assessment: Accurately assessing risks can be complicated and subjective, especially for unforeseen events
- Measuring effectiveness: Establishing reliable metrics to measure the effectiveness of the ERM program is often challenging
The bigger picture of ERM
So, when you think of ERM, it is really about being proactive and organized in identifying, assessing, and controlling risks all over your organization. It’s not just about keeping your assets safe; it’s also about helping you grow while being aware of and managing potential vulnerabilities.
Managing risk doesn’t just mean reducing loss but also finding ways to move forward with surety and feeling prepared to face whatever comes next.
Remember that you’re building a future-proof foundation with enterprise risk management. Keeping up with the current complicated threat landscape, an automated tool to make things more flexible and faster is called for.
Using Sprinto and other tools makes establishing ERM much easier because they automate important parts of compliance and risk monitoring. Such tools let you focus on your business’s big goals.
For example, in Sprinto, you get a comprehensive view of your organization’s current risk profile using the Risk report highlighting impact, mitigation, treatment, assessments and pending tasks.
Frequently asked questions
1. What is the difference between traditional risk management and ERM?
Traditional risk management typically focuses on specific risks within departments, whereas ERM takes a comprehensive view, assessing and managing risks across the entire organization in a strategic manner.
2. How often should an ERM program be reviewed?
An ERM program should be reviewed regularly, typically annually or semi-annually, to adapt to new risks and changing business conditions.
3. Can small businesses implement ERM?
Yes, small businesses can implement ERM by adapting the framework to their scale and using cost-effective tools and practices.
Pansy
Pansy is an ISC2 Certified in Cybersecurity content marketer with a background in Computer Science engineering. Lately, she has been exploring the world of marketing through the lens of GRC (Governance, risk & compliance) with Sprinto. When she’s not working, she’s either deeply engrossed in political fiction or honing her culinary skills. You may also find her sunbathing on a beach or hiking through a dense forest.
Explore more
research & insights curated to help you earn a seat at the table.


















