Cloud security controls are anything and everything that protects your cloud infrastructure from cyber threats and attacks. It ranges from identity and access management (IAM) to network security, encryption, and compliance monitoring.
There are some basic cloud security examples that you must be aware of and some complex ones that may be needed in a very intricate infrastructure. It all depends on your specific needs.
This blog covers them all, along with types, cloud security frameworks, and how governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) aid security controls for cloud computing to their maximum benefit.
Let’s take a deep dive.
| TL;DR Cloud security controls are incomplete without visibility, automation, access management, integrations, and event management. Critical cloud security controls align with governance, risk management, and compliance monitoring functions. Implementing a cloud security control model with GRC tools includes configuring IAM, automating monitoring, enabling continuous assessments, centralizing incident response, and monitoring metrics. |
What are cloud security controls?
Cloud security controls are measures or protocols to protect data, applications, networks, and infrastructure in a cloud environment. These controls defend against unauthorized access and other threat vectors.
A cloud security control model provides layered defenses to detect threats, protect data integrity, and ensure compliance. Given the complexity of cloud environments, such controls help mitigate risks posed by data breaches, service interruptions, and evolving cyber threats.
What are the important types of cloud security controls?
Understanding the different types of cloud security controls makes it easier to gauge their use cases, advantages and disadvantages, and the risks that come with them. The four main types of cloud security controls are:
1. Preventive Controls
A company that is hosting customer data in the cloud may use Identity and Access Management (IAM) to make sure that only authorized employees can access sensitive information. This is an example of preventive cloud security control.
Preventive controls are the first line of defense in cloud security, actively blocking unauthorized access or actions before they happen.
2. Detective Controls
Detective controls work behind the scenes to monitor activities and alert you to suspicious behaviors. Examples include Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems that aggregate logs and flag anomalies and intrusion detection systems (IDS) that scan for known attack patterns.
3. Corrective Controls
Corrective cloud security controls limit downtime, reduce data loss, and help organizations bounce back quickly from security incidents. They focus on mitigating the impact of security incidents after they occur.
Corrective controls include tools like automated backups to restore lost data and disaster recovery solutions that ensure business continuity after breaches or system failures.
4. Deterrent Controls
The most common and effective example of deterrent cloud security controls are compliance certifications like ISO 27001, SOC 2, etc and warnings displayed on the website.
While deterrent controls don’t directly stop attacks, they reduce the likelihood of an attack by making the organization a less appealing target. They also promote accountability by clearly defining consequences for non-compliance or misuse.
What are the benefits of cloud security controls?
Cloud security controls, while offering flexibility and scalability, are inherently vulnerable to various threat actors due to their remote accessibility and shared resources. Implementing controls is essential to protect sensitive data, ensure greater visibility into potential threats, and aid in maintaining compliance with common regulatory standards.
Here are some key benefits of cloud security controls:
1. Enhances data security
Cloud security controls ensure that sensitive data is encrypted, monitored, and protected from unauthorized access.
Features like multi-factor authentication, role-based access controls, and real-time threat detection allow businesses to minimize the risks of data breaches and unauthorized use.
2. Ensures scalability
As businesses grow, so do their security needs. Cloud security controls are designed to scale seamlessly. This means that whether a business is adding new users, applications, or services, the same high level of security is maintained without needing manual intervention or significant infrastructure updates.
3. Mitigates security threats
There are constant changes in the threat landscape. This calls for cloud security controls to use automated tools to detect and block malicious activities in real-time.
From phishing to malware attacks, these controls are designed in such a way that they can quickly identify suspicious activity, reduce vulnerabilities, and respond faster to prevent data loss or breaches.
4. Supports compliance
Many industries require compliance with strict regulatory standards (like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2). Cloud security controls help businesses stay compliant by providing built-in monitoring and reporting tools.
For example, ISO 27017 provides guidelines specifically tailored for cloud service providers, hence, enhancing the security of cloud-based environments. It builds upon the common standard ISO 27001, adding cloud-specific controls to help organizations manage cloud security risks effectively.
Such tools ensure that security measures are properly implemented and data is handled according to the necessary regulations and reduces the risk of non-compliance penalties.
5. Reduces costs
Investing in cloud security controls saves businesses money over time. Companies can avoid costs like incident recovery, legal fees, and fines by automating security tasks, reducing manual effort, and preventing expensive security breaches.
In the long run, cloud security helps protect sensitive data while keeping expenses down.
Implement, manage, & monitor cloud security controls
What are the key elements needed for cloud security controls?
Cloud security controls can have a wide purview of elements and protocols. However, there are some elements you cannot miss, regardless of the size of your organization or complexity.
The following elements of cloud security controls are a must-have:
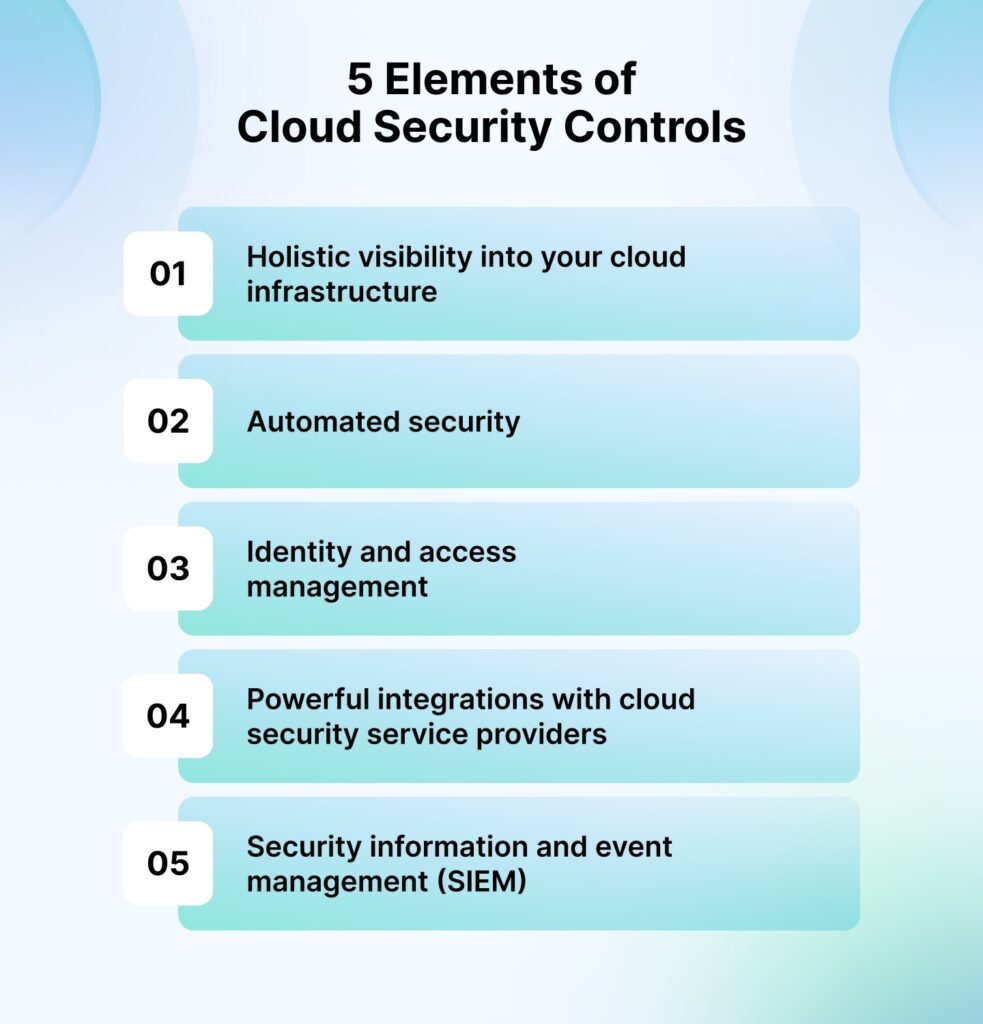
1. Holistic visibility into your cloud infrastructure
Cloud environments are usually very complicated with resources spread across multiple service providers. If you don’t have granular visibility, you won’t know if anything goes wrong.
Continuous monitoring and real-time dashboards are the way to go for every cloud security control. Such visibility allows you to quickly identify risks; and you can respond to threats as they occur.
2. Automated security
Manual security processes can’t keep up with ever-evolving threats. This exposes the cloud environment to risks, as security measures are either delayed or incomplete.
GRC automation is a great option to consider for automation security controls and risk controls. It standardizes responses to security events and also documents these actions.
3. Identity and access management (IAM)
IAM solutions control who has access to which resources in your infra and manage permissions in a structured way. This minimizes the risk of over-permissive access, which is a leading cause of data breaches in the cloud.
Look for tools and controls that can automatically detect and alert for policy violations, thereby ensuring continuous adherence to security protocols without manual oversight.
4. Powerful integrations with cloud security service providers
Without integrations, your cloud infrastructure is incomplete. Organizations often struggle to integrate security tools across different platforms, resulting in fragmented and siloed data.
Consider integrating with cloud security service providers (e.g., AWS Security Hub, Google Cloud Security Command Center) for a unified security approach. This combined with security automation will ensure that all cloud environments are protected consistently.
5. Security information and event management (SIEM)

SIEM solves the problem of monitoring and analyzing logs across multiple environments, which can be overwhelming for your security teams. However, not addressing them can lead to overlooked events and longer response times for incidents.
Security controls for cloud computing must contain SIEM solutions for real-time analysis of security alerts for quick threat detection and response.
How do you integrate critical cloud security controls into your GRC framework?
Governance, risk, and compliance controls play a foundational role in ensuring that your cloud environment meets industry standards.
Critical cloud security controls are not just technical measures you need to implement, they must ethically align with your organizational policies, detect and mitigate risks, and achieve regulatory requirements as per your industry.
The relationship between a few critical cloud security controls with your GRC framework can be established in the following ways:
1. Governance
Policies and oversight of cloud resources are key functions of critical cloud security controls. They include IAM, encryption, monitoring, etc. Such oversight is also included in the Governance controls of a GRC framework. Having said that, the similar controls between the two include:
- Identity and access management (IAM): Controls who has access to cloud resources through role-based access and permissions.
- Policy management: Establishes and enforces security policies across the cloud environment.
- Security configuration management: Ensures cloud resources are set up according to security best practices.
- Logging and monitoring: Tracks and logs user activities and system changes for visibility and accountability.
- Audit trails: Maintains records of all actions within the cloud for governance oversight and traceability.
2. Risk
Identifying, evaluating, and mitigating risks in a cloud infrastructure involves several controls like intrusion detection, endpoint security, data loss prevention (DLP), vulnerability management, etc. Such controls reduce the likelihood and impact of incidents which in turn align with the risk management objectives of GRC.
Cloud security examples of such controls are:
- Encryption (Data at rest and in transit): Protects data privacy by encrypting sensitive information both when stored and during transmission.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Identifies and mitigates potential threats to the cloud environment.
- Endpoint security: Secures devices accessing cloud resources, preventing unauthorized access points.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Monitors and controls data movement to prevent unauthorized sharing or leakage.
- Backup and disaster recovery: Protects against data loss by enabling rapid data recovery in case of cyber incidents or system failures.
- Vulnerability scanning and patch management: Regularly identifies and addresses software vulnerabilities.
- Network security (firewalls, segmentation): Controls data flow and protects cloud networks from unauthorized access or attacks.
3. Compliance
Many regulatory frameworks (e.g., SOC 2, GDPR, HIPAA) require specific cloud security controls to protect sensitive data and ensure data privacy. Your cloud service provider must be able to integrate with a compliance or GRC automation platform to combine critical security controls with your cloud operations.
On a similar note, common cloud security control frameworks include:
| Framework | Description | Best suited for |
| CIS controls for cloud security | Prioritized, actionable security controls for cloud environments. | Organizations of all sizes, especially those new to cloud adoption. |
| CSA cloud controls matrix (CCM) | Comprehensive security controls aligned with major compliance standards. | If you are seeking compliance with specific standards (e.g., PCI DSS, HIPAA). |
| NIST cybersecurity framework (CSF) | A structured approach for identifying, protecting, detecting, responding to, and recovering from cybersecurity threats in cloud environments. | Small and medium businesses for a flexible and adaptable framework that can be tailored to their specific needs. |
| ISO 27001 | Standard for information security management systems (ISMS) applicable to cloud environments. | Organizations that prioritize a comprehensive approach to information security management, including cloud security. |
Stay Ahead with Automated Cloud Security Controls
Can you implement cloud security controls with a GRC tool?
Yes, you can definitely implement cloud security controls with GRC tools backed by powerful integrations. If the app integration is not present, then make sure that the platform supports API integrations, so you don’t have to worry about siloed data.
The implementation of your cloud security controls with the help of a GRC tool can be done with the following six steps:
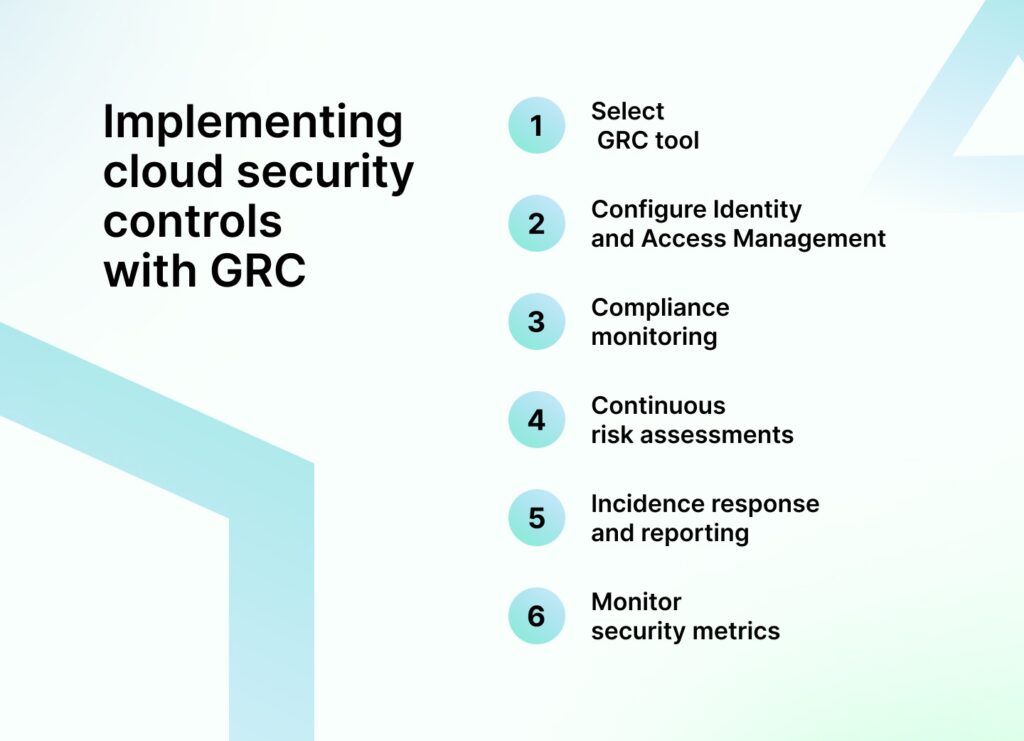
1. Select a GRC tool with cloud security and integration capabilities
Begin by choosing a GRC tool that allows plug-and-play to cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, or specific security tools your organization already utilizes.
If native integration is not available, ensure the tool offers API support and can simply integrate easily with cloud services without resulting in siloed data.
2. Configure identity and access management (IAM)
Use the GRC tool for IAM policy establishment in the cloud environment. In this manner, you can have a central permission system and MFA enforced as well as account users who are regularly audited in how to enforce security policies.
3. Automate compliance monitoring
Set up the GRC tool to continuously monitor compliance by tracking real-time activities and assessing them against regulatory standards, like SOC 2, GDPR, and HIPAA.
The tool would flag any deviations while generating compliance reports and help keep your cloud in check with relevant frameworks.
4. Enable continuous risk assessment
The GRC tool should integrate with cloud security controls such as encryption, intrusion detection, and vulnerability scanning.
The platform should aid in real-time identification and assessment of risk, and eventual mitigation and thus update your risk profiles automatically, giving you alerts if a threat or vulnerability arises.
5. Centralize incident response and reporting
A good GRC automation platform should help create and manage the incident response plan in the cloud. With the introduction of cloud security controls, the GRC tool can automatically activate response actions, log incidents, and keep a record for compliance reporting.
6. Monitor and report on security metrics
With the GRC tool, you will configure dashboards and reporting features to enable monitoring of access logs, data flows, and encryption statuses. This way, you will always be updated on changes in your cloud environment about security and compliance.
The smarter and cost-effective way forward
A strong cloud security control model along with GRC automation will not only advance your business’s security posture but also adapt defense capabilities to evolving threats. But the problem for most remains the same: too many tools and measures with minimum effort and budget.
But what if a single tool provided you with all the above solutions at no extra cost?
Enter Sprinto: A GRC automation platform that acts as an enabler to fulfill your cloud security posture with its automated workflows and holistic control dashboard.
Point in case: Makeforms, an AI-powered data management tool, saved 50% of costs while complying with 11 security frameworks with Sprinto.
“A lot of GRC tools promise to get you compliant in 2-4 weeks, but this is contingent on you putting in a lot of effort, which wasn’t possible for us as a small, busy team. With Sprinto, this became a reality with minimal effort.” – Partik Ghela, Founder, Makeforms.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the types of cloud security?
Cloud security types include identity & access management (IAM), data encryption, network security, application security, compliance management, and disaster recovery. Each type protects different aspects of cloud infrastructure and services.
2. What are the five C’s of security?
The five C’s of security are Company, Compliance, Confidentiality, Control, and Communication. These fundamental principles guide organizations in developing and maintaining comprehensive security strategies.
3. What is a cloud control?
A cloud control is a security measure or policy implemented to protect cloud resources, such as access restrictions, monitoring systems, encryption protocols, or compliance requirements.
4. What is a cloud security tool?
A cloud security tool is software designed to protect cloud-based assets and data. Examples include firewalls, encryption software, vulnerability scanners, and security information and event management (SIEM) systems.
Pansy
Pansy is an ISC2 Certified in Cybersecurity content marketer with a background in Computer Science engineering. Lately, she has been exploring the world of marketing through the lens of GRC (Governance, risk & compliance) with Sprinto. When she’s not working, she’s either deeply engrossed in political fiction or honing her culinary skills. You may also find her sunbathing on a beach or hiking through a dense forest.
Explore more
research & insights curated to help you earn a seat at the table.























