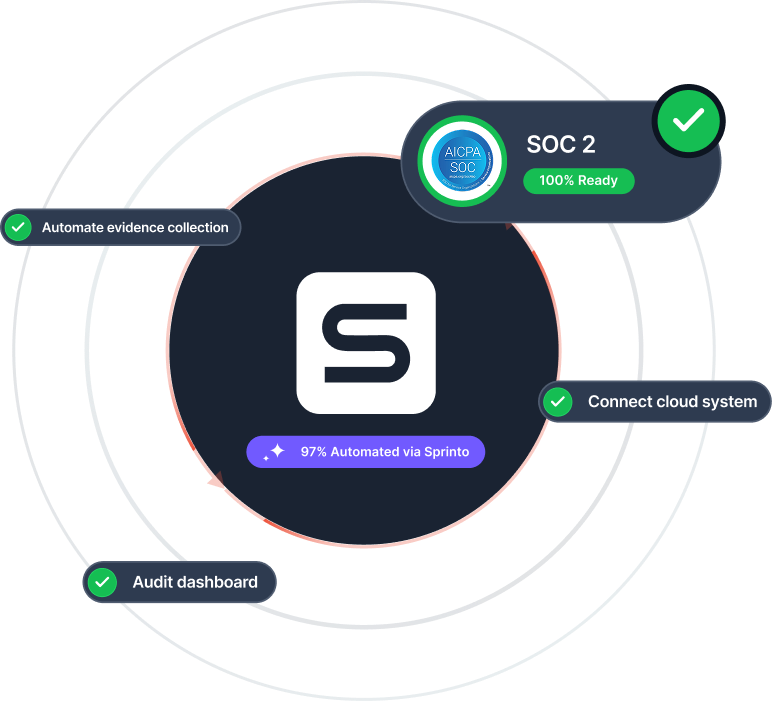
Must-Know Compliance Frameworks
An Overview of Compliance
Must-Know Compliance Frameworks
Overview of Compliance Implementation Process
Overview of Continuous Compliance
Building a Compliance Paper Trail
Educating Teams for Compliance Success
Control Monitoring Overview
Evaluating Compliance Readiness Posture
Audit Management Made for Compliance
Timeframes in Compliance
Breaking Down Compliance Cost
Navigating Compliance in Startups
What Does Compliance Mean for SMEs
Aligning Enterprise Strategy with Compliance
An Overview of Compliance Benefits
What Makes Compliance Difficult
From general-purpose standards to industry-specific mandates, compliance frameworks define how businesses manage risk, data, and regulatory exposure. Some of the most widely adopted include:
SOC 2, ISO 27001 — Information security for cloud-first and global tech organizations
GDPR, CCPA — Data privacy and consumer protection standards
HIPAA, PCI DSS — Healthcare and payment data compliance
COBIT, ISO 38500, COSO — Governance and IT control alignment
ITIL, NIST (800-53/CSF) — Operational service and cybersecurity posture
TISAX, SOX, CMMC — Industry-specific, financial, and defense-grade compliance
Each framework has distinct goals, but leading companies design a unified control layer that maps across them — eliminating redundancy and accelerating audit-readiness.
SOC 2, ISO 27001 — Information security for cloud-first and global tech organizations
GDPR, CCPA — Data privacy and consumer protection standards
HIPAA, PCI DSS — Healthcare and payment data compliance
COBIT, ISO 38500, COSO — Governance and IT control alignment
ITIL, NIST (800-53/CSF) — Operational service and cybersecurity posture
TISAX, SOX, CMMC — Industry-specific, financial, and defense-grade compliance
Each framework has distinct goals, but leading companies design a unified control layer that maps across them — eliminating redundancy and accelerating audit-readiness.
A Quick Overview of Compliance Framework
Sprinto, your ally in all things compliance, risk, and governance.