In the last four years, Indian financial institutions have reported over 248 major breaches—a clear sign that piecemeal regulations have left India’s financial sector entangled in fragmented, reactive efforts. The consequences? It has destabilized markets, eroded investor and customer trust, and complicated operations.
So what now? Well, the era of fragmented measures is over. It’s time to embrace concerted, proactive measures to write a new chapter of growth. Enter SEBI’s Cybersecurity and Cyber Resilience Framework (CSCRF)—a decisive shift that replaces outdated methods with proactive, integrated resilience to meet today’s dynamic threats.

What happens to the previous cybersecurity directives?
The consolidated CSCRF proposes to supersede the previously issued SEBI cybersecurity circulars between 2015 and 2023 to be complied with by Market Infrastructure Institutions (MIIs), Stockbrokers/Depository Participants, Mutual Funds/Asset Management Companies (AMC), KYC Registration Agencies (KRAs), Qualified Registrars to an Issue / Share Transfer Agents (QRTAs), Portfolio Managers.
What’s new?
Wider Coverage:
- In contrast to earlier regulations that only covered large-cap institutions, the CSCRF now applies to a wider range of entities, including Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs), Credit Rating Agencies (CRAs), and Venture Capital Funds (VCFs), among others. This expansion suggests a broader regulatory impact and increased compliance requirements for more financial institutions.
Introduction of a new Cyber Capability Index:
- Standardized benchmarking helps regulatory bodies measure the pulse of the industry as a whole, thus a new Cyber Capability Index for Qualified Regulated Entities (REs) and Market Infrastructure Institutions (MIIs) has been introduced. This index likely serves as a benchmarking tool to assess these entities’ cyber readiness and capabilities, enhancing their overall cybersecurity posture and aligning with best practices.
Mandate for Continuous Monitoring:
- All REs are required to establish Security Operations Centers (SOCs) for continuous monitoring of security events. This mandate emphasizes the importance of ongoing vigilance and real-time threat detection to mitigate potential cyber risks.
Third-party Compliance with Cybersecurity Standards:
- There is a heightened focus on supply chain security, requiring REs to ensure their third-party vendors comply with stringent cybersecurity standards. This is crucial to prevent supply chain attacks, which have become a significant risk vector.
Incident Response Team Requirements:
- The establishment of an Incident Response Team is mandated. The team’s responsibilities include maintaining records of all cyber incidents and managing the response and resolution processes. This structured approach aims to enhance an organization’s response to cyber incidents.
Dedicated Cybersecurity Committee:
- All REs must form a dedicated cybersecurity committee comprising senior management and IT experts. This committee will ensure that cybersecurity is a board-level priority and facilitate informed decision-making regarding cyber risks and strategies.
For industry, it sets a new security baseline
Adopting the CSCRF significantly enhances Bolster’s cybersecurity defenses, streamlines compliance, and ensures a standardized security framework across the sector. Here’s how:
Bolster’s readiness to mitigate and respond to threats
Adopting CSCRF will necessitate upgrades to existing cybersecurity measures, ensuring that entities can defend themselves against the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber-attacks.
Comprehensive Coverage
By superseding all prior directives on cybersecurity from SEBI, CSCRF simplifies the regulatory landscape, making it easier for businesses to understand and meet their compliance obligations.
Standardization and Uniformity
CSCRF introduces a standardized approach to cybersecurity, which means that all covered entities will follow the same set of guidelines and standards, facilitating a uniform security posture across the sector.
For businesses, it’s costly now but promises dividends tomorrow
The new SEBI mandate is undeniably comprehensive and it demands significant investments in infrastructure, teams, and processes for businesses to comply.
However, this framework aligns with other established standards like ISO27001, setting a robust baseline for security across the financial industry that streamlines business partnerships and unlocks new opportunities for Indian enterprises.
“It’s an investment in resilience. While the initial cost is high, it fortifies India’s financial sector, aligning with global standards“
Rachna Dutta, Infosec Consultant
These benefits of this investment will become apparent over time:
- Ease of doing business: Since every business in the space is expected to share a common security baseline by default, exchanges, partnerships, and vendor contracts would become easier.
- Unlocks new shores: The comprehensive mandate shares DNA with the principles of SOC2 and ISO27001, CIS v8, and NIST 800-53, allowing businesses and services in the Indian financial sector to comply with other frameworks with minimum additional lift and compete in foreign markets.
- Spurs growth and foreign investments: This strategic move builds trust among private and public investors, boosting their confidence in purchasing financial services and driving sector growth.
Who is affected?
The CSCRF is applicable to the following REs and MIIs:
- Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs)
- Bankers to an Issue (BTI) and Self-Certified Syndicate Banks (SCSBs)
- Clearing Corporations
- Collective Investment Schemes (CIS)
- Credit Rating Agencies (CRAs)
- Custodians
- Debenture Trustees (DTs)
- Depositories
- Designated Depository Participants (DDPs)
- Depository Participants through Depositories
- Investment Advisors (IAs)/ Research Analysts (RAs)
- KYC Registration Agencies (KRAs)
- Merchant Bankers (MBs)
- Mutual Funds (MFs)/ Asset Management Companies (AMCs)
- Portfolio Managers
Building Blocks of the CSCRF Framework
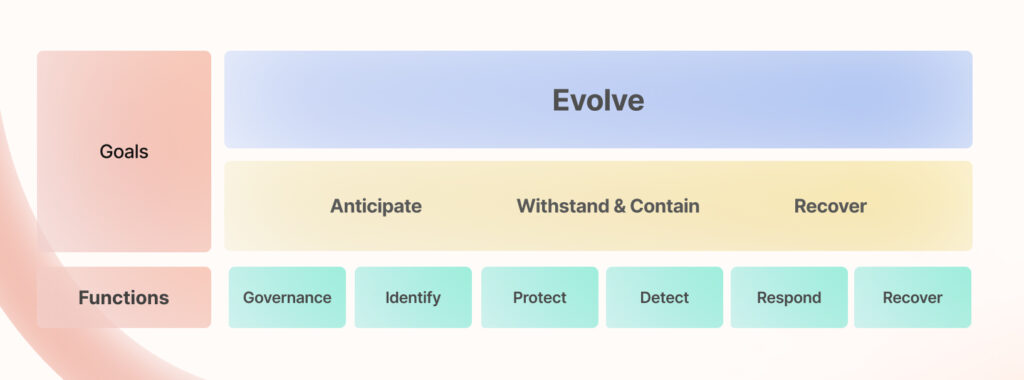
The framework outlined in SEBI’s CSCRF directive is grounded in the Five foundational stages of threat management, urging companies to evolve how they approach risk and mitigation. These stages represent an evolution from disjointed and checklist-style efforts to security where organizations can proactively identify risks, detect them swiftly, and build robust mechanisms to mitigate or respond to threats in case of a breach.
This hints at the evolution towards the strength of integrated efforts when managing risks in financial institutions.
STAGE I – Governance
- Leadership and Accountability: The first step to cyber security is establishing a robust foundation. This includes senior management laying the framework and the board actively championing cybersecurity, ensuring clear ownership and responsibility at every level. By defining roles and holding teams accountable, leaders cultivate a culture of security and resilience.
- High-level policy: You can consider cybersecurity policies as your manual for managing cyber risks that outlines processes and desired outcomes. This phase is critical to align your cyber security initiatives perfectly with SEBI’s guidelines and required regulatory standards.
STAGE II – Identify
- Discovering assets under risk: You can’t protect what you can’t identify. This step involves discovering the assets that might pose a risk to the business or its customers if compromised. The SEBI directive urges to review of systems, software, documents, and network architecture to discover critical infrastructure that needs protection.
- Foreseeing Supply Chain Risks: The framework insists on managing concentration risks for third-party service providers, advising pre-procurement vendor assessments, and ensuring adequate manpower for operational continuity.
STAGE III – Protect
- Documenting policies: As a part of the next stage, organizations need to establish a comprehensive cybersecurity policy approved by the Board and overseen by the Technology Committee. As per the directive, it should cover aspects like asset management, vulnerability assessments, change management, authentication, encryption, and data privacy.
- Implementing Access Control: Access privileges should be regulated =based on documented rules. To establish this, the new framework advises implementing the principle of least privilege and zero-trust model, using Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for critical systems.
- Conducting Training: Cybersecurity is a team sport, and every employee can either be the weakest link or the first line of defense. To truly mitigate threats, we must equip people to identify and avoid them.
STAGE IV – Detect
- Implementing Continuous Monitoring: Organizations must now establish continuous, near real-time monitoring methods that scan systems for anomalies and trigger alerts and remediation workflows.
STAGE V – Respond
This stage involves developing and implementing strategies to address security incidents effectively once they are detected.
It can be broken down into 3 steps:
- Response Planning: Developing a cyber crisis management plan, including incident reporting and recovery SOPs.
- Communication: Sharing cyber threat intelligence data with regulatory bodies like SEBI, reporting incidents promptly, and managing public communications for high-impact cyber-attacks.
- Analysis and Improvement: Collecting and analyzing data to prepare for root cause analyses, with bi-annual updates to the response plan.
STAGE VI – Recovery
This stage focuses on restoring systems and operations to normal functioning after a security breach or attack. To ensure an effective transition from crisis to normalcy, the recovery process is structured around two critical components:
- Recovery Planning: Developing a robust recovery plan aligned with Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO).
- Communication: Manage communication strategies through oversight committees and coordinate with relevant stakeholders during recovery operations.
How do the requirements differ for entities based on their size?
The CSCRF framework categorizes regulated entities based on their size, operational complexity, and risk profile, enabling the adoption of customized cybersecurity measures.
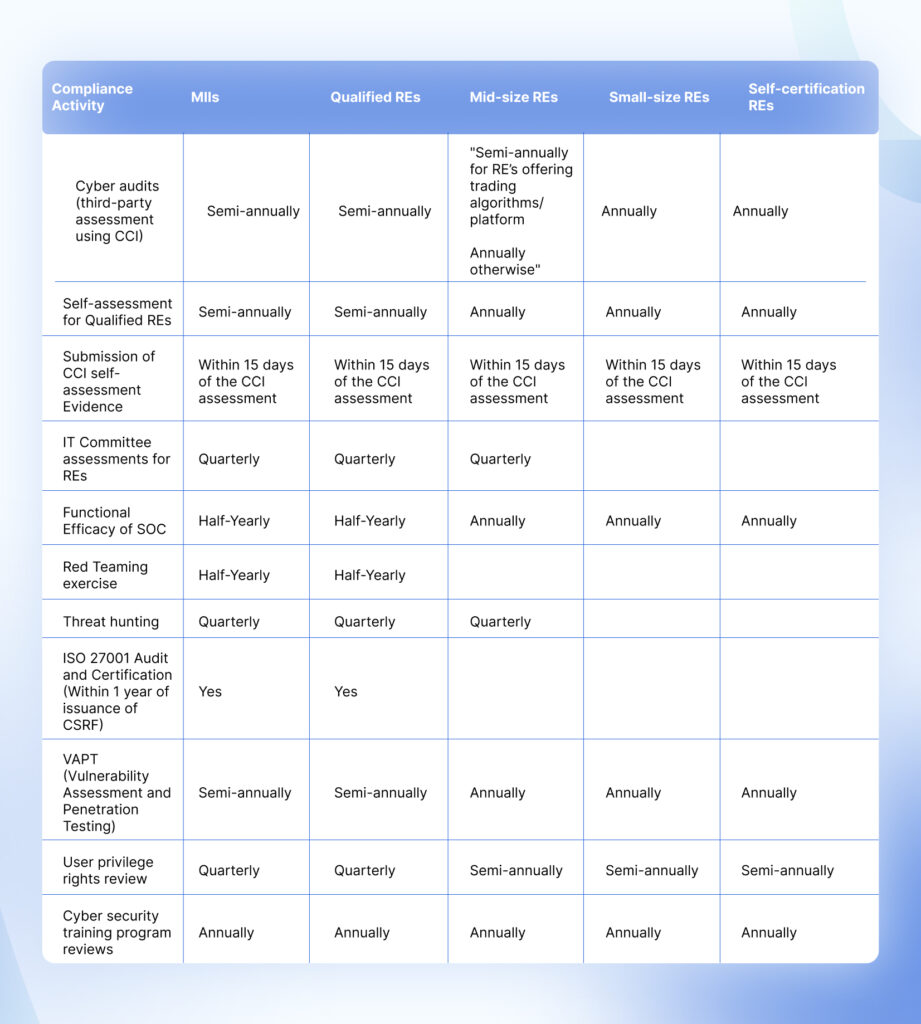
Adapt in time or risk action
The updated Cyber Security & Resilience Framework (CSCRF) mandates stricter compliance measures and even tighter timelines. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties, heavy operational restrictions, and reputational harm.
- For entities where the cybersecurity and cyber resilience circular already exists, effective January 01, 2025.
- For all other entities where the CSCRF is being applied for the first time, it will become effective on April 1, 2025.
Your roadmap to certification
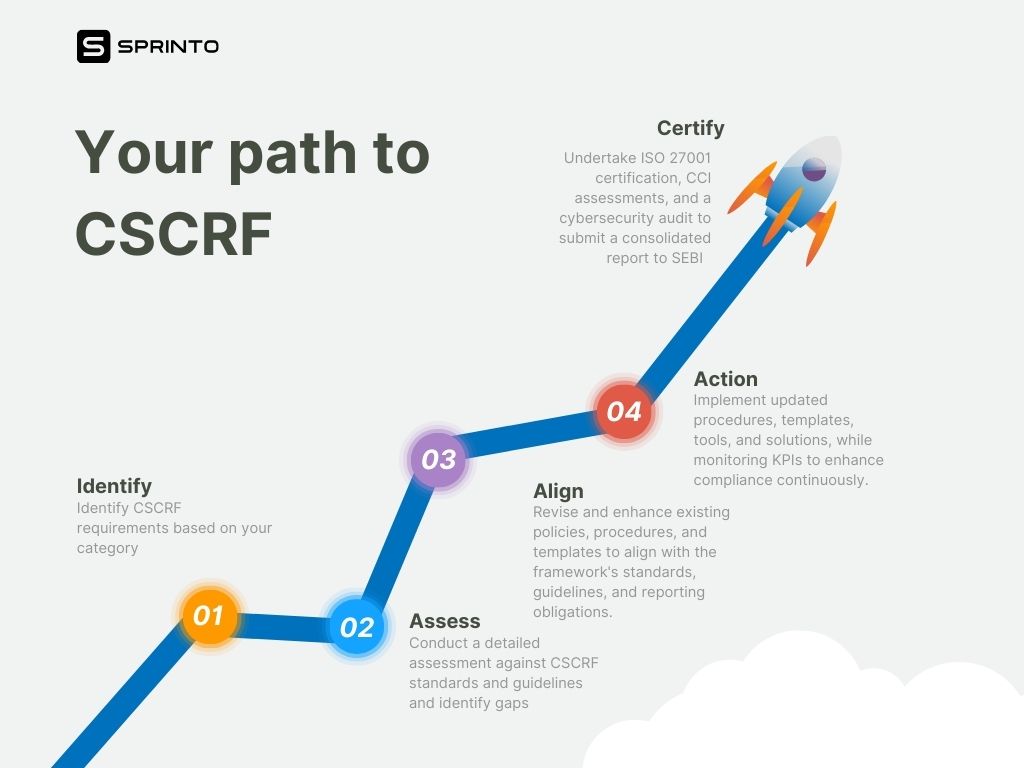
Get CSCRF certified with Sprinto
Complying with CSCRF involves establishing controls and practices that overlap with frameworks such as ISO 27001, SOC 2, and NIST. Sprinto has ready-to-launch compliance programs for these frameworks, with control-criteria pre-mapping, customizable pre-built policy templates, and automated evidence collection to maintain a trail of audit-grade evidence of control performance.
With 200+ integrations, Sprinto connects with your systems and infrastructure to automatically collect evidence. It also lets you easily deploy custom tests and monitor additional security controls directed by CSCRF that are bolted over control requirements of ISO 27001 and other standards. You enjoy the same level and depth of automation for these custom tests, thus making complying with the CSCRF easier, faster, and more cost-effective.
Intrigued? Talk to our experts today.
Virgil
Virgil is a marketer at Sprinto who combines his media savvy with his cybersecurity expertise to craft content that truly resonates. Known for simplifying complex cybersecurity and GRC topics, he brings technical depth and a storyteller’s touch to his work. When he’s not busy writing, he’s likely exploring the latest in cybersecurity trends, debating geopolitics, or unwinding with a good cup of coffee.
Related blogs
research & insights curated to help you earn a seat at the table.
















