What is GDPR Article 30?
Vimal Mohan
Jul 29, 2022

Does your organization fall under the purview of Article 30 of GDPR? Do you find it difficult to interpret the jargon? Are you still looking for a step-by-step guide to help you understand Article 30 of GDPR compliance?
In this article, we have detailed everything you need to know about Article 30 to help with your compliance processes.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has 11 chapters and 91 articles with varied complexity. To become GDPR compliant or maintain continuous compliance, organizations of all sizes must comply with several requirements. Article 30 of GDPR is one such requirement.
GDPR Article states, ‘ Each controller and, where applicable, the controller’s representative, shall maintain a record of processing activities under its responsibility.’
Before we dive deeper into GDPR Article 30, let’s take a minute to analyze if this requirement applies to your organization?
If your organization processes the personal data of the citizens of the European Union, you fall under the purview of GDPR.However, if your organization employs less than 250 employees, you are exempted from being compliant.
This is applicable only if:
1) Your organization processes data that doesn’t threaten users’ rights.
2) The data subject your organization processes doesn’t include sensitive personal data relating to users.
Will someone penalize your organization for non-compliance?
Upon non-compliance, the GDPR lead supervisory authority could impose fines of Euro 1,000,000 or 2% of your organization’s global annual turnover.
Article 30 of the GDPR mandates that every organization has a clear Record of Processing Activities (ROPA).
A ROPA helps the GDPR compliance supervisory authorities have a clear road map of:
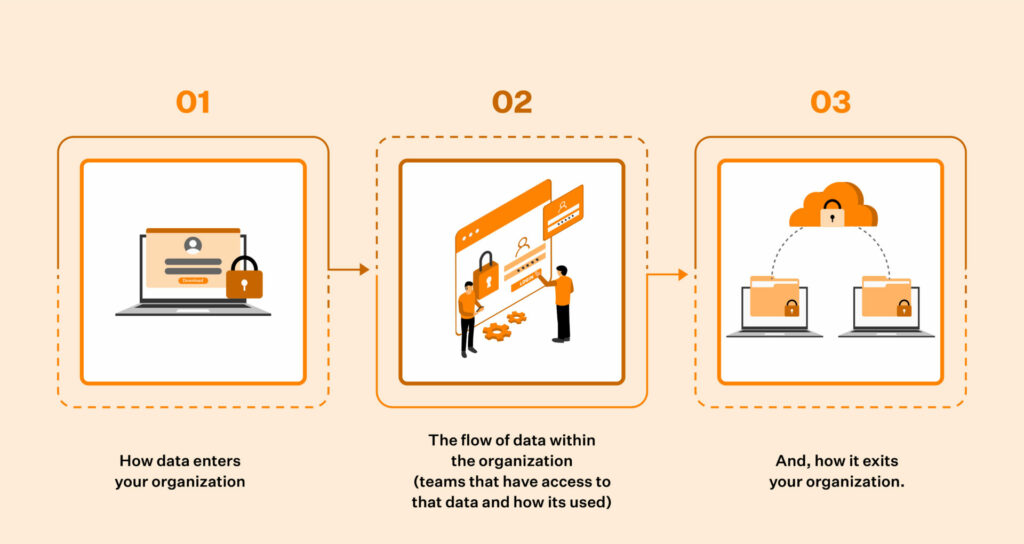
This overview helps them understand the policies and measures you’ve implemented as a business unit to ensure data security.
Records of Processing Activities under GDPR
The ROPA report represents your organization’s compliance status. According to GDPR Article 30 Records of Processing Activities, Controllers or Processors are mandated to comply with this requirement.

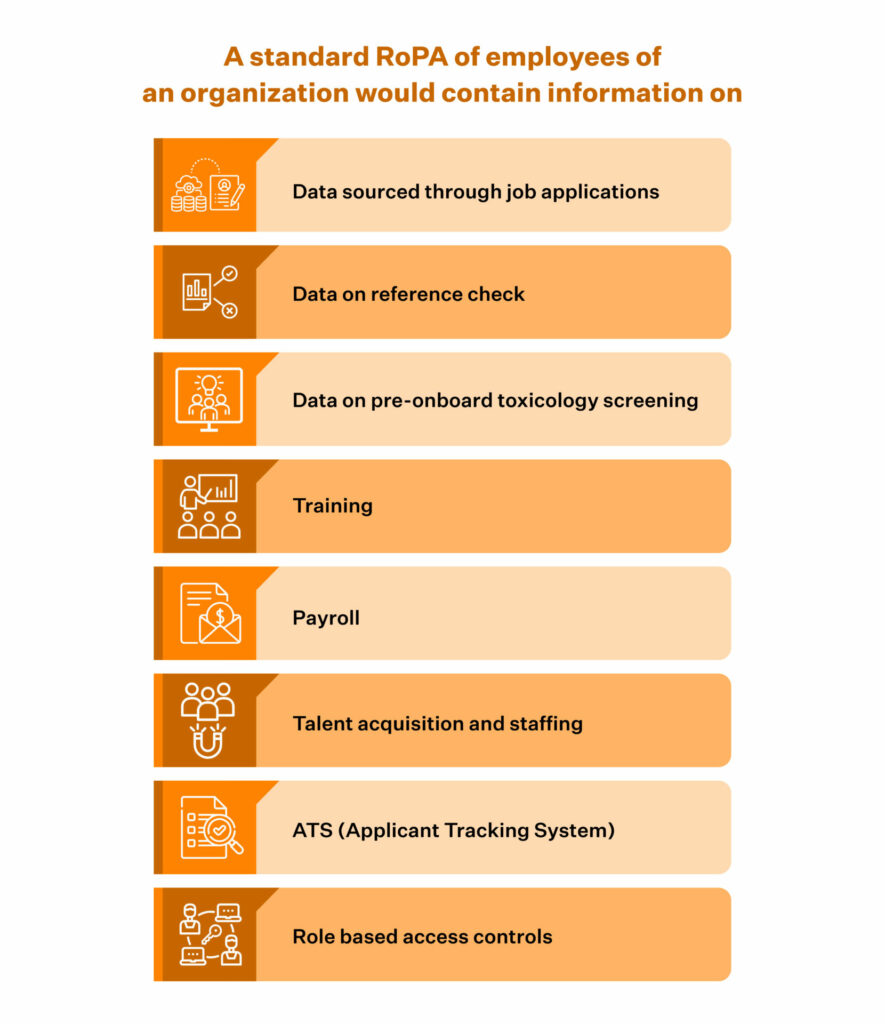
And a standard ROPA report should contain:
1) Name of the organization
2) Contact details
3) Data Protection Officer (DPO) of the organization
4) The reason for processing personal data
5) Individual categorization – Is the individual an employee, a contractor, a user and so on.
6) Who does the information collected relate to?
7) A list of all recipients your organization shares that data with
8) If any of the recipients are outside the EU, specifics of such data transfers
9) How long does your organization hold the data within your business environment?
10) A list of physical and technical measures and policies your organization has to ensure data security.
11) Methods used for obtaining consent
Did you know:
GDPR Article 30 Requirements
A GDPR Article 30 requires all organizations to maintain a consistent record of all their audit activities to ensure continuous data protection.
An Article 30 report or a ROPA is reviewed by a GDPR supervisory authority to assess whether your organization is taking all the recommended steps to ensure data integrity and security.
To maintain continued compliance, you are expected to submit physical and electronic ROPA reports immediately to the supervisory board.
Your organization’s Privacy Policy should include all the details of your data processing activities with more information on:
1) Period of Data Holding
2) The Intent of Use
3) Information on the Rights of the Data Subject.
How does Article 30 of the GDPR affect my business?
The common misconception of GDPR is that only organizations with over 250 employees (with a few exceptions) are required to become compliant if they process data of the citizens of the EU.
With internet-based companies catering to a global audience, obtaining data and cross-functional use of multiple data sets have become increasingly common.
This brings even the smallest of organizations under the purview of the GDPR. Becoming GDPR compliant and maintaining continuous compliance prevents heavy administrative fines and brand defamation.
Article 30 of GDPR compliance helps organizations ascertain the types of personal data they process and map the flow of data sets within their environment. This allows them to lay a foundation that covers aspects of other requirements.
Your organization should:
*Develop its DPIA (Data Privacy Impact Assessment) template
*Draw guidelines to comply with the salient points of Article 15 (Data storage, physical and technical safeguards)
*Analyze internal systems to locate vulnerabilities and deploy fortifying measures.
*Have evidence of why their data processing activities are legal
*Information on their GDPR privacy policy
*Reports on regular internal audits
*Information on employee GDPR training on data mapping and organizational security measures
How to create a GDPR Article 30 Report?
Creating an efficient GDPR Article 30 Compliance Report is creating a data map on a single service offering of your business ecosystem, identifying vulnerabilities, and deploying appropriate safeguards to strengthen your security posture. And
deploy the learnings from the first activity and repeat the process in an organization-wide capacity.
Here’s a summary of how to create your GDPR Article 30 report:
1. Define the scope of the processing activities with respective business function heads.
2. Collate information on business functions’ assessment reports
3. Identify gaps and remediation methods
4. Update the report whenever new virtual or physical storage assets are introduced to the business ecosystem.
5. A templated view of this information.
Using an excel-based GDPR Article 30 template helps you embellish the key highlights you wish to include in your ROPA report. However, the manual process of complying with Article 30 opens avenues for incorrect implementation of regulated guidelines.
Lack of end-to-end visibility results in inefficient mapping and, ultimately, an insecure security posture. Upon review, a ROPA like this leads to non-compliance with the GDPR.
A compliance automation program such as Sprinto helps you automate the GDPR data mapping process, scan and identify vulnerabilities, suggest remediation measures, and adds new rules to sync new virtual assets and vendors to the RoPA scope and audit. Thus, leaving no avenues for non-compliance.
An automated ROPA report also doubles up as evidence when the regulatory authorities ask to produce documentation of suitable safeguards.
How to ensure your Records of Processing Activities is up to date?
Every business is dynamic and constantly adds more cloud assets, onboarding new vendors and deploying tools to expand business avenues and expedite production speeds.
To continuously achieve a strong security posture, your organization should constantly deploy methods to scan for vulnerabilities and deploy patches to mitigate risks.
Likewise, a GDPR Article 30 report will become outdated if it is not worked upon periodically.
Things to do to ensure an up-to-date GDPR report:
* Identify the risk and schedule a review process. For example, a quarterly review is recommended if you identify your organization as high-risk. For medium risk, a check every six months; for low-risk, an annual review is prompt.
* Integrate Privacy Impact Assessment(PIA) and Data Privacy Impact Assessment (DPIA) into your Article 30 report.
* Ensure that Vendor Management is synced with Article 30 of GDPR compliance.
Becoming GDPR compliant (if applicable) and maintaining continued compliance is essential to avoid the heavy costs associated with non-compliance. Unfortunately, the manual approach towards becoming GDPR compliant leaves businesses non-compliant even after months of legal activities and deploying technical controls. See how Sprinto can help automate your GDPR compliance journey by reducing Time to Compliance and costs.
FAQ
What is Article 30 of GDPR?
Article 30 of GDPR talks about the processing activities conducted by controllers, processors, and sub-processors. It emphasizes the steps organizations should include in their processing activities to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive user data.
What is inventory of processing in Article 30?
To remain GDPR compliant, organizations must maintain a record of all their processing activities, including information on the processing any data set undergoes. Inventory of processing gives an auditor a detailed overview of how organizations to process data and the measures they’ve implemented to ensure continuous compliance.
What constitutes record keeping according to Article 30 of GDPR?
An organization is compliant with Article 30 of GDPR if they have records on how they collect user data, records on where it is stored and in what form, records of data transfer (both internally and to third-party service providers), records of alterations, records of deletion, and records of processing for government agencies.
Vimal Mohan
Vimal is a Content Lead at Sprinto who masterfully simplifies the world of compliance for every day folks. When not decoding complex framework requirements and compliance speak, you can find him at the local MMA dojo, exploring trails on his cycle, or hiking. He blends regulatory wisdom with an adventurous spirit, navigating both worlds with effortless expertise
Grow fearless, evolve into a top 1% CISO
Strategy, tools, and tactics to help you become a better security leader
Found this interesting?
Share it with your friends
Get a wingman for
your next audit.
Schedule a personalized demo and scale business

Sprinto: Your growth superpower
Use Sprinto to centralize security compliance management – so nothing
gets in the way of your moving up and winning big.


