HIPAA Compliant Database
Vimal Mohan
Mar 20, 2024

The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a federal law launched in the United States of America in 1996 to protect the PHI & ePHI of its citizens and residents from being misused and abused and prevent healthcare fraud.
Becoming HIPAA compliant takes work, especially if you go the DIY route. Storing and securing PHI (Protected Health Information) the right way is integral to becoming HIPAA compliant. HIPAA guidelines now require organizations processing PHI and ePHI to present a strong security posture equipped to protect PHI to become compliant.
If your organization is in the process of revamping its current database to meet the requirement of a HIPAA compliant database or is starting out on your HIPAA compliance journey, then this article is for you. Learn how businesses can strengthen and fortify their database by following the HIPAA guidelines.
Why should you store data in a HIPAA compliant database?
HIPAA mandates that organizations safeguard the integrity and privacy of critical patient data during their processing activities. In this era of cloud storage and computing, vast volumes of patient data are securely stored in cloud servers globally.
According to an EMISOFT report, over 560 health care providers were victims of ransomware activities, resulting in leaks of secure patient health information. The estimated loss was a whopping USD 915 million that year.
Bad actors and hackers always look for vulnerabilities in cloud storage, access control, and production practices to name a few.
Healthcare organizations, therefore, must strengthen their database’ security policies and implement measures to be on the right side of the HIPAA security rule.
7 Steps to make your database HIPAA compliant
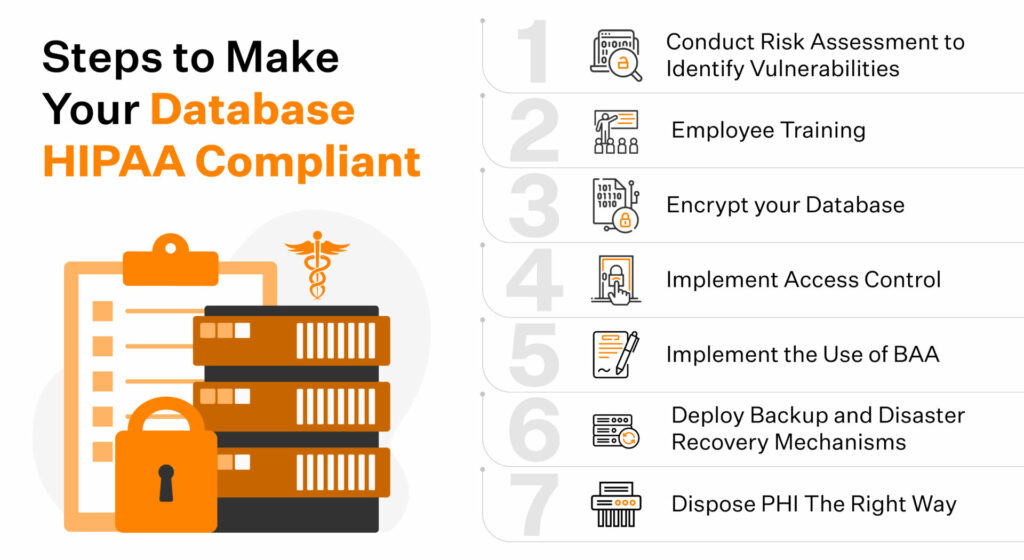
It is essential to implement administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to make a database HIPAA compliant. We’ve listed the seven steps you can implement in your organization’s HIPAA compliance journey.
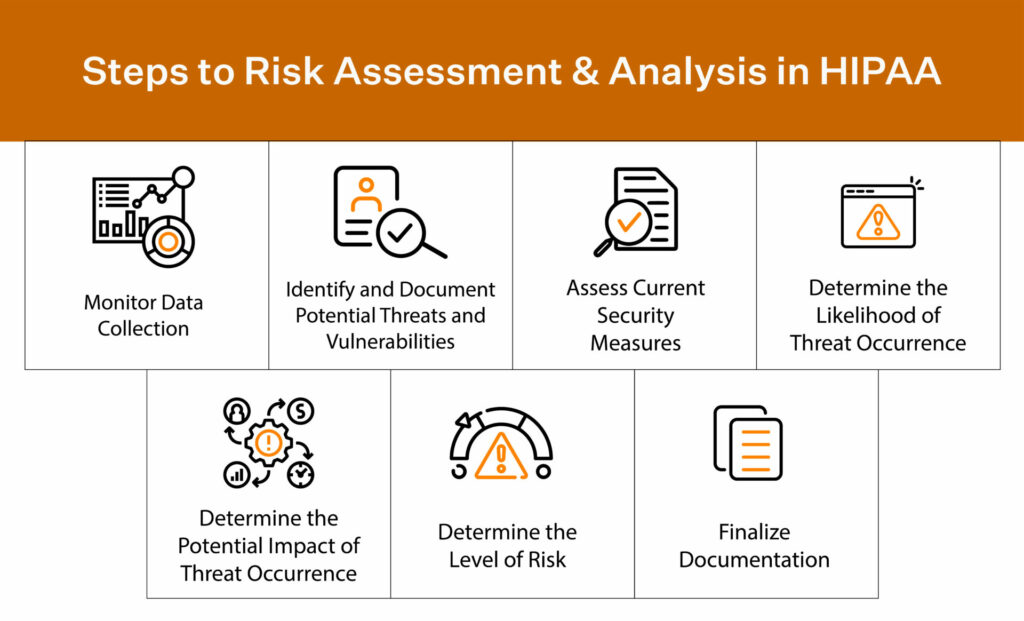
Step 1: Identify vulnerabilities by implementing risk assessment
Internal risk assessments are a great way to determine the risks your organization takes on by processing PHI and identify countermeasures needed to prevent a breach incident.
A risk assessment also gives you insights into your current vulnerabilities and also enables you with the data sets required to predict future vulnerabilities. These data-driven future projections of your security posture enable you to shuffle the resources required to meet that future need.
Organizations should conduct periodic vulnerability assessments and deploy patches where needed for a strong security posture. New security measures should also be implemented depending on the volume of PHI they process and the risks they’ve identified. Most organizations conduct their risk assessments on a quarterly, half-yearly, or yearly basis.
Step 2: Train Your Employees
All your employees interact with cloud assets regularly, not just your developers and engineers. Training your employees keeps them informed of the current security landscape and educates them on the different ways hackers and bad actors penetrate secure systems.
Training your employees on phishing attacks, best practices when using cloud assets, and best practices when handling patient data paves the path for building a culture where security is a collective responsibility and not just in the OKRs of the security teams.
Step 3: Protect Your PHI Database by Encrypting It
All your production and staging assets should only be stored in an encrypted state. Data encryption strengthens your security posture by making confidential information inaccessible even if your secure systems are breached.
Step 4: Access Control
Controls, either in the form of data controls, access controls, or physical controls, enable organizations with the ability to flag off malicious activities in real time. With access controls, organisations can limit access to secure systems to only those job roles that require access to sensitive data to perform duties effectively.
The thumb rule of security is that the risk of a breach is directly proportional to the number of people with access to it. Therefore, organizations must use access control to minimize unauthorized access and limit potential vulnerabilities.

Step 5: Enforce BAA when working with vendors
Business Associate Agreements (BAA) are legal contracts that HIPAA-compliant organizations sign with vendors and service providers to ensure holistic data protection.
BAA ensures that external organizations working with you also uphold and prioritize data security the same way you do and follow HIPAA guidelines when processing PHI.
This legal contract is used when PHI is shared or transmitted from one business to another for processing. Enforcing BAA protects the PHI after it leaves your organization and when your vendors access it.
Organizations that breach a BAA not only risk becoming non-compliant with HIPAA but are also levied heavy administrative fines. In addition, their brand suffers irreparable damage.
Step 6: Implement backup and disaster recovery plan
To build a HIPAA compliant database, your organization must deploy methods and policies around backup and disaster recovery. A data recovery mechanism ensures that your organization is equipped with the technology stack required to deploy backups and get information back online during a cyber attack.
It is a best practice to run regular checks on how your backup systems function. Analyze their response times and recovery periods periodically and log that data. In addition, logging all your data recovery exercises allows you to conduct a comparative analysis of historical data with current metrics.
The results of these comparisons are often used to identify areas of improvement and make future projections. These data driven projections help organisations plan their next moves and start charting solutions for the future.
Step 7: Plan to dispose of your old data
HIPAA does not dictate how organizations dispose of sensitive data.
However, it is essential to note that the risk of a cyber attack is directly proportional to the amount of time the data is stored and the nature of data stored. Databases storing sensitive personal data and PHI are often prime targets for security incidents.
When disposing of data, ensure that appropriate measures are deployed to prevent unauthorized access of disposed of data.
Deploying high-security file-wiping mechanisms is an excellent way to go.
The Way Ahead
Making your organization’s storage formats HIPAA compliant is not an easy process. While using a compliance checklist to get started is a great first step, they are not all that you need to do.
A database is made secure by consistently developing existing security systems and deploying newer versions of upgraded security software and encryption models.
To present and maintain a HIPAA compliant database, monitor your security systems continuously, identify current and future threats, deploy real-time alert mechanisms to alert you when unauthorized access is made, use state-of-the-art encryption models and enforce policies and procedures that build toward developing an org-wide security culture.
Also, Find out how to secure HIPAA compliant gmail.
How Sprinto makes your database HIPAA compliant
Database compliance is an essential part of HIPAA. However, organizations often regard compliance as a one-time activity. The need for more visibility of their compliance and security posture and the inconvenience of manually tracking controls and deploying patches across multiple cloud assets makes compliance maintenance a daunting task for organizations.
Eventually, organizations deprioritize conducting periodic risk assessments and continuous monitoring of their security systems to look for vulnerabilities and deploy patches. Unfortunately, this results in inefficient controls that weaken the organization’s overall security posture, thus making them vulnerable to data breaches—the path to non-compliance gets paved.
Sprinto is purpose-built to give you the visibility required to monitor all your security systems in real-time, continuous monitoring, Sprinto identifies segments of your security profile that need immediate attention and automatically alerts the stakeholders responsible within your organization. This helps you maintain a strong security posture and to remain compliant on an ongoing basis.
Sprinto does the heavy lifting in the compliance process so you can focus on what matters to you the most. Product development and business expansion!
Becoming HIPAA compliant is a breeze with Sprinto. Talk to our experts today to start your compliance journey the Sprinto way!
FAQs
1. Why do you need a HIPAA compliant database?
If your organization processes PHI of citizens and residents of the US or works with covered entities or business associates, then you must be HIPAA compliant. The HIPAA privacy rule mandates that organizations dealing with sensitive personal data apply measures to safeguard the privacy and integrity of patient data by protecting it from unauthorized access.
2. How to create a HIPAA compliant database?
To make your database HIPAA compliant, ensure that you:
- Periodically conduct risk assessments and apply remedial measures
- Train your employees on how to access and store information securely
- Use encryption modules to protect data in the event of a data breach
- Enforce legal contracts with the vendors you share your data with
- Train your staff on how to dispose of data securely
- Maintain disaster recovery and other management systems to bring your systems back online after an incident.
3. How to create a HIPAA compliant database?
A proactive approach to safety instead of a reactive one. Spend time and resources towards:
- Employee training
- Updating firewalls
- Conducting risk assessments
- Applying remediation measures
- Providing training to respond in the event of a data breach
- Implementing data controls and access controls
- Implementing measures to ensure sensitive patient data is not accessed when stored in physical forms
Vimal Mohan
Vimal is a Content Lead at Sprinto who masterfully simplifies the world of compliance for every day folks. When not decoding complex framework requirements and compliance speak, you can find him at the local MMA dojo, exploring trails on his cycle, or hiking. He blends regulatory wisdom with an adventurous spirit, navigating both worlds with effortless expertise
Grow fearless, evolve into a top 1% CISO
Strategy, tools, and tactics to help you become a better security leader
Found this interesting?
Share it with your friends
Get a wingman for
your next audit.
Schedule a personalized demo and scale business

Sprinto: Your growth superpower
Use Sprinto to centralize security compliance management – so nothing
gets in the way of your moving up and winning big.


